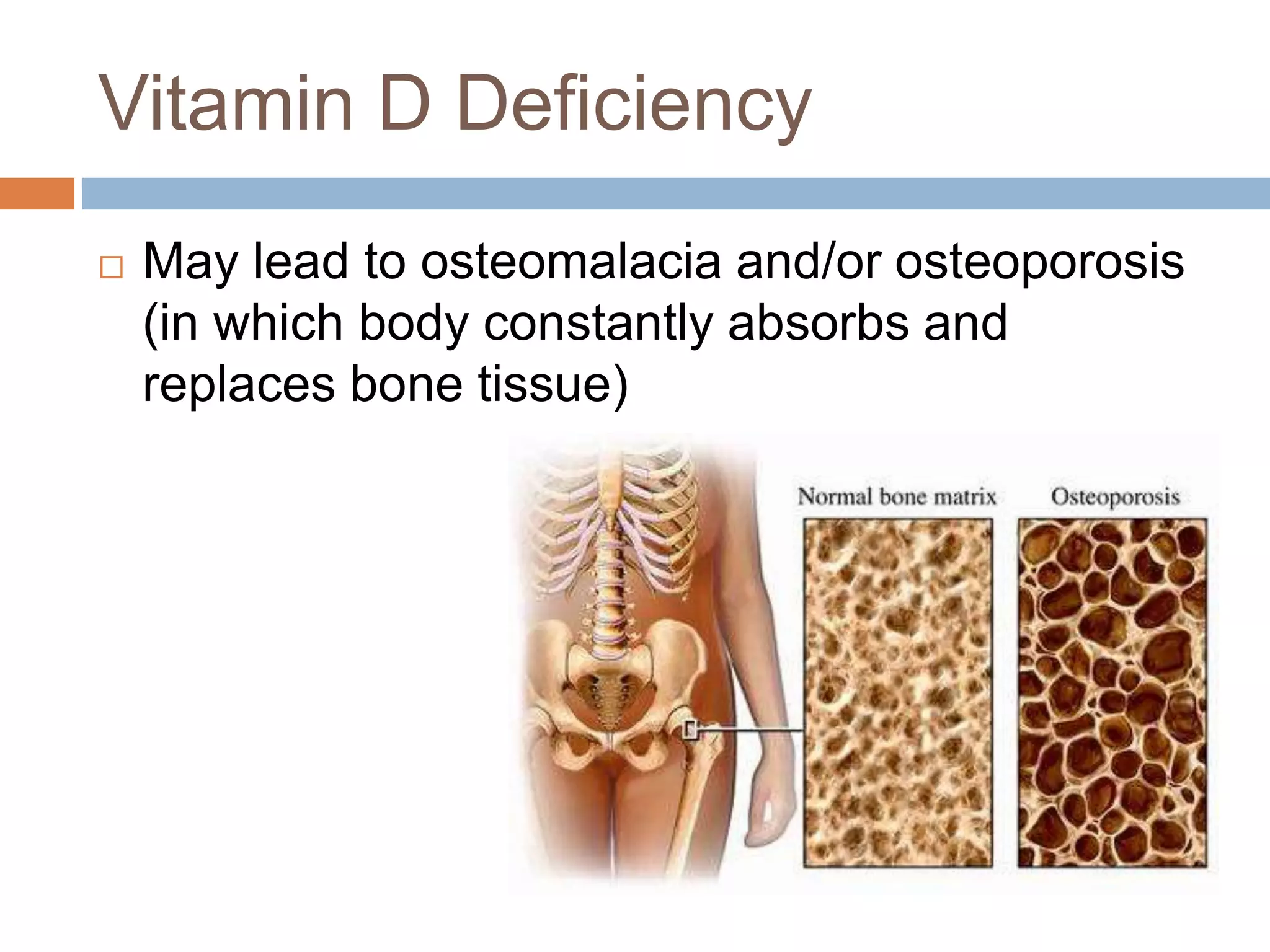
Vitamins are essential nutrients that the body cannot produce on its own and must be obtained from food or supplements, categorized into fat-soluble (A, D, E, K) and water-soluble (B vitamins, C). Each vitamin plays specific roles in health, such as vitamin A aiding vision and immune function, vitamin C acting as an antioxidant, and vitamin D supporting bone health. Deficiencies or excesses in these vitamins can lead to various health issues, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet.