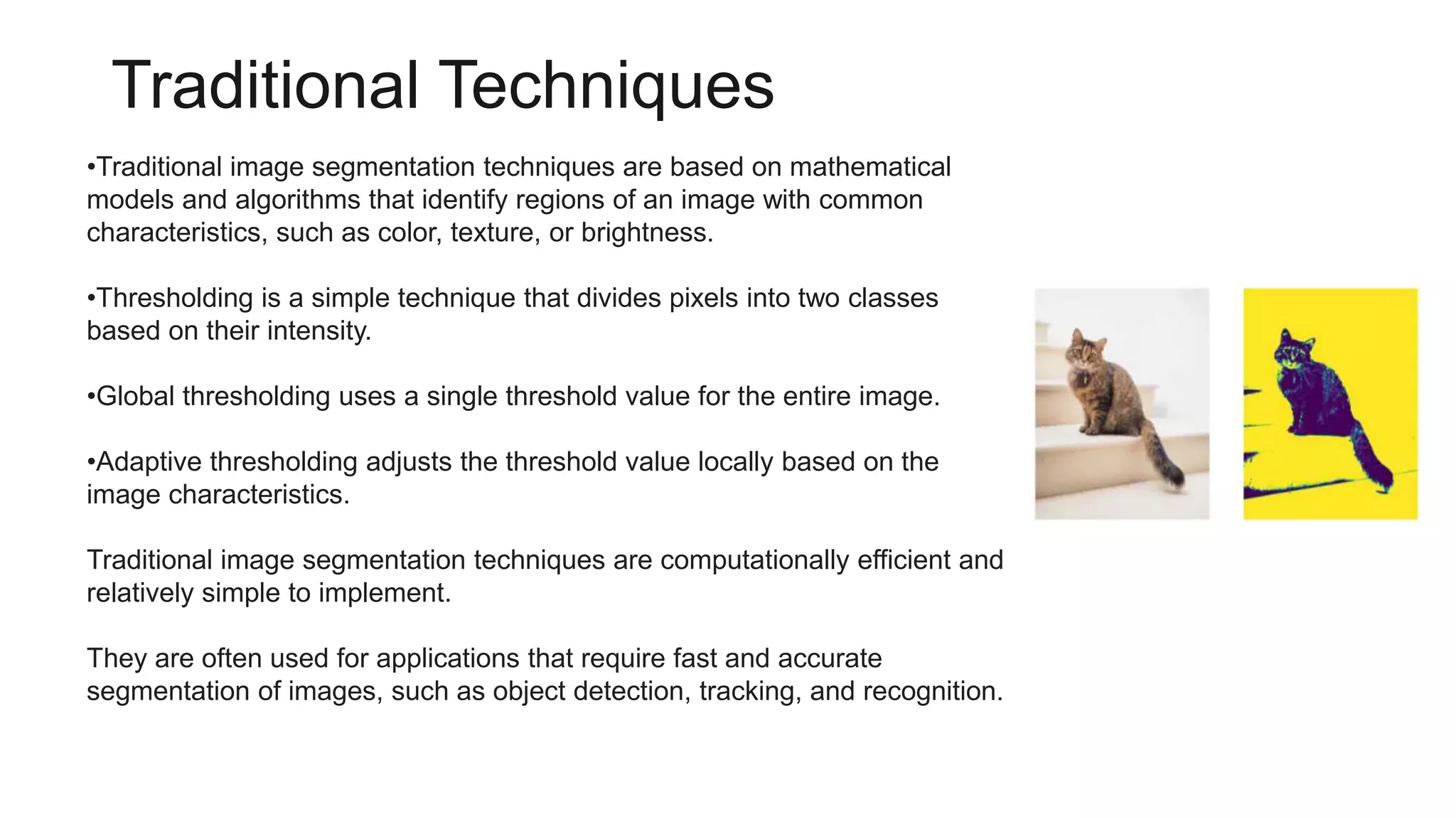
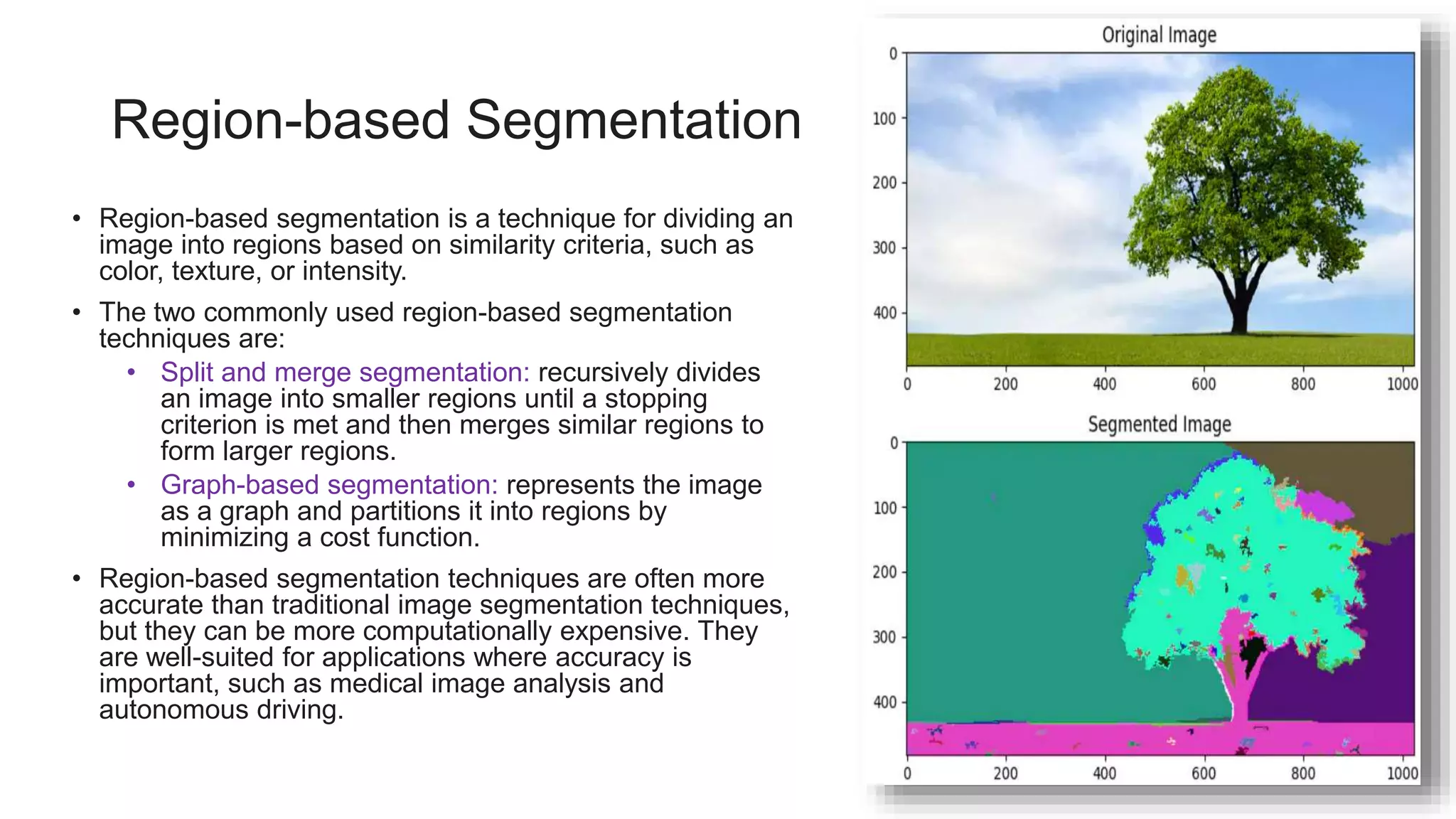
Image segmentation is a method of dividing a digital image into subgroups called segments to reduce complexity and enable analysis. It involves assigning labels to pixels to identify objects or elements. It is the first step for image analysis and enables applications like medical imaging, autonomous driving, robotics, and satellite imagery analysis. The main types of image segmentation are instance segmentation, which detects each object, semantic segmentation, which labels each pixel by class, and panoptic segmentation, which combines both. Traditional techniques like thresholding and region-based techniques are fast but less accurate, while deep learning techniques like U-Net, SegNet, and DeepLab are more accurate but complex.