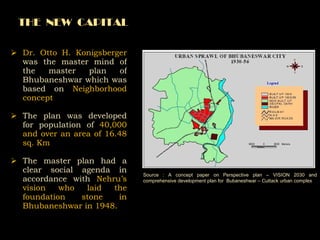
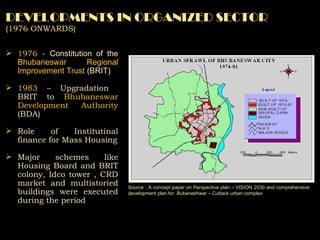
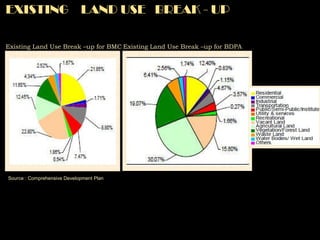
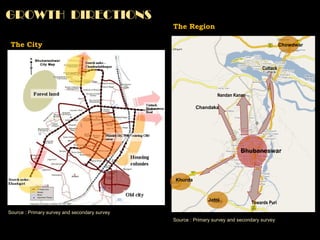
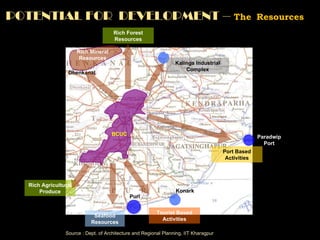
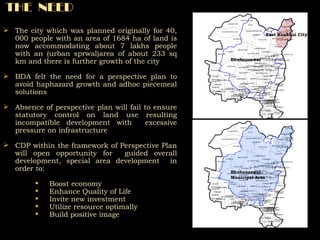
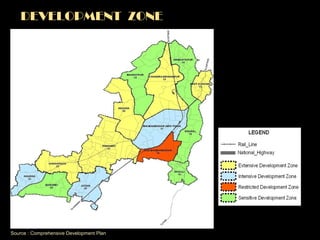
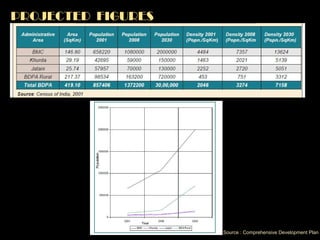
The document summarizes the history and development of Bhubaneswar, India from an ancient city to its current plans to become a world-class capital city. It describes Bhubaneswar's origins as the capital of the Kalinga kingdom in the 3rd century BC and its growth as a center of temples. In the 20th century, it replaced Cuttack as the capital of Odisha state due to its better climate and land. A master plan in the 1940s laid the foundation for Bhubaneswar's development. Recent plans include expanding infrastructure, housing, and economic development to support a projected population of 3 million by 2030 and establish Bhubaneswar as a center for health, education, and