- The document describes a virtual clinical examination tool called Interactive Paper Patients (IPPs) that allows students to examine and manage simulated patients in a structured question-and-answer format with an examiner.
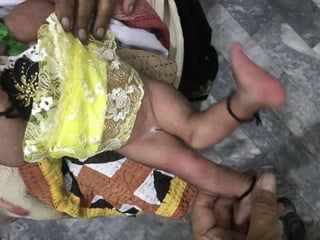
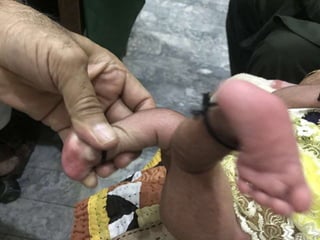
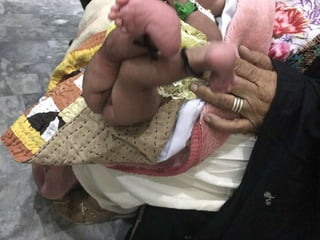
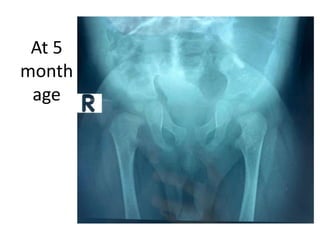
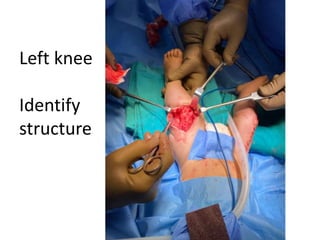
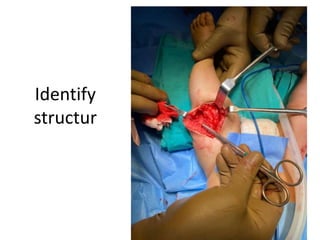
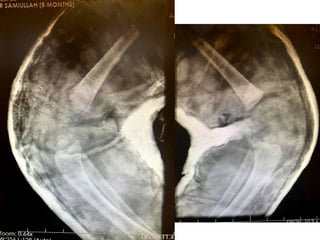
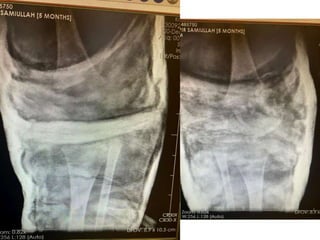
- An example is provided of a case involving a 2-week old infant with clinical findings suggestive of congenital knee deformity. The examiner guides the student through the case by revealing details in phases and asking questions to assess understanding.
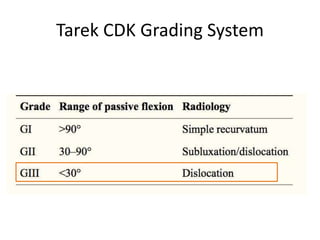
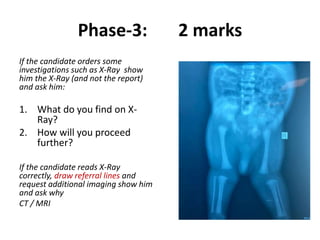
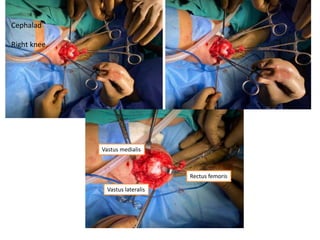
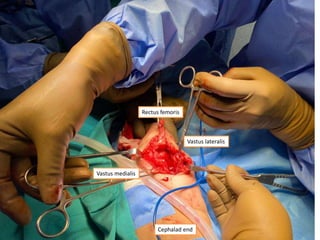
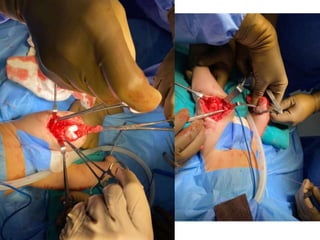
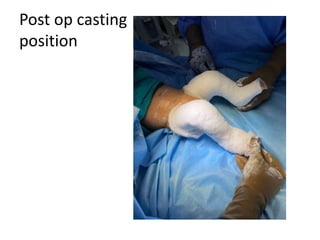
- In later phases, the student is shown x-rays, asked to interpret findings and propose management, which may involve non-operative or operative treatment such as a V-Y plasty procedure to correct pathoanatomy like quadriceps contracture.