The document provides demographic and historical information about the Vikings from Scandinavia. It can be summarized as follows:
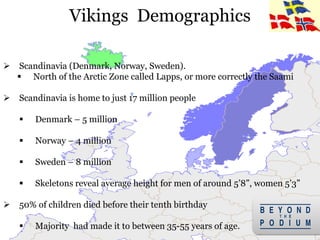
1) The Vikings originated from Scandinavia (Denmark, Norway, Sweden) and ranged from the Arctic zone south to North Africa and east to Russia between 800-1066 AD.
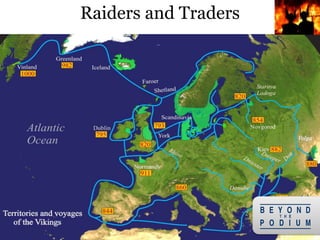
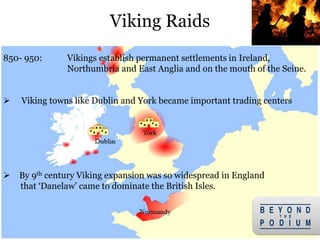
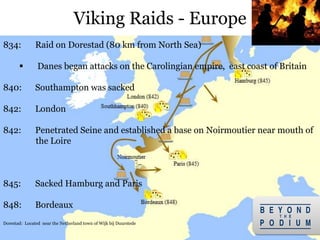
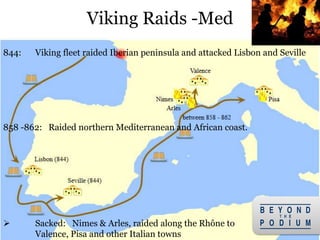
2) They were both fierce raiders, attacking coastal European regions in hit-and-run raids, as well as traders who established new trade routes.
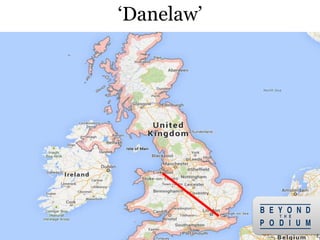
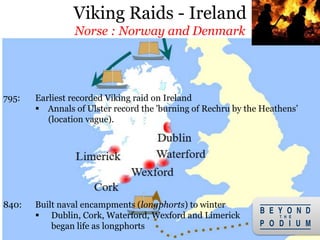
3) The Vikings first began exploring beyond Scandinavia in the 8th century, with the Swedes traveling east and opening up Russia, the Danes going southwest to conquer England and raid France, and the Norse traveling northwest to conquer Ireland and settle Iceland,