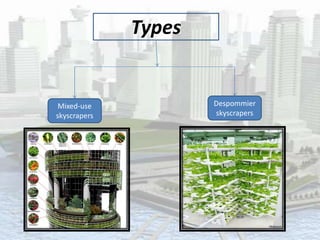
Vertical farming is the practice of growing plants in controlled environments often within skyscrapers, utilizing techniques like hydroponics and artificial lighting. It has historical roots dating back to early 20th century concepts, with current proposals focusing on mixed-use and hermetically sealed skyscrapers. While vertical farming offers advantages such as increased crop production and resource conservation, it also faces challenges including high energy costs and environmental concerns related to pollution and fossil fuel dependency.