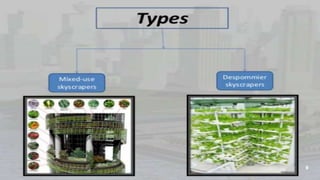
Vertical farming is the practice of growing crops in stacked layers or vertically. As the world population grows to 9.2 billion by 2050, vertical farming can help address issues of limited arable land and food security. Vertical farms use technologies like LED lighting, hydroponics, and aeroponics to grow plants faster and with higher yields than traditional farming, while using less water, land, and agrochemicals. Potential disadvantages include high initial costs and energy usage, but vertical farming offers environmental and sustainability benefits for urban food production.