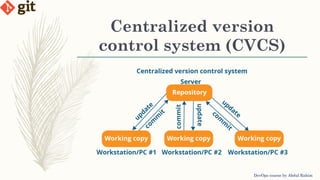
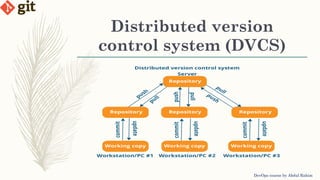
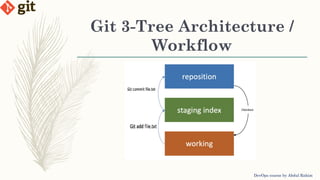
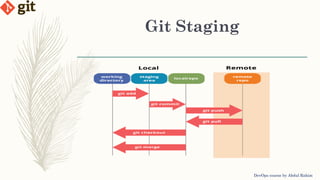
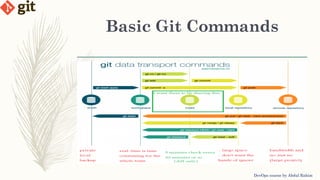
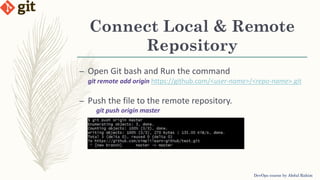
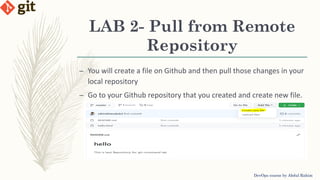
This document provides an introduction to version control systems and Git. It explains what version control is, the advantages it provides, and the different types of version control systems including local, centralized, and distributed. It then describes Git in more detail, covering its architecture, features, basic commands, and how to initialize and connect a local and remote Git repository. The document concludes with instructions for a lab on using basic Git commands.