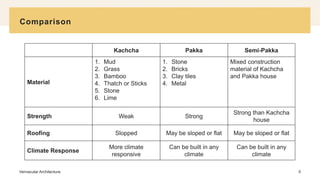
This document defines and discusses vernacular architecture. It begins by explaining that vernacular architecture refers to domestic buildings designed using local materials and traditions to address local needs and environmental conditions. It then provides more details on the characteristics of vernacular architecture, including that it is not based on theoretical principles but responds directly to the site, uses local resources, and can accept changes over time based on community values. Finally, it divides vernacular architecture into three categories - Kachcha, Pakka, and Semi-Pakka - based on the materials used and strength, and compares the features of each.