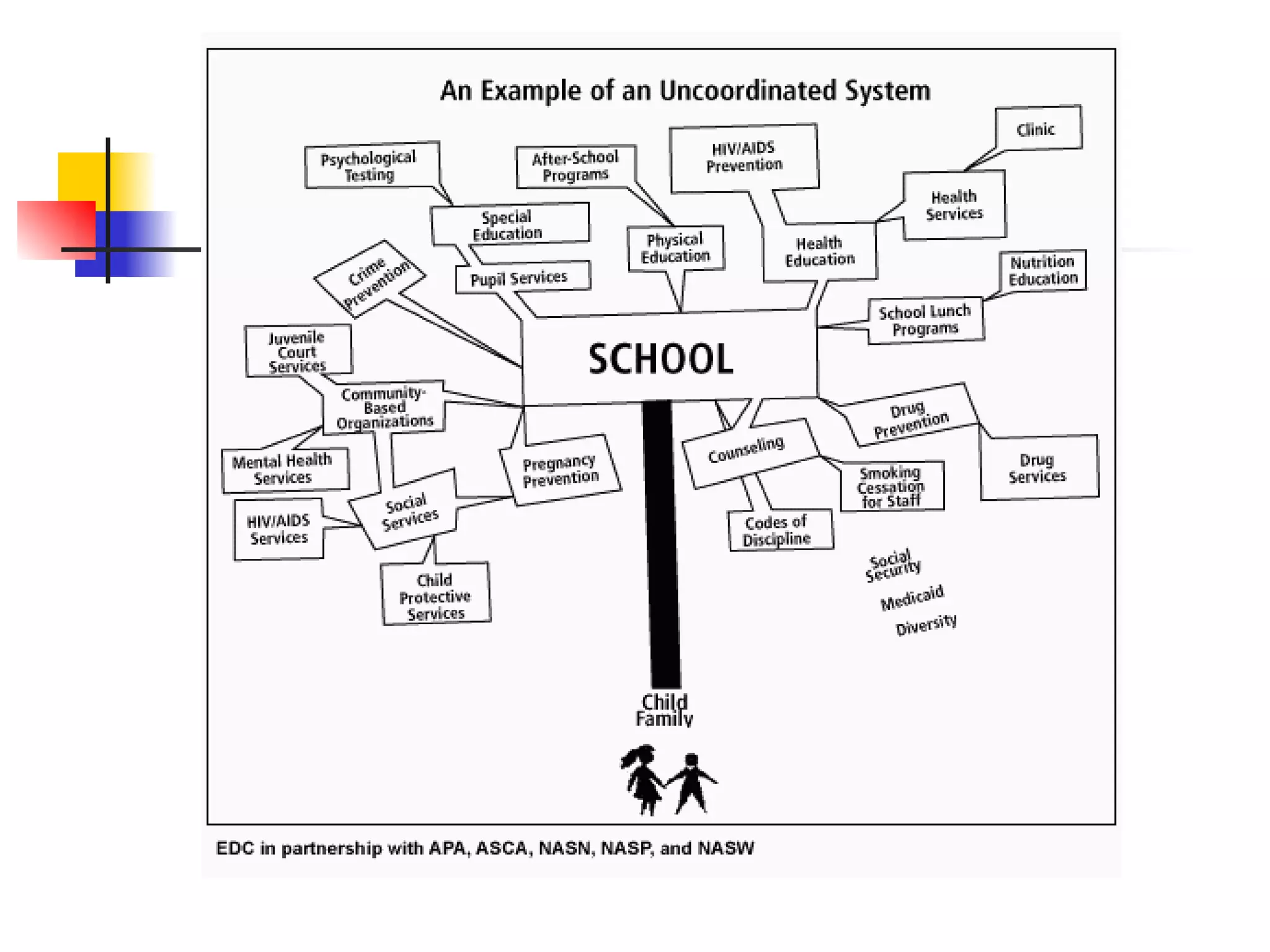
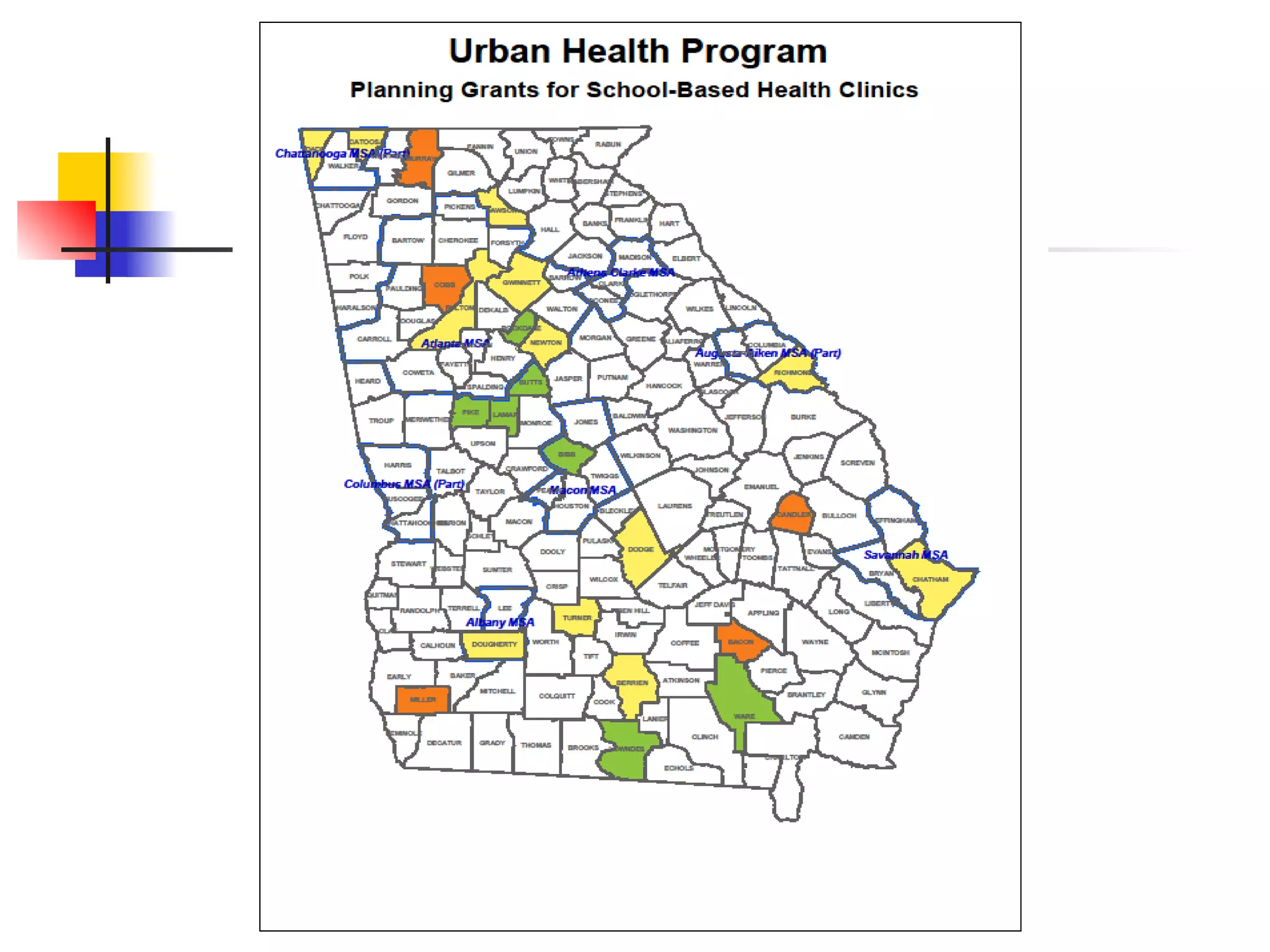
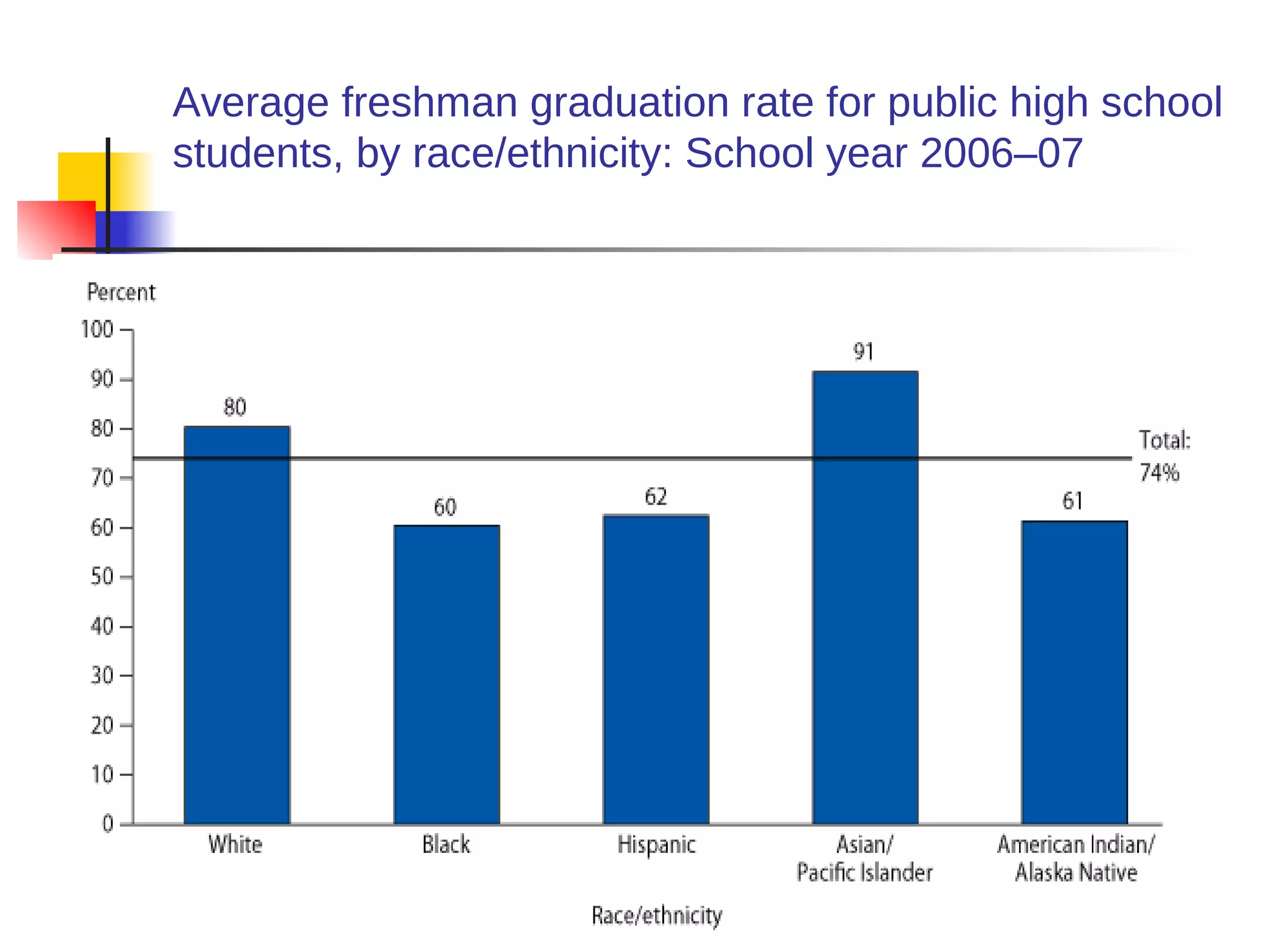
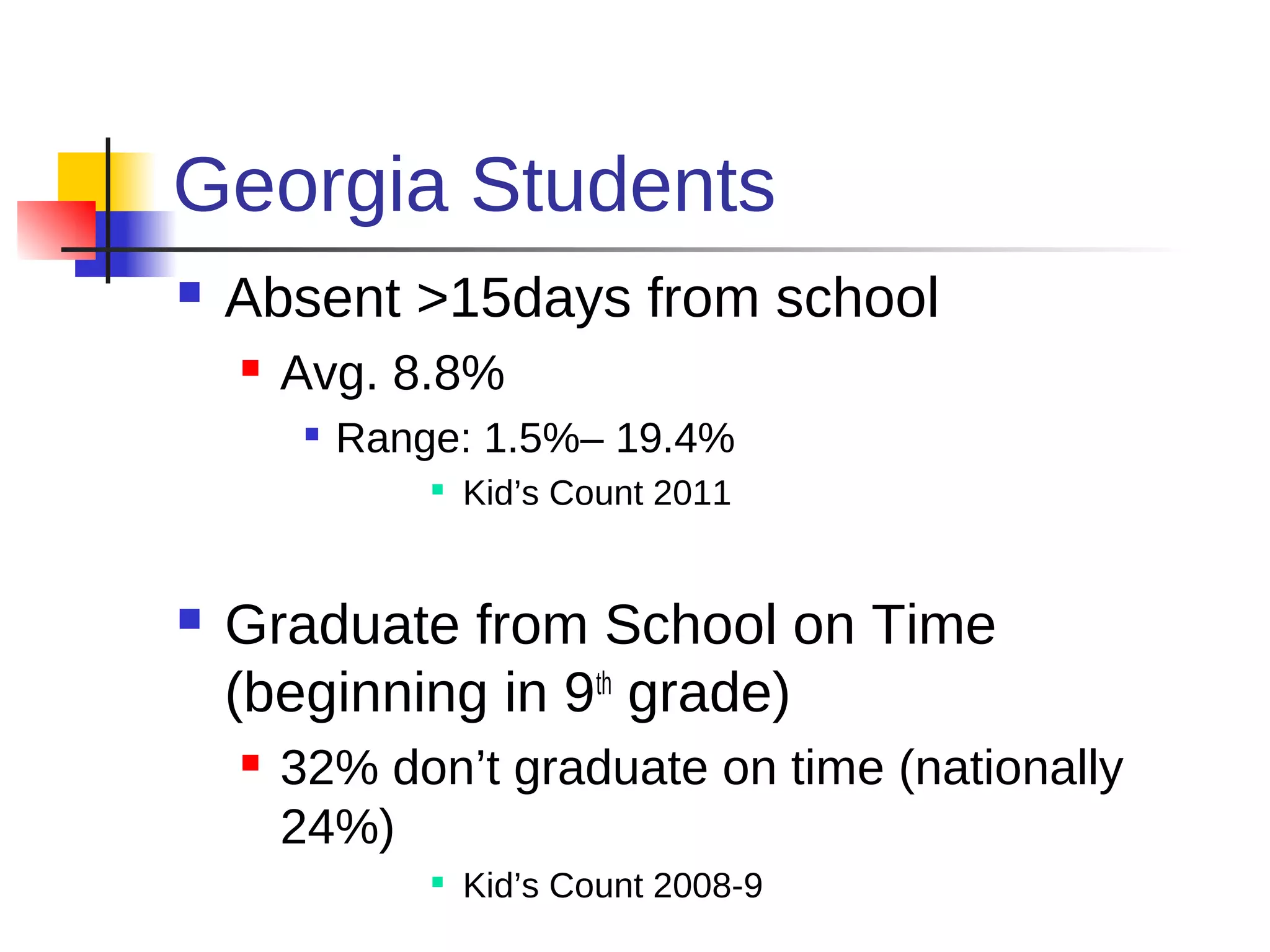
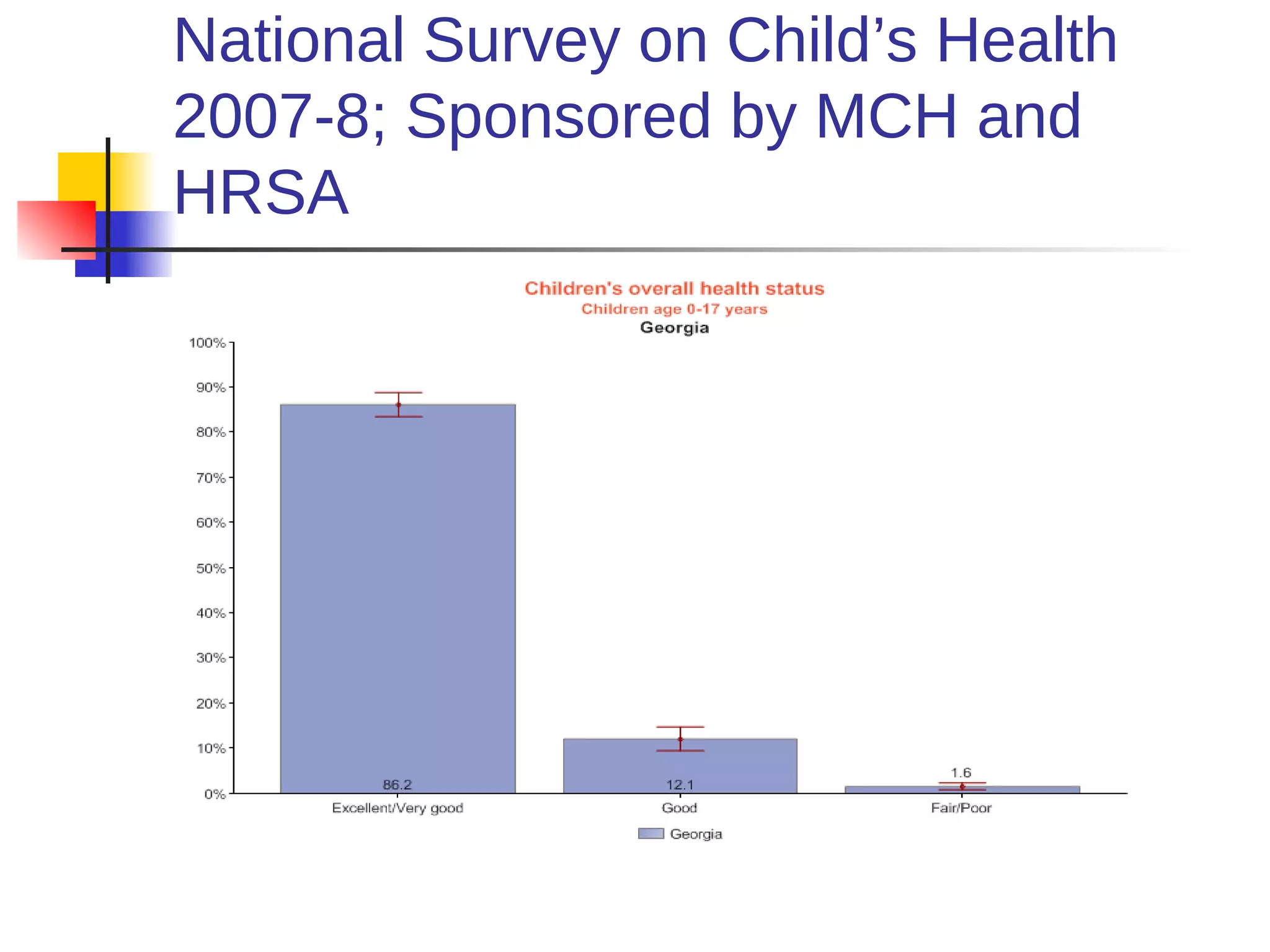
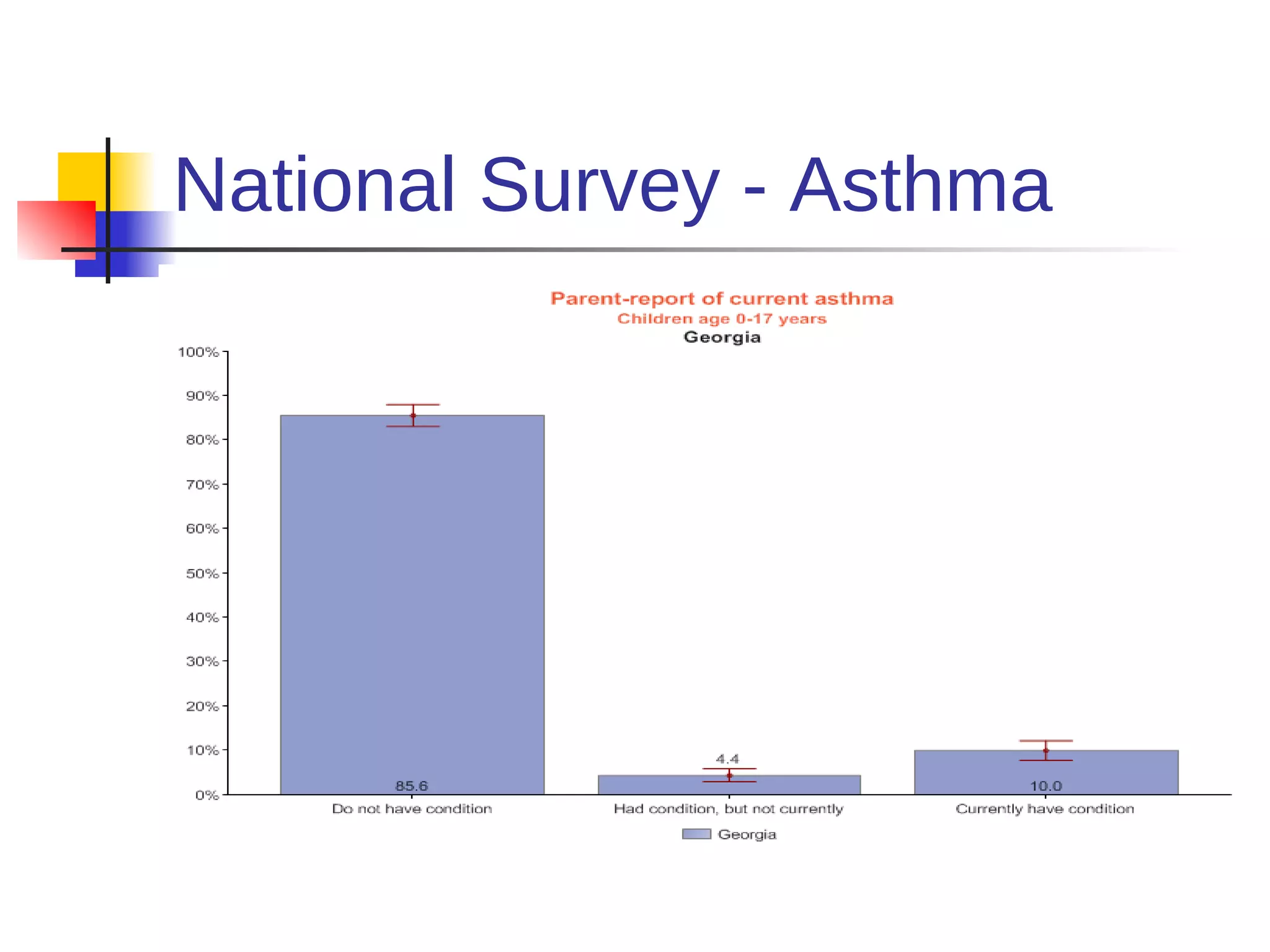
This document discusses the relationship between health, education, and academic achievement. It finds that:
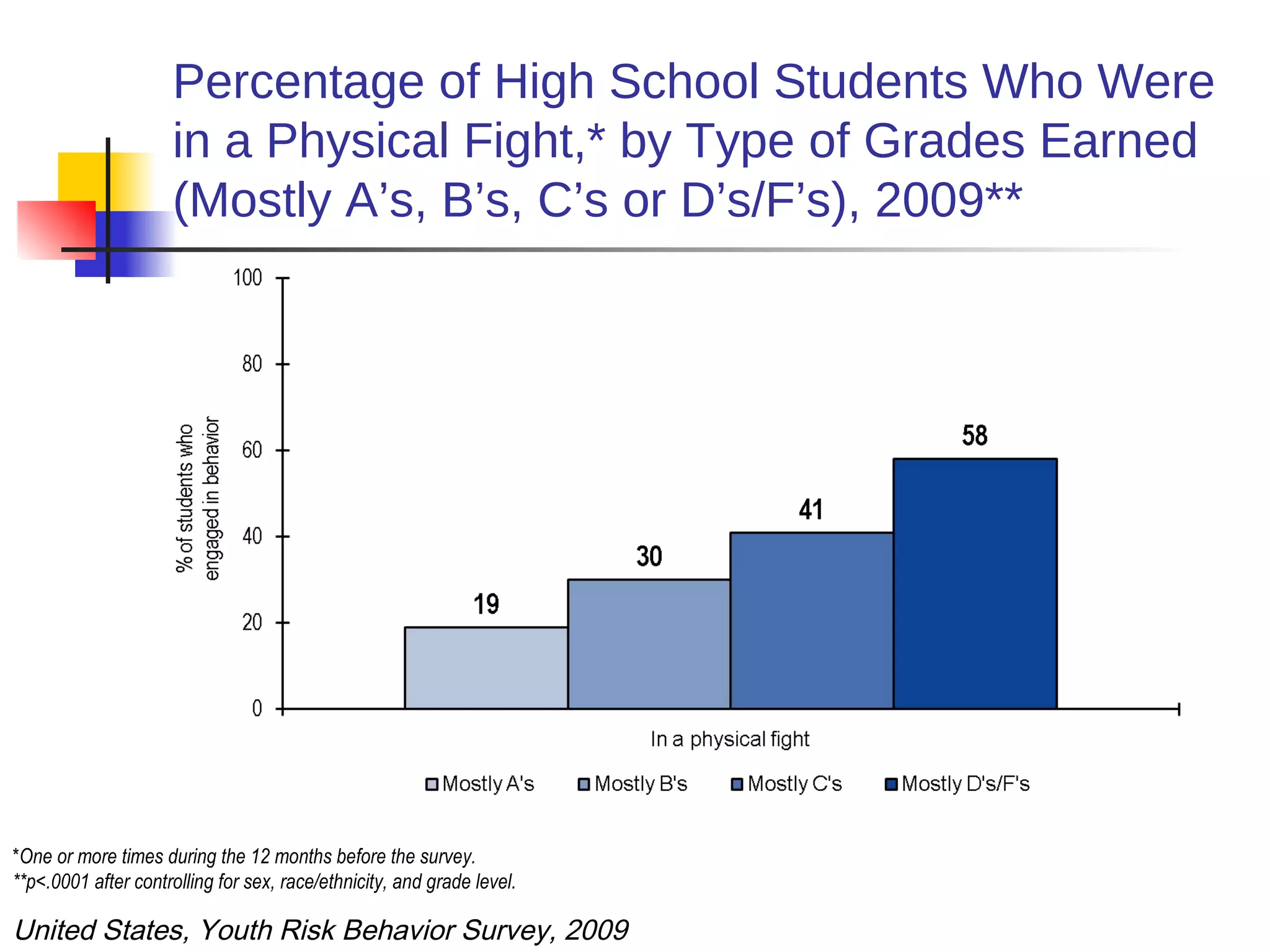
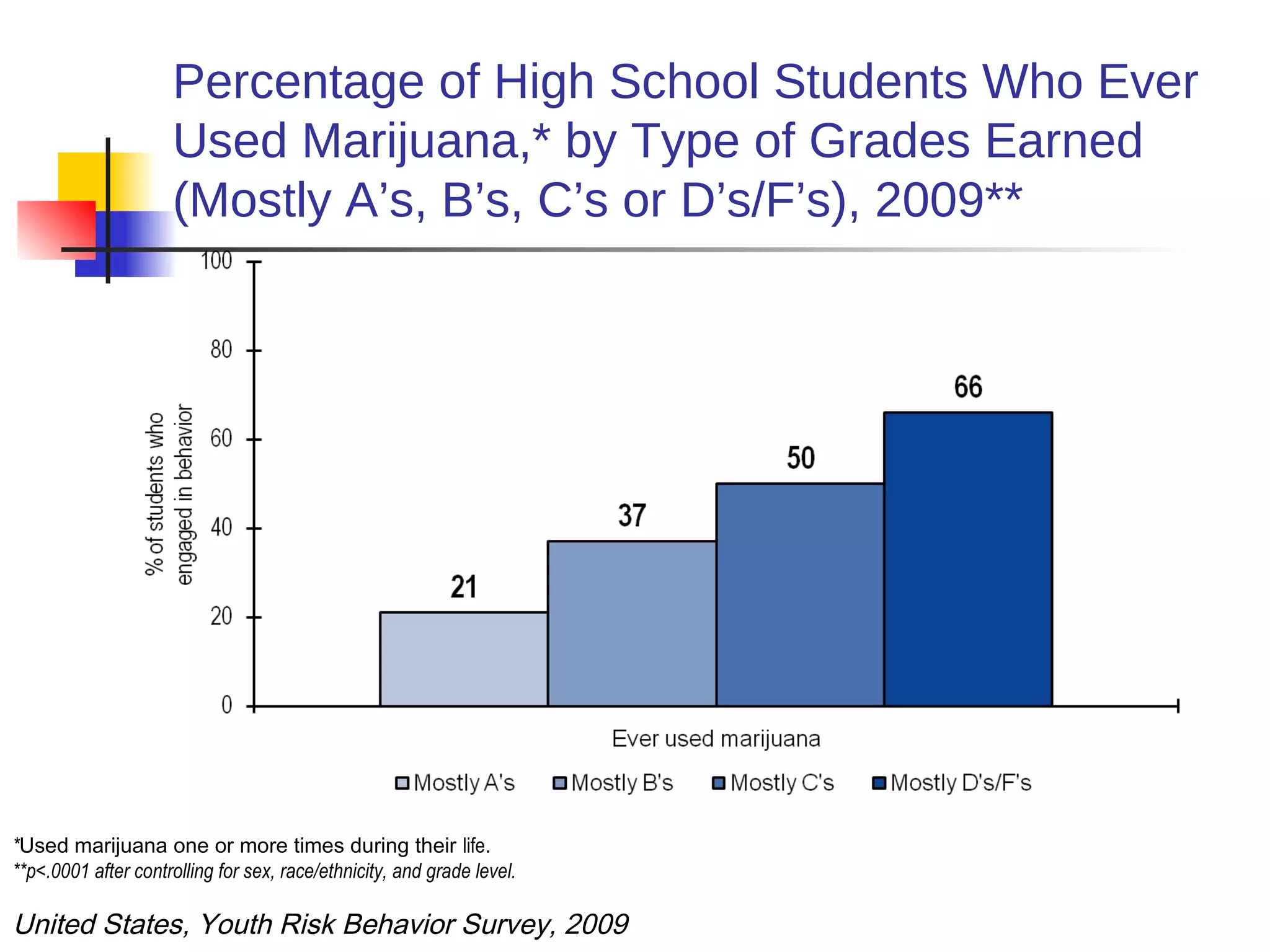
1) Poor health can negatively impact academic performance, as issues like hunger, chronic illness, and risky behaviors increase absenteeism and decrease focus.
2) Academic underachievement is linked to poorer long-term health outcomes, as less education correlates with riskier behaviors and less job/life opportunities.
3) Conversely, academic success is positively associated with better health, as higher-achieving students are less likely to engage in risky behaviors and develop chronic diseases. Addressing students' health needs can thus help improve their educational outcomes.






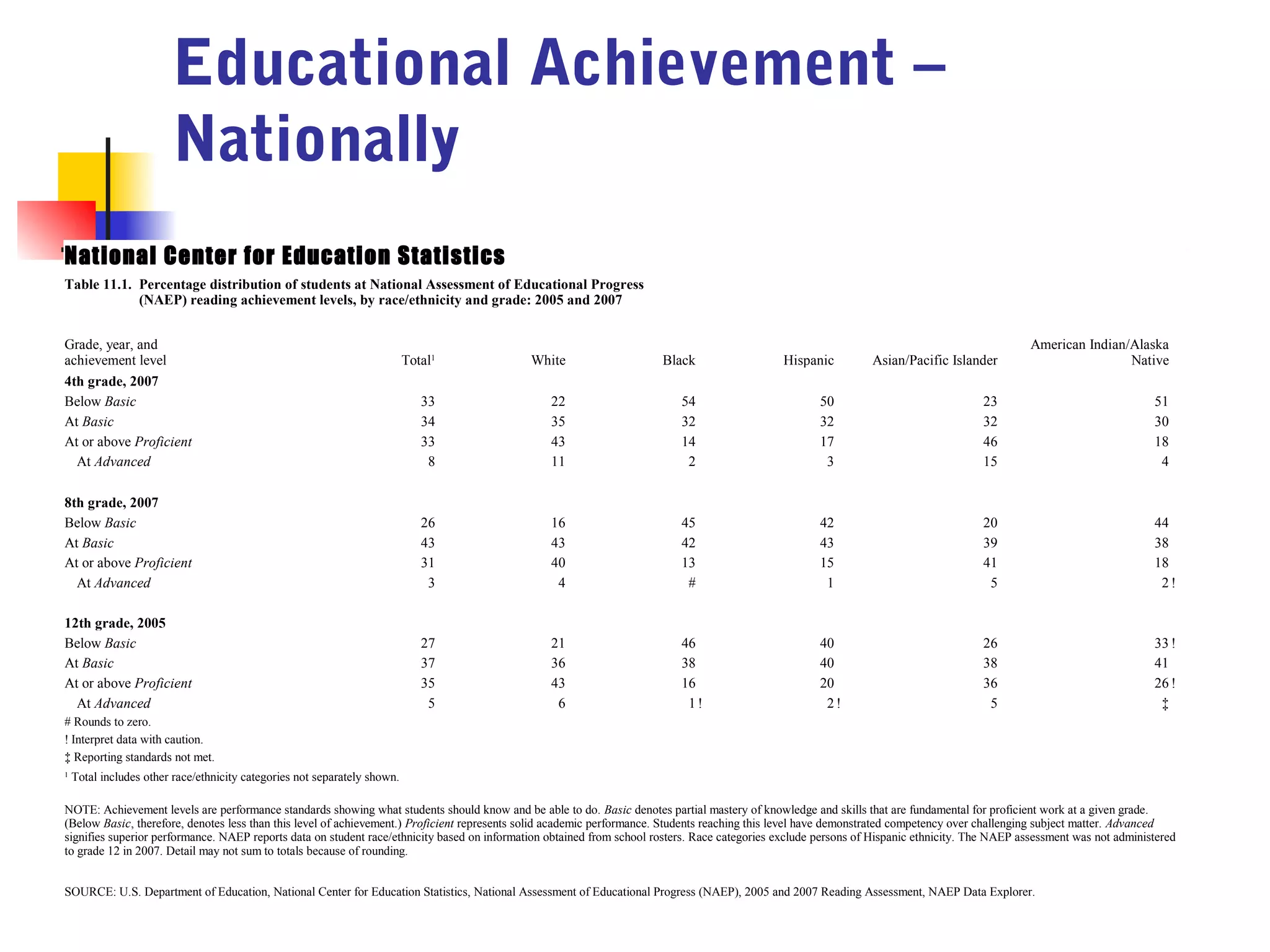
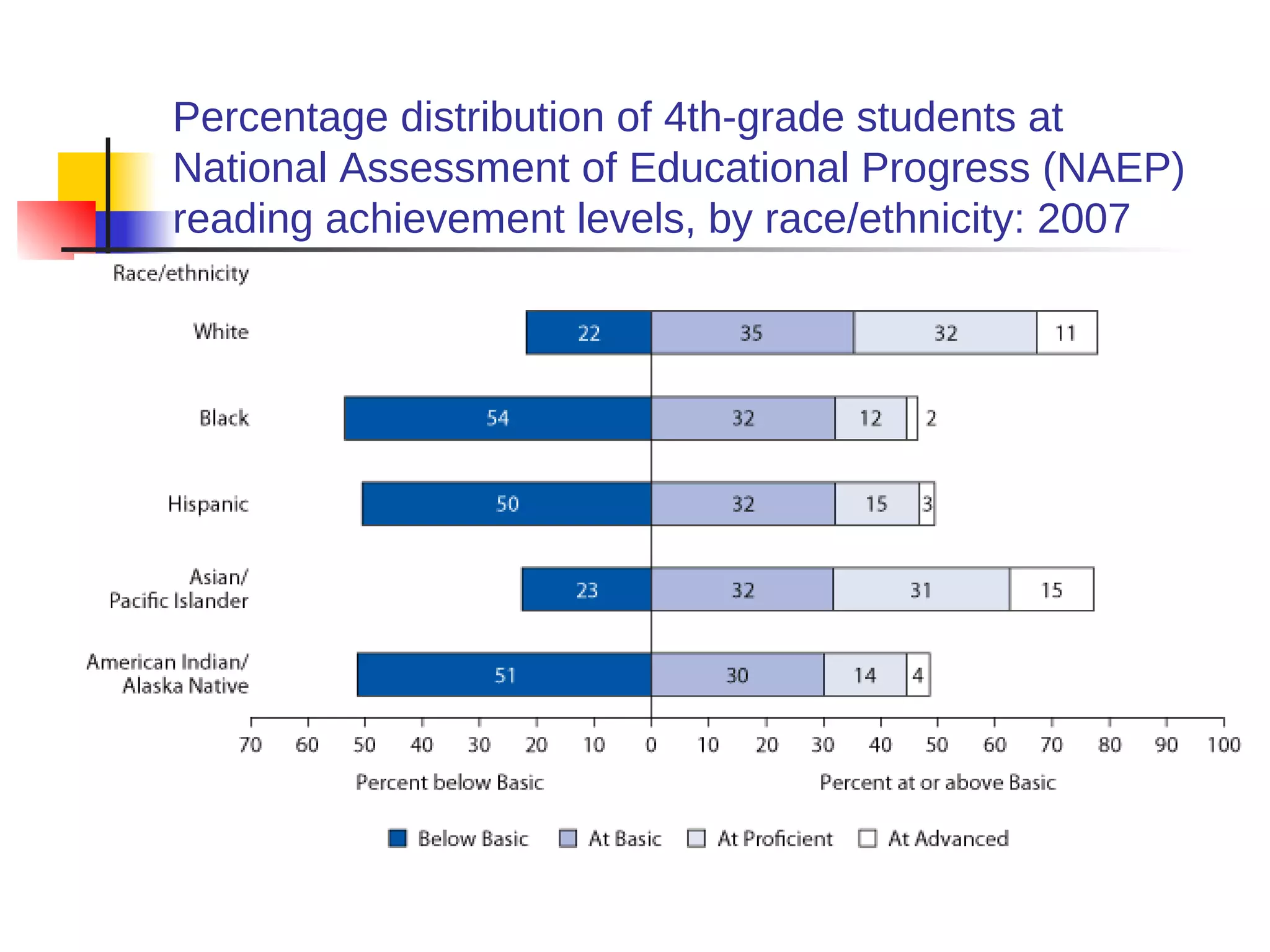
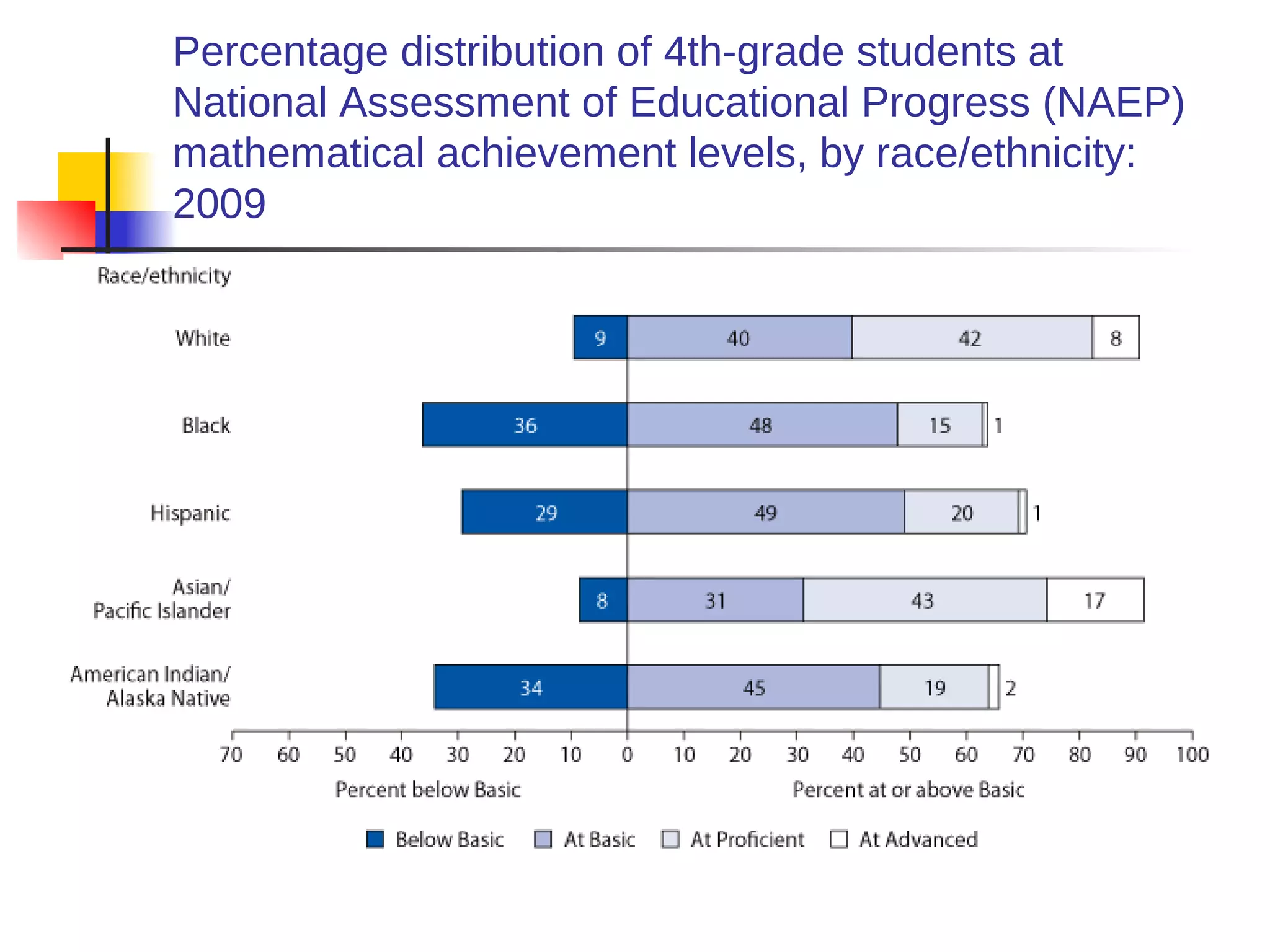
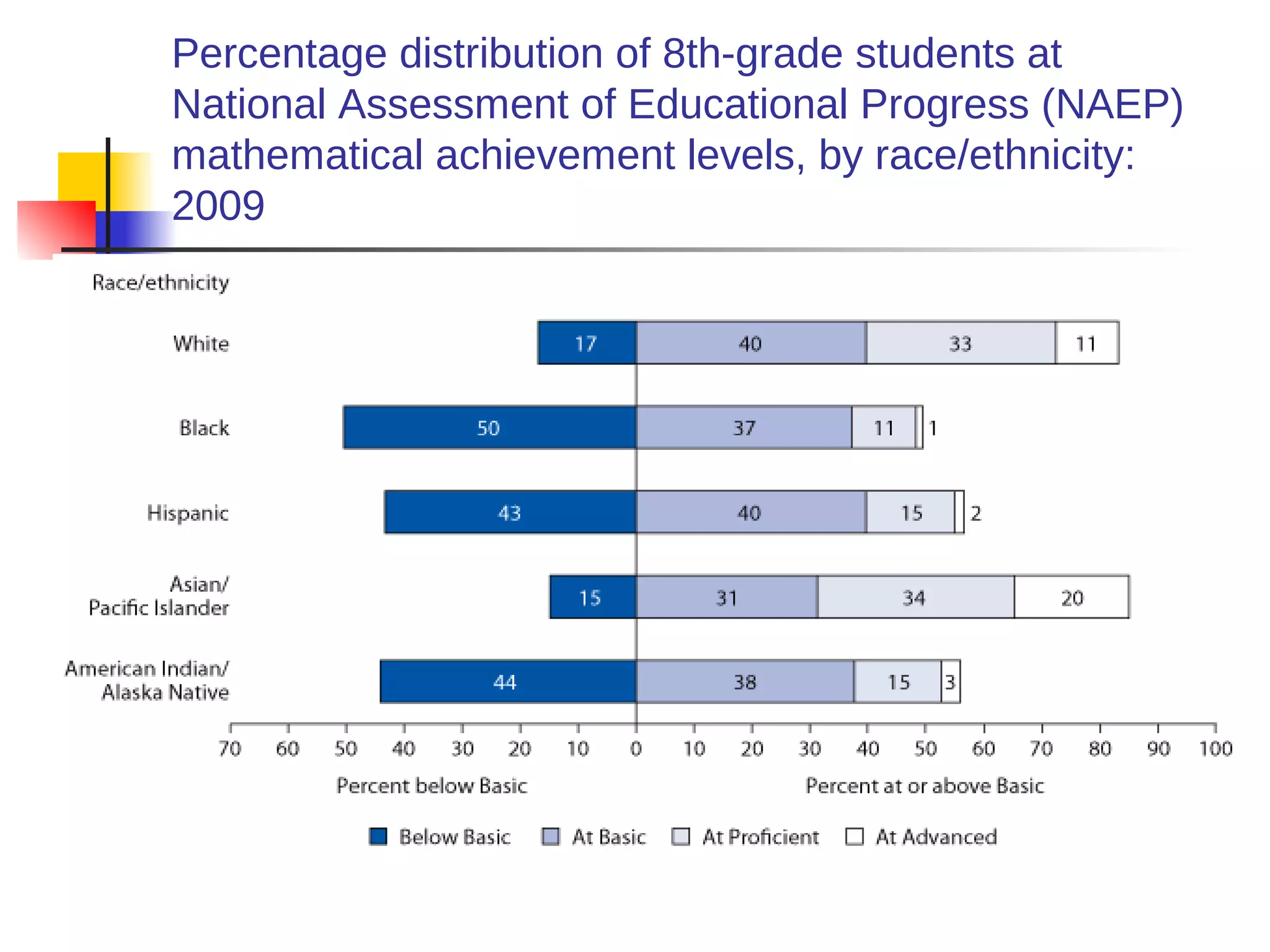
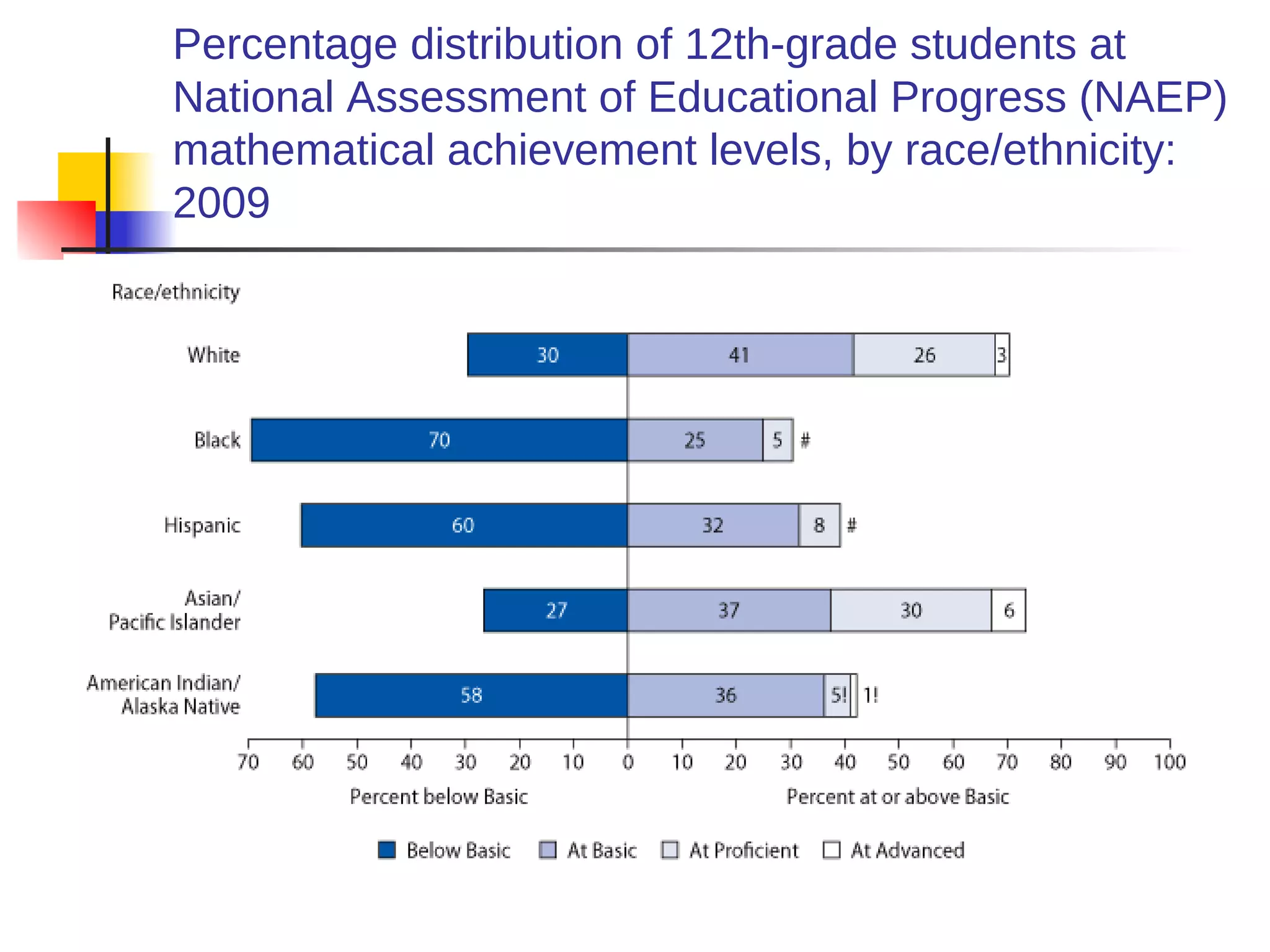
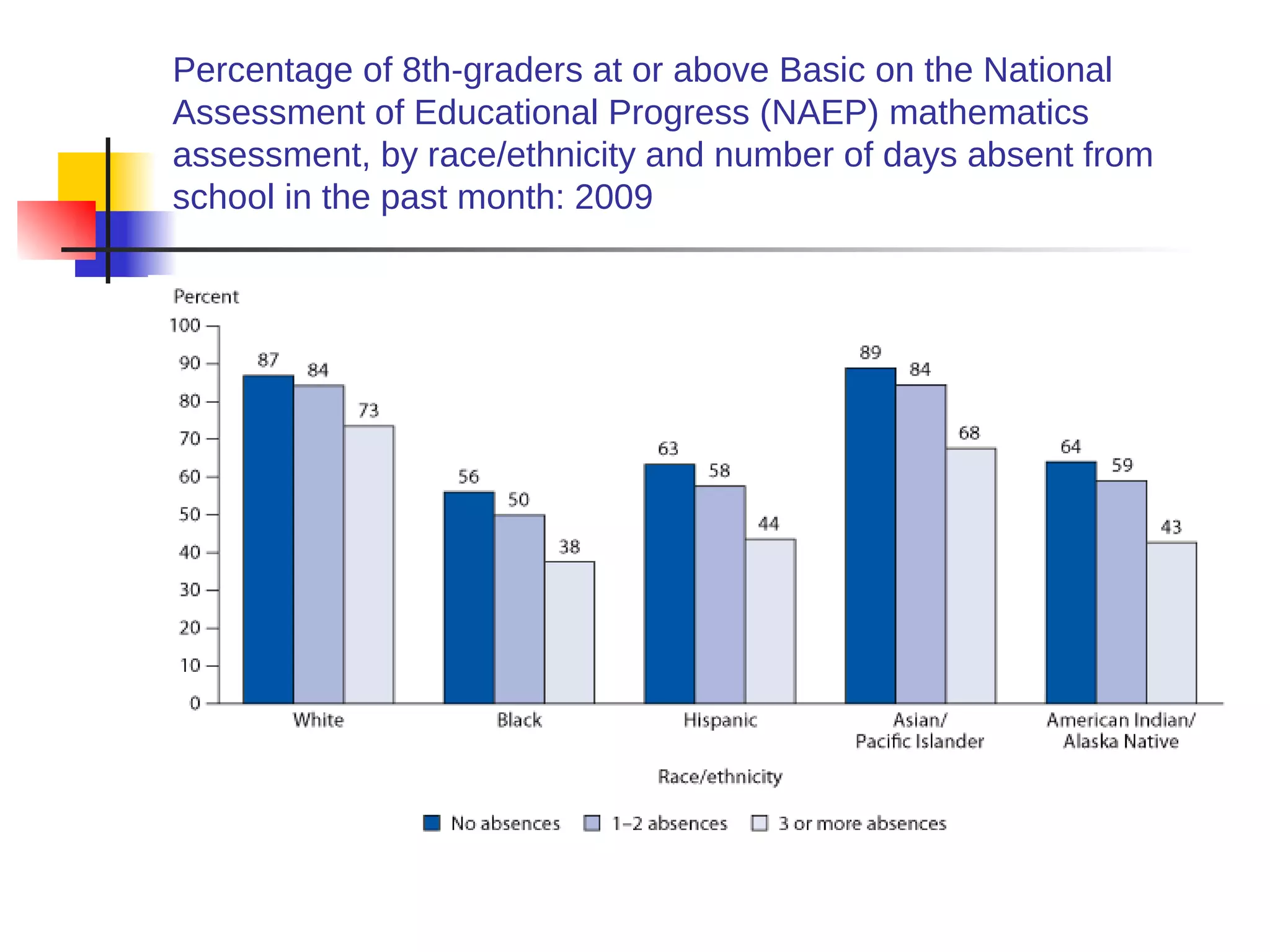








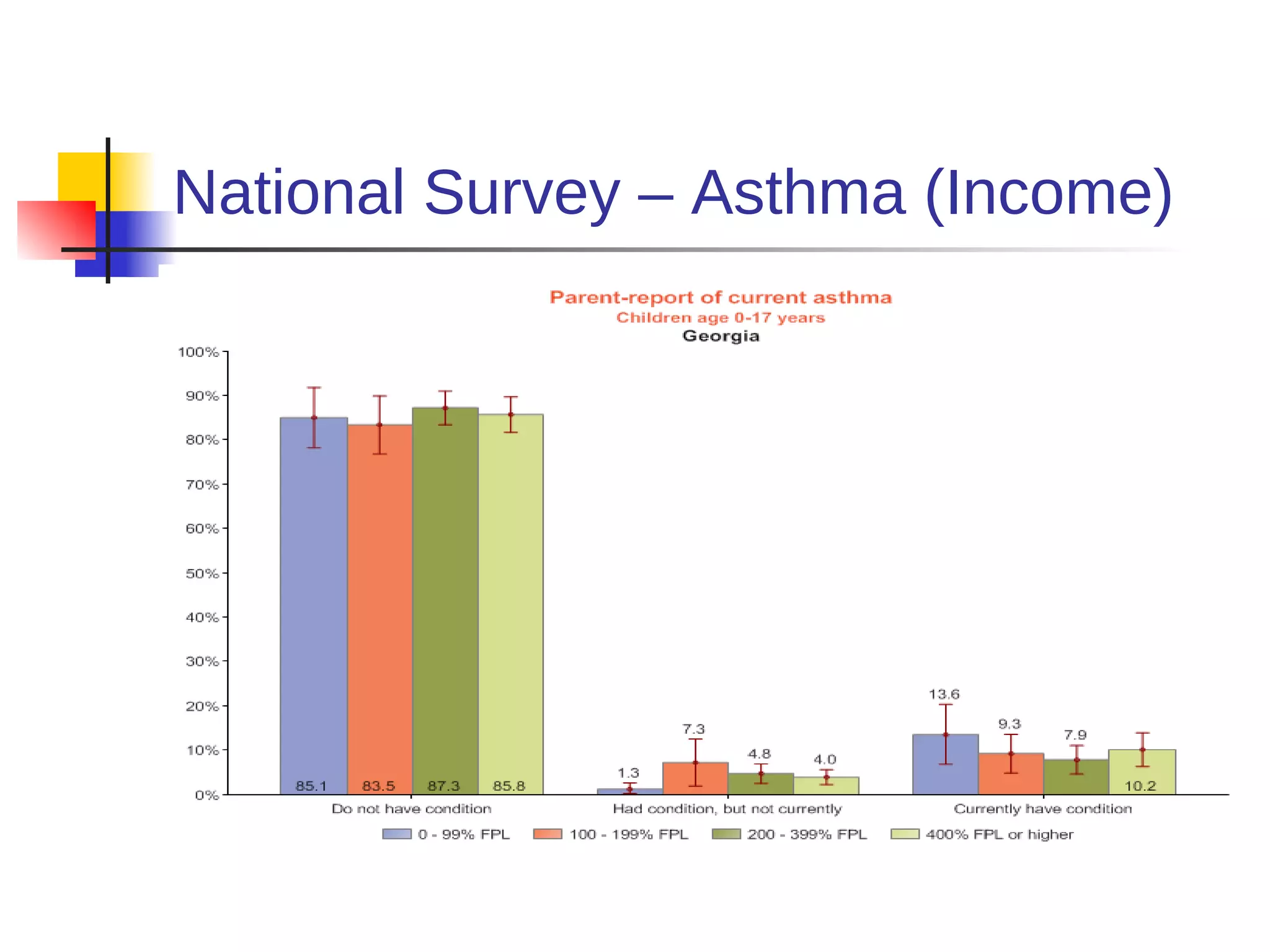
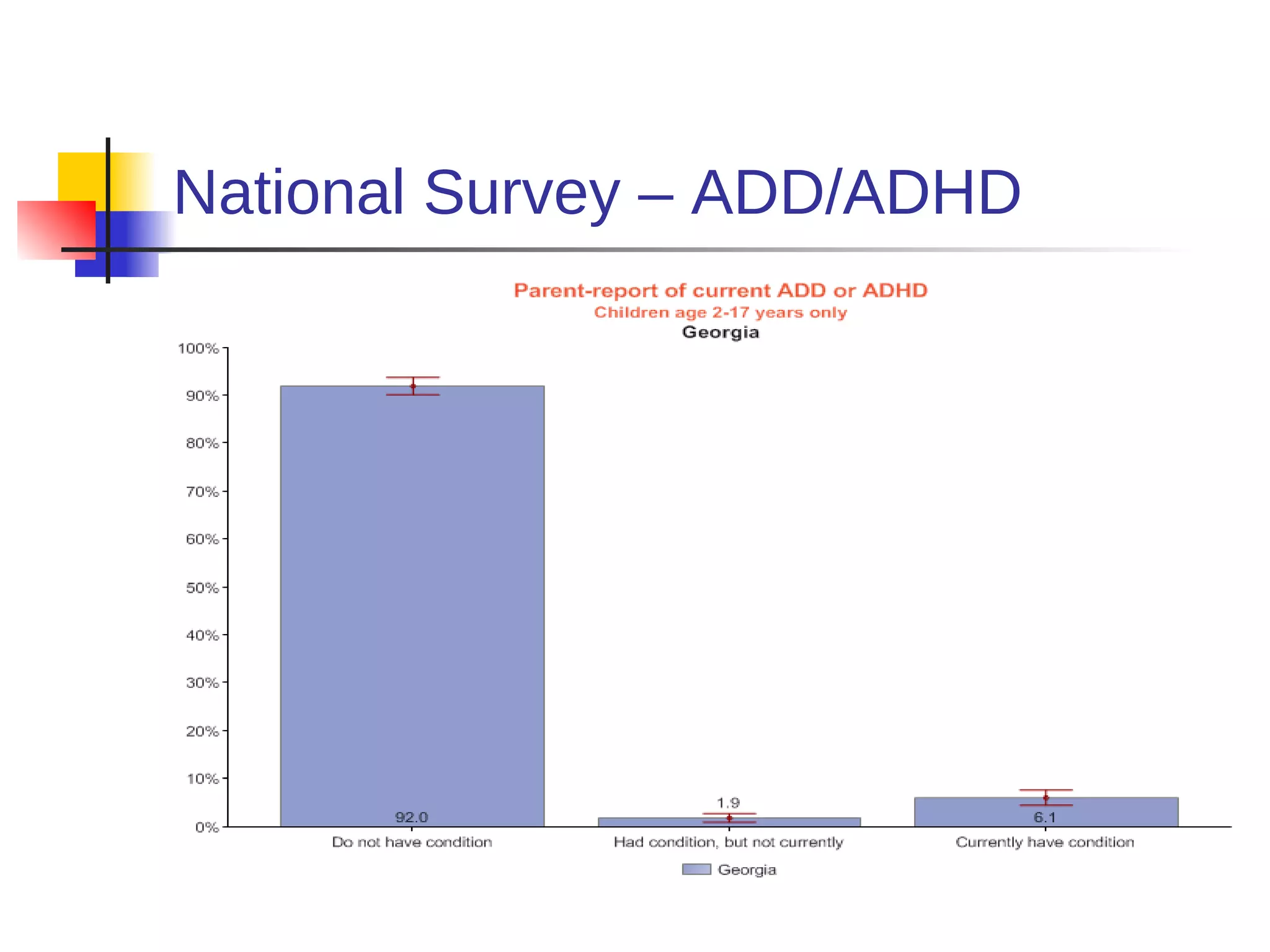
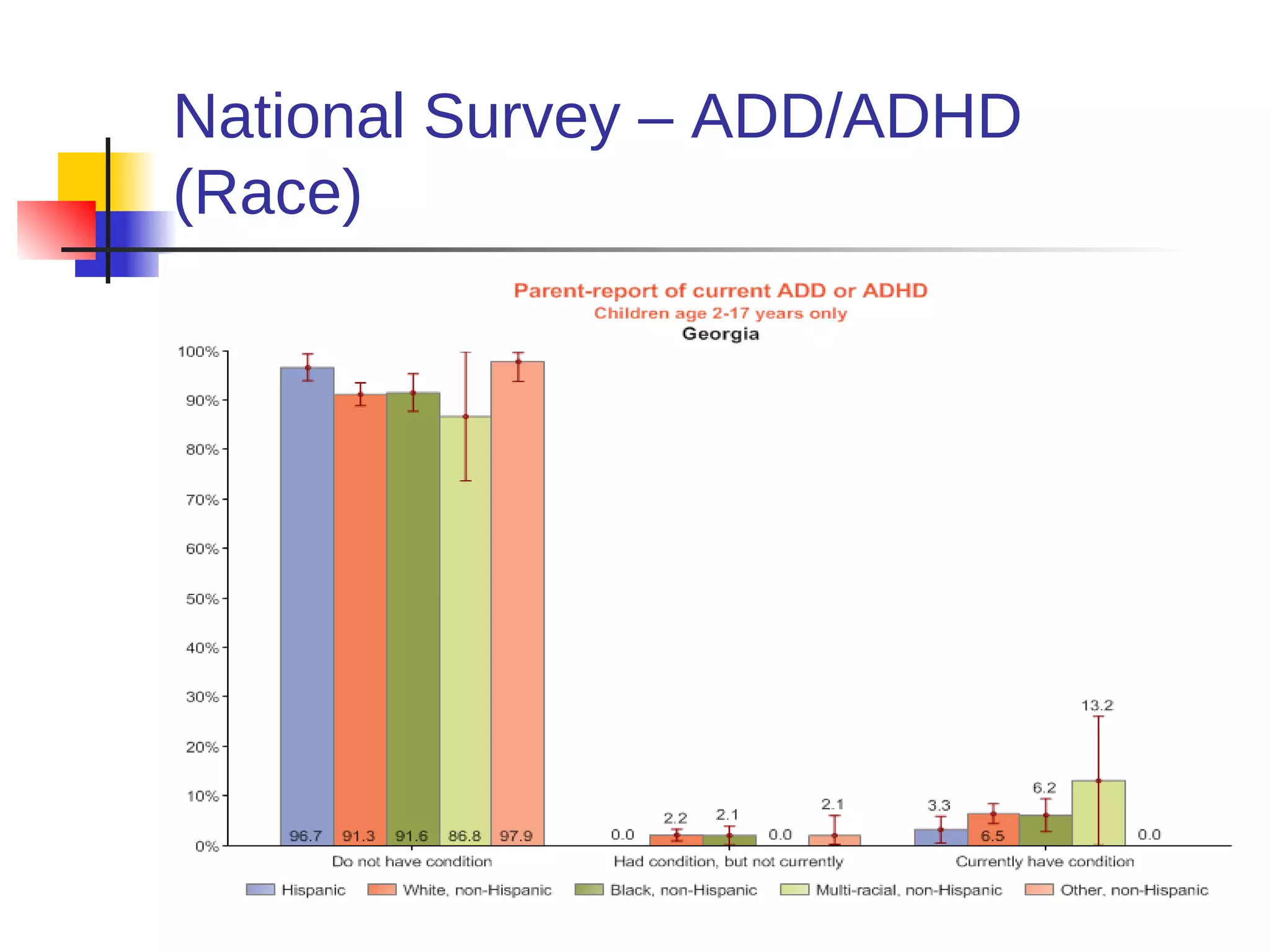
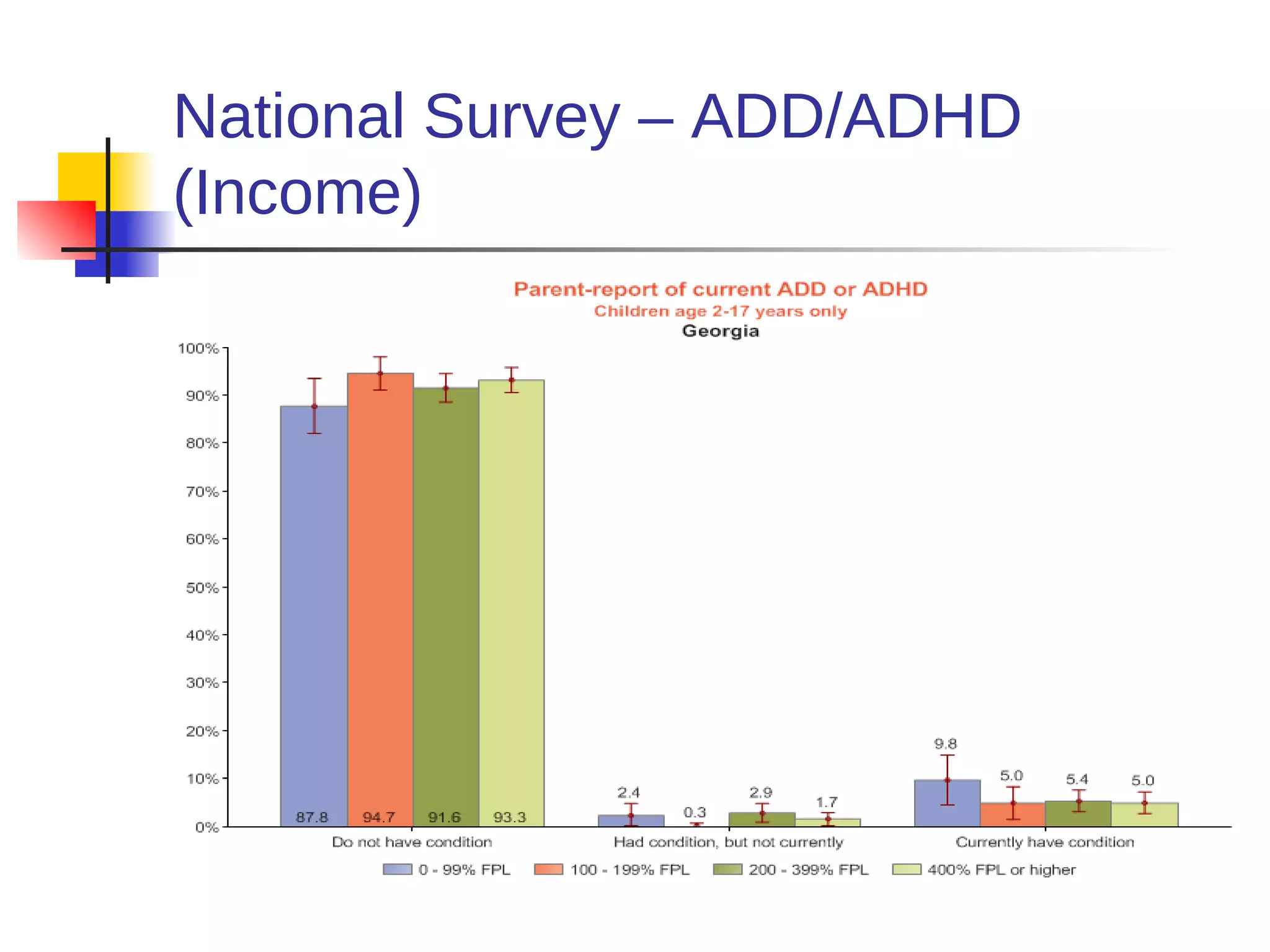
















![American Cancer Society
“[Children] …who face violence, hunger,
substance abuse, unintended pregnancy, and
despair cannot possibly focus on academic
excellence. There is no curriculum brilliant
enough to compensate for a hungry stomach
or a distracted mind.”
— National Action Plan for Comprehensive
School Health Education. 1992](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vedajohnson-121128113507-phpapp01/75/Veda-johnson-50-2048.jpg)