This document discusses control statements and loops in Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET). It covers conditional statements like If-Then, If-Then-Else, and If-Then-ElseIf. It also covers different types of loops in VB.NET including Do While, For Next, and For Each loops. Finally, it touches on VB.NET arrays, including how to declare, initialize, and use multidimensional and fixed size arrays.


![If-Then Statement
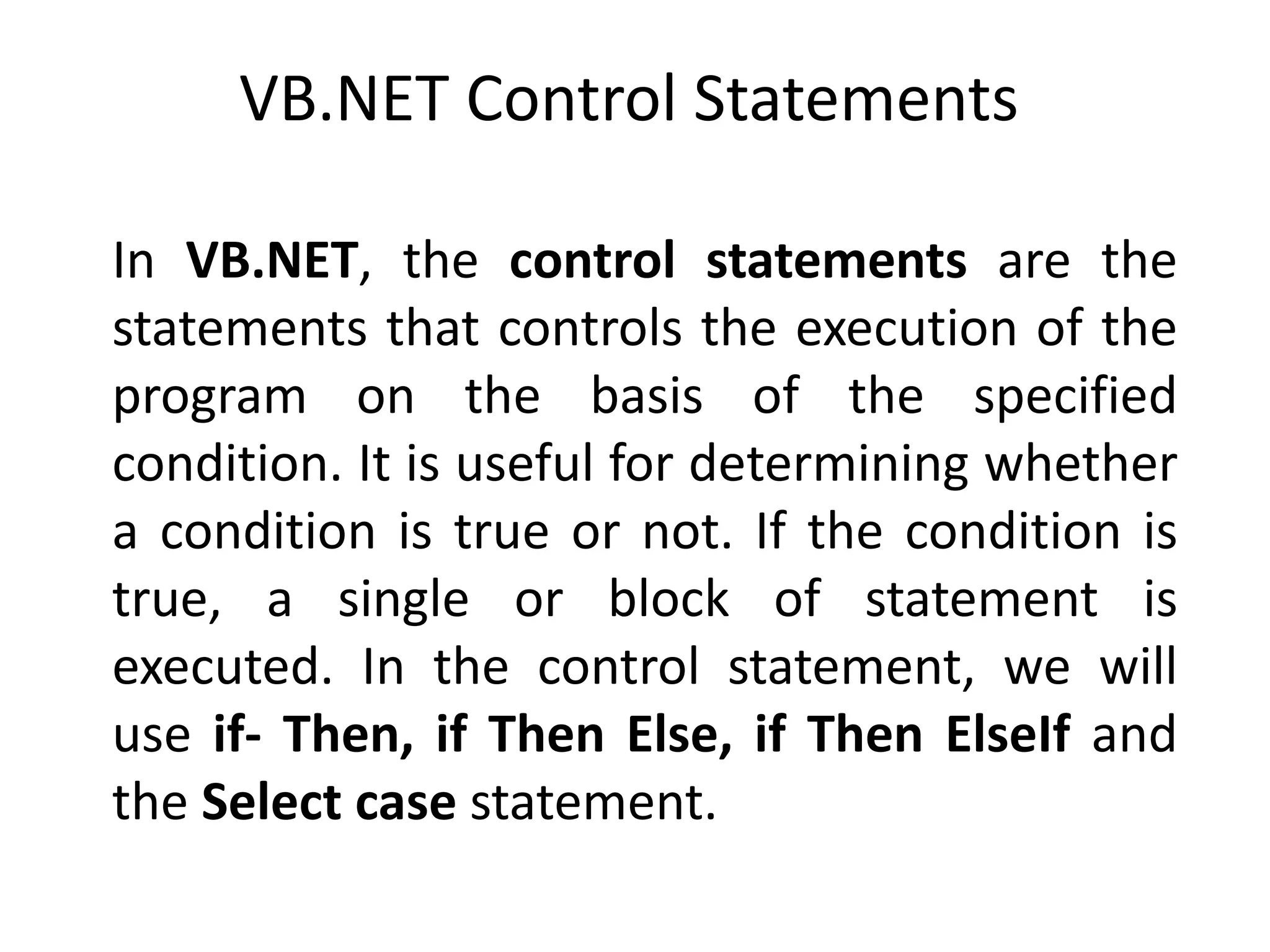
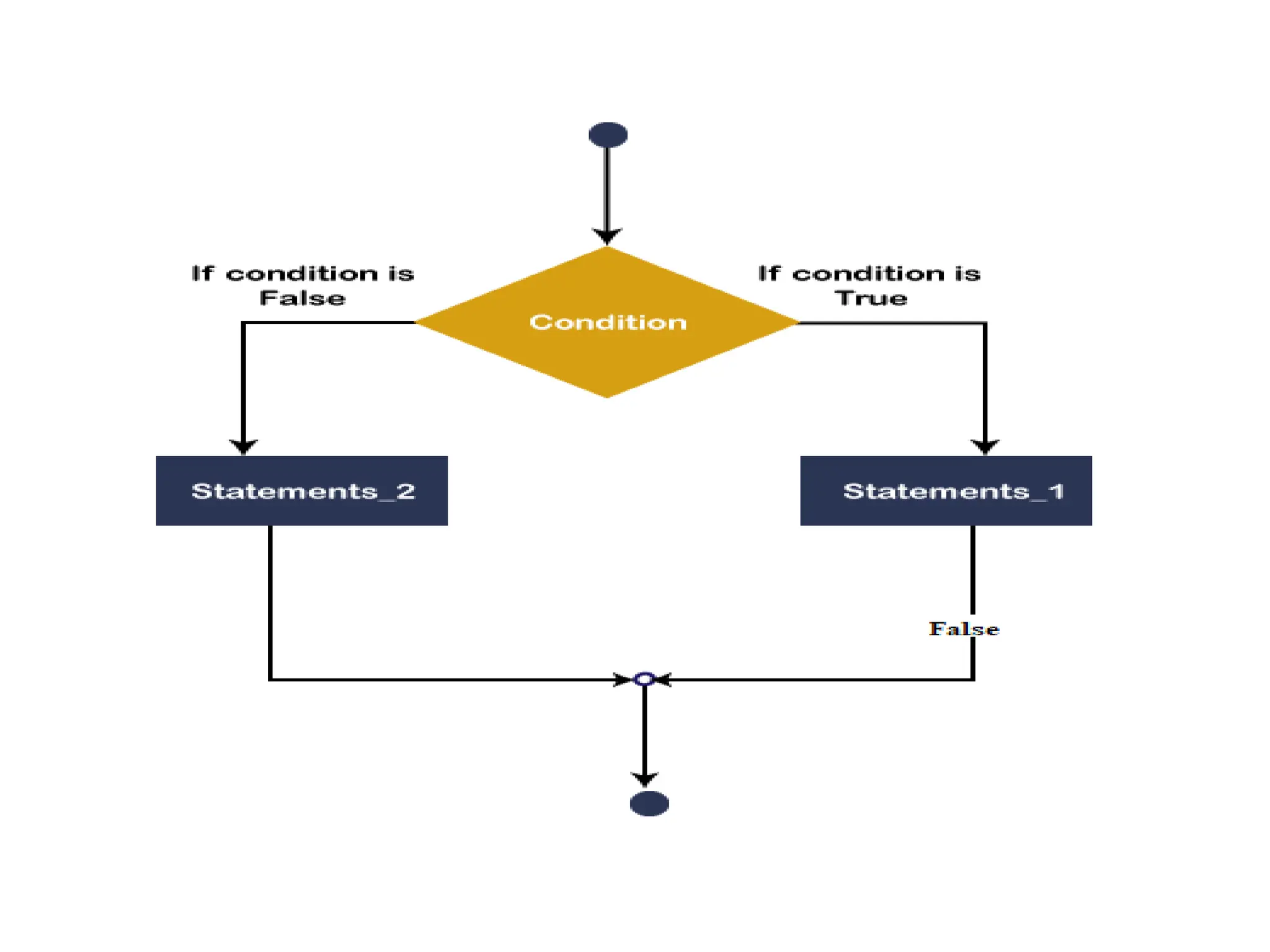
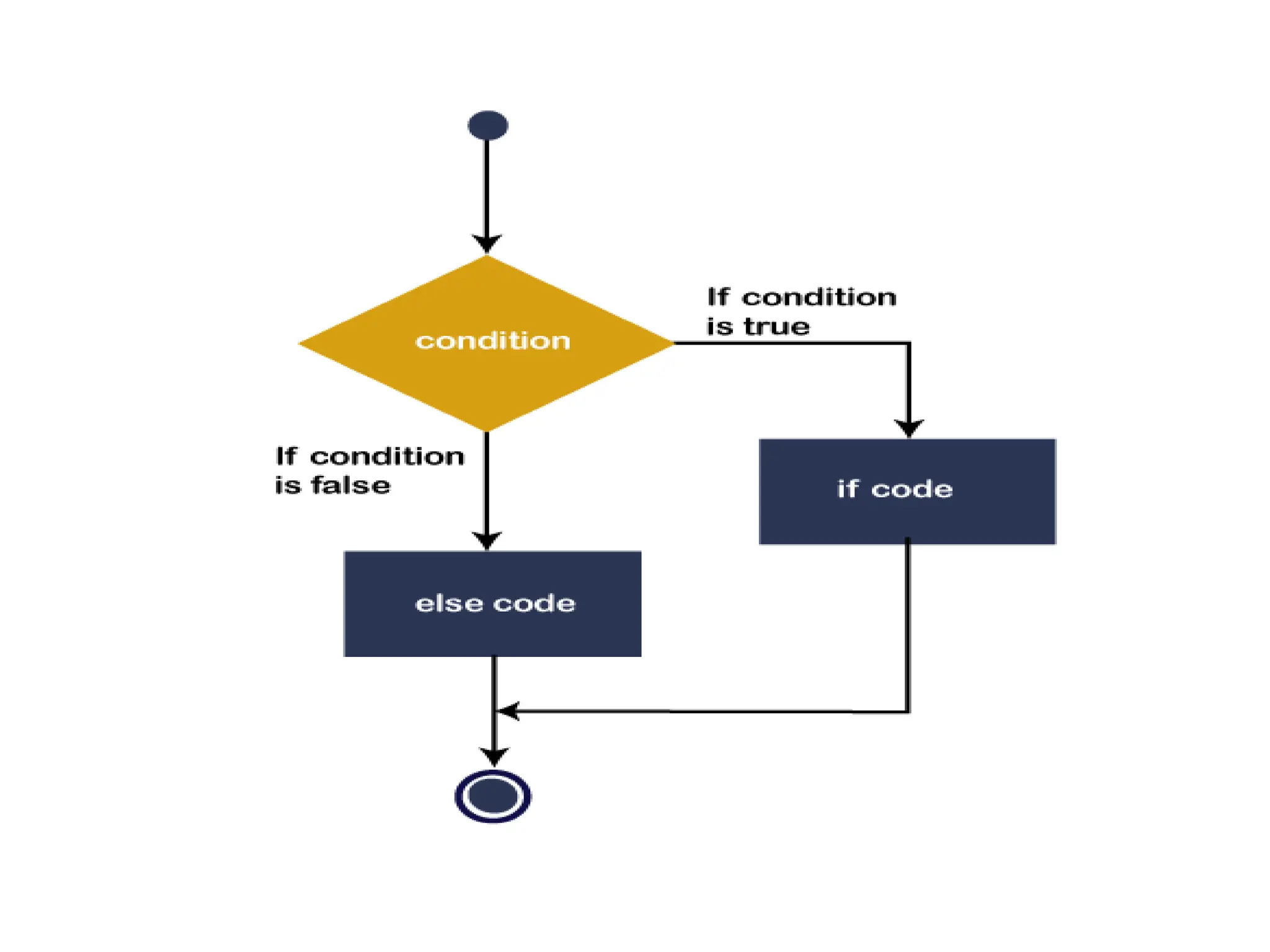
• The If-Then Statement is a control statement
that defines one or more conditions, and if the
particular condition is satisfied, it executes a
piece of information or statements.
If condition Then
[Statement or block of Statement]
End If](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbunit1-231128055649-7a05143a/75/VB-unit1-pptx-5-2048.jpg)




![Do While Loop
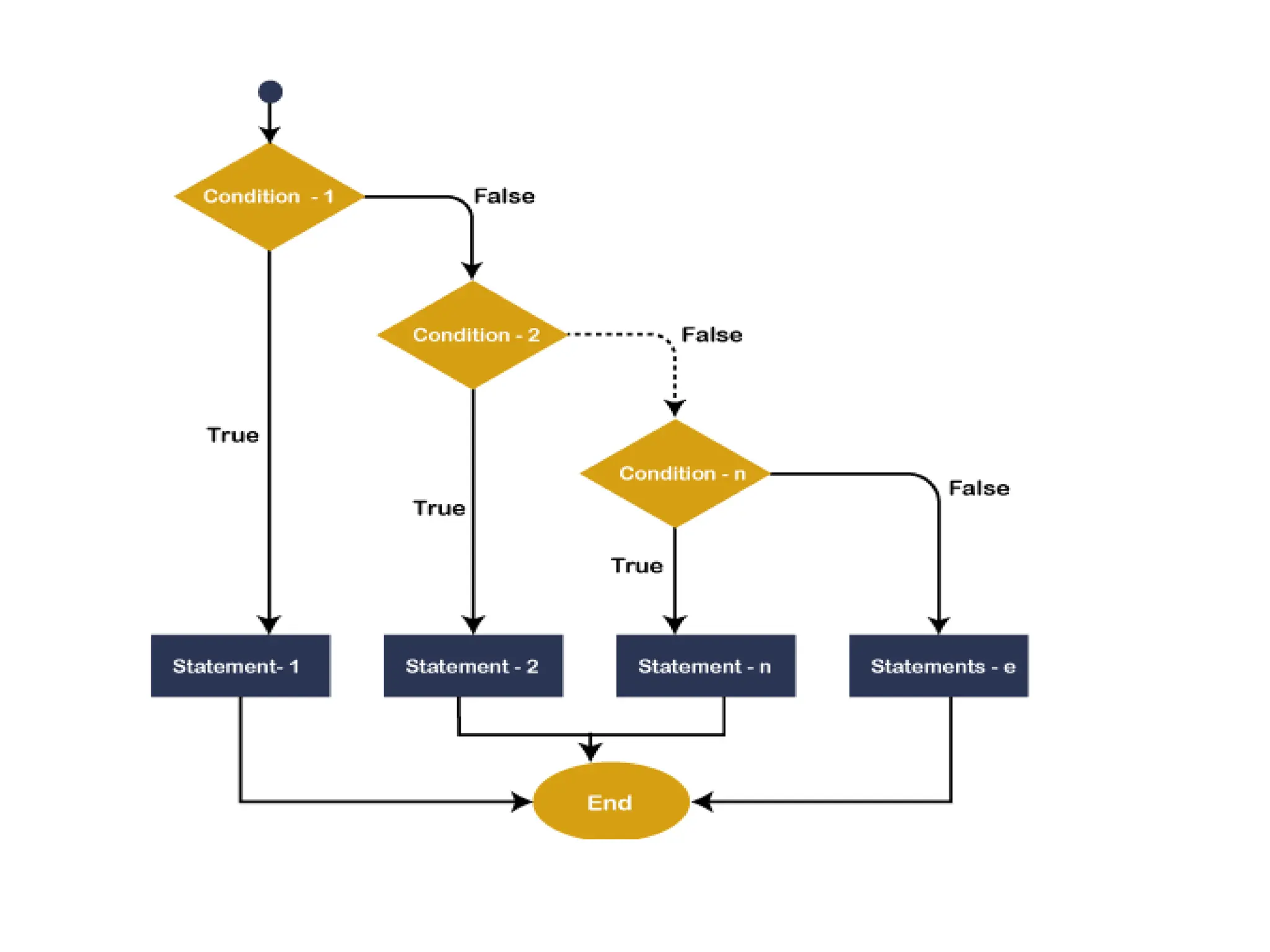
• In VB.NET, Do While loop is used to execute
blocks of statements in the program, as long
as the condition remains true.
Do
[ Statements to be executed]
Loop While Boolean_expression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbunit1-231128055649-7a05143a/75/VB-unit1-pptx-12-2048.jpg)

![For variable_name As [ DataType ] = start To end
[ Step step ]
[ Statements to be executed ]
Next](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbunit1-231128055649-7a05143a/75/VB-unit1-pptx-14-2048.jpg)

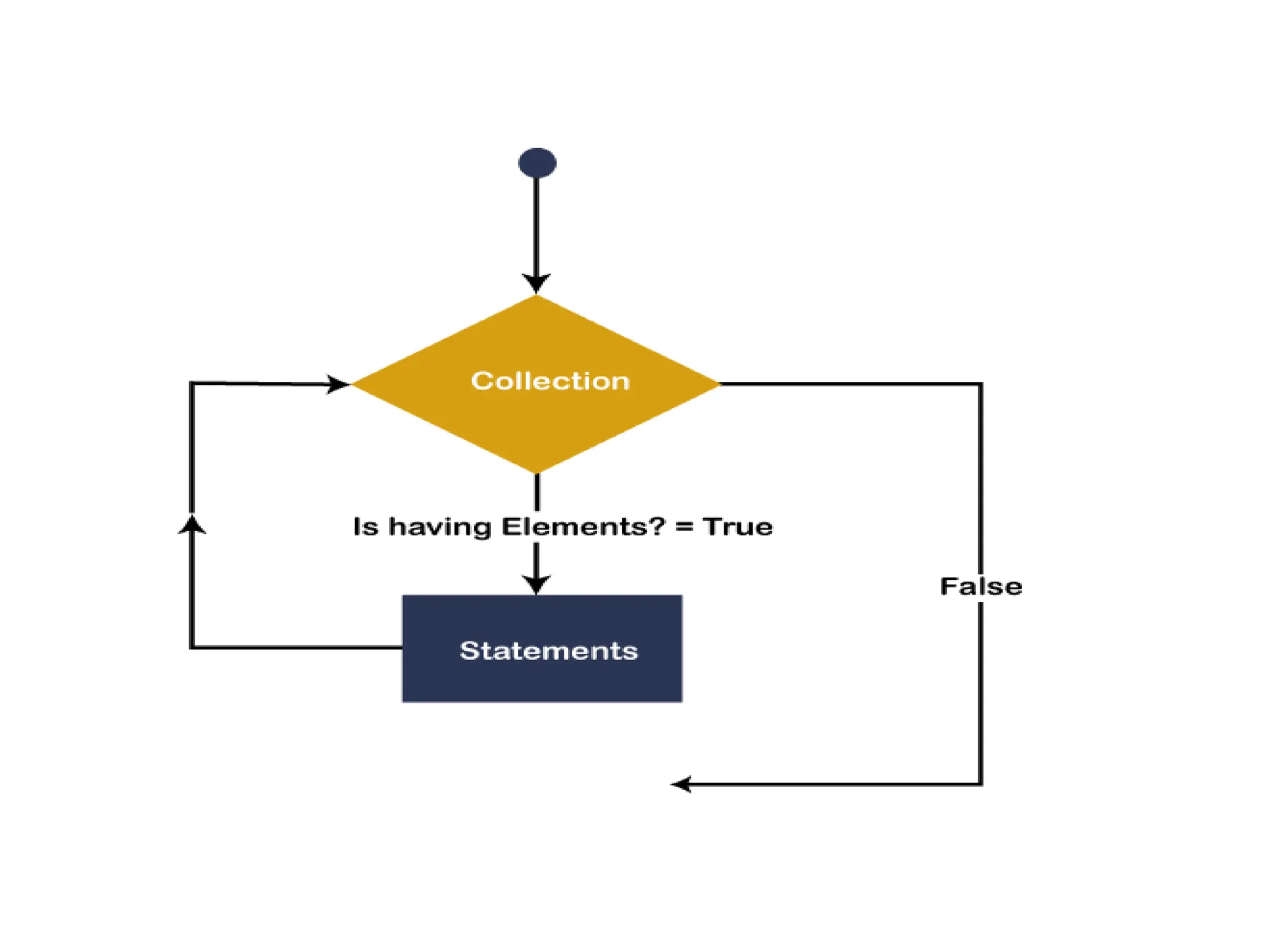
![For Each var_name As [ DataType ] In Collection
_Object
[ Statements to be executed]
Next](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbunit1-231128055649-7a05143a/75/VB-unit1-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
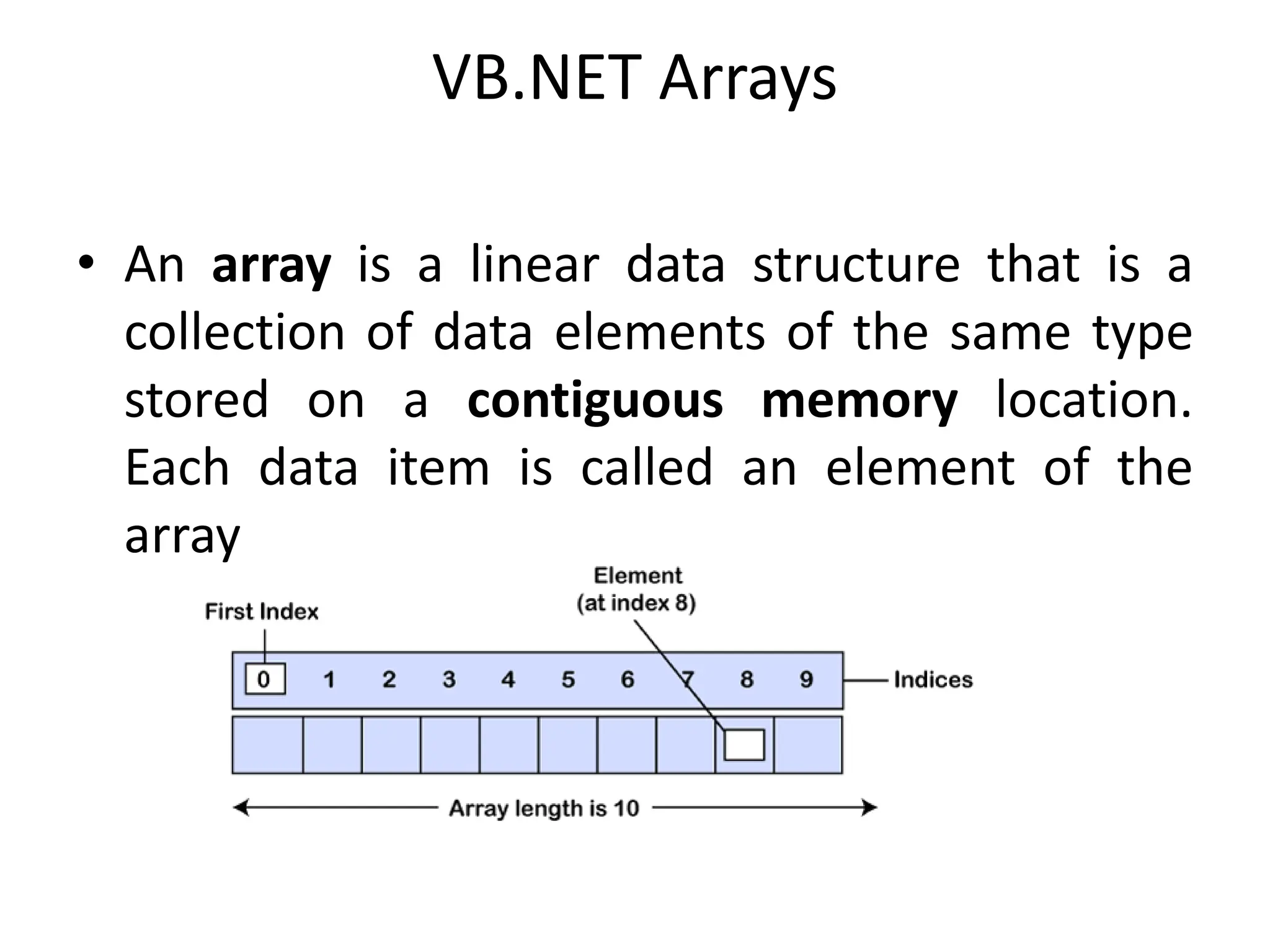
![Declaration of VB.NET Array
• We can declare an array by specifying the data
of the elements followed by parentheses () in
the VB.NET
Dim array_name As [Data_Type] ()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbunit1-231128055649-7a05143a/75/VB-unit1-pptx-19-2048.jpg)