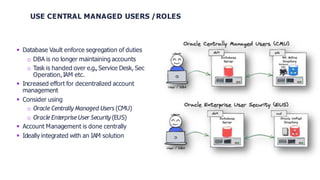
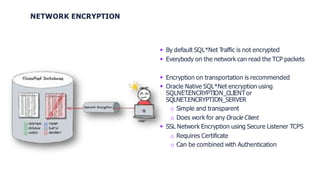
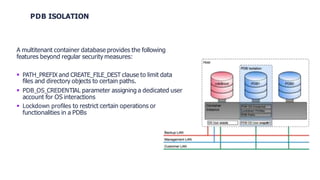
This document provides an agenda and overview of Oracle Database Vault. It discusses Database Vault features like realms and rule sets that provide controls for privileged accounts and enforce separation of duties. It provides recommendations for prerequisites like an existing security concept and hardening. It also discusses alternatives to Database Vault like activity monitoring tools and the importance of accompanying measures like Transparent Data Encryption.