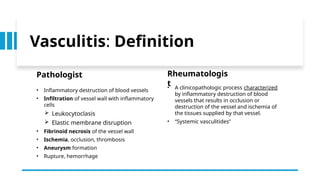
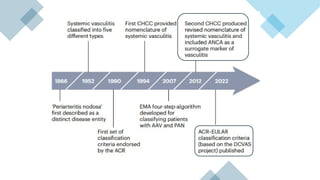
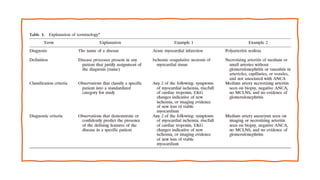
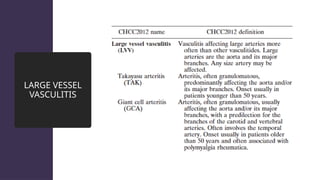
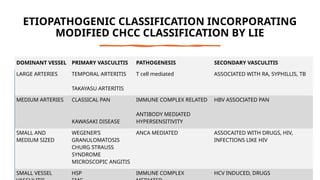
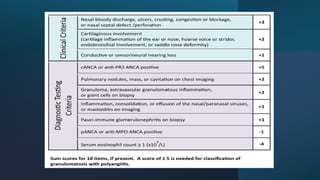
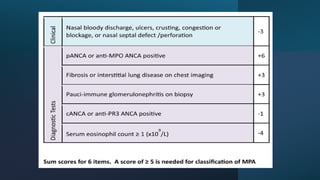
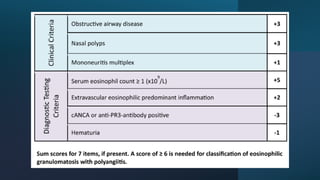
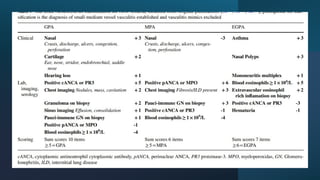
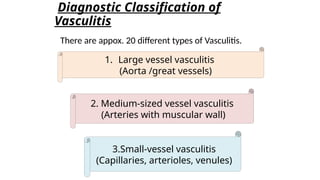
The document provides a comprehensive overview of vasculitis, defining it as the inflammatory destruction of blood vessels leading to various complications such as ischemia and hemorrhage. It classifies vasculitis into three categories based on vessel size: large vessel vasculitis, medium vessel vasculitis, and small vessel vasculitis, and outlines various associated conditions and etiologies. It also highlights the diagnostic classification and different types of vasculitis based on their pathogenesis.