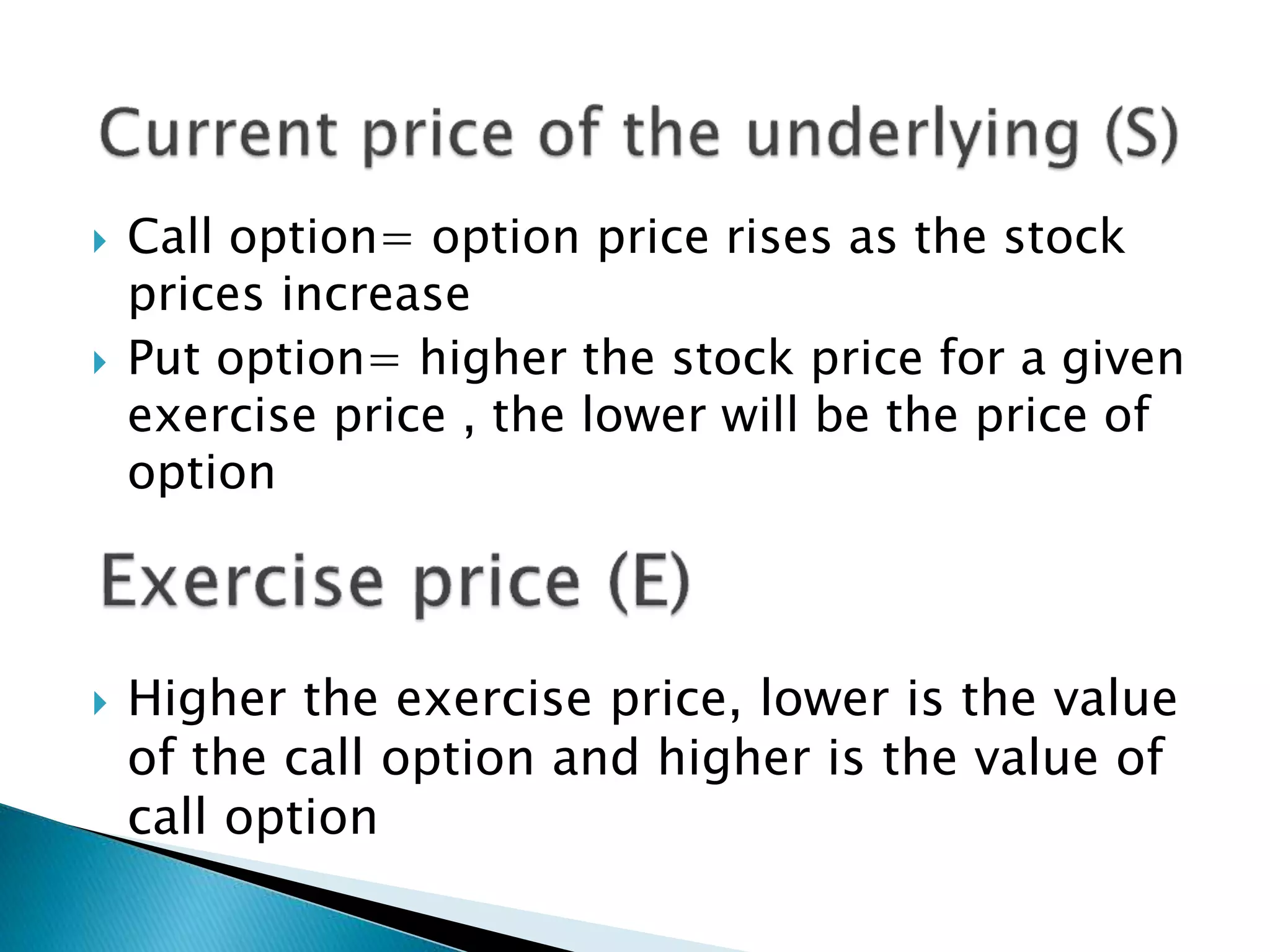
The document discusses key concepts related to option pricing models. It provides explanations of intrinsic value, time value, put-call parity, binomial option pricing model, and Black-Scholes option pricing model. The binomial model uses a discrete-time approach to value options, while Black-Scholes uses a continuous-time approach and calculus. Both aim to determine the fair price of an option based on factors like the underlying asset price, strike price, time to expiration, risk-free rate, and volatility.
































![ Discrete time model
Length of the time interval remains constant
throughout the tree
Volatility remains constant throughout the
tree
The probaility of an up movement and down
movement remains same in the entire tree]
Binomial tree is recombinant
Option price is calculated by backward
process calculation(from expiration to the
present)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valuationofoptions-210510054909/75/Valuation-of-options-34-2048.jpg)








![1. Estimate the highest value of the call
Cu=Su-E
2. Estimate the lowest value of the call
Cd=(Maximum(Sd-E),zero)
3. Estimate the probability of increase in the spot
price of the underlying shares on the expiration
date. (It is calculated with the help of expected
return of the investor or the risk free rate of
return)
E(r)=[(p*percentage increase)+(1-p*percentage
decrease)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valuationofoptions-210510054909/75/Valuation-of-options-43-2048.jpg)
![4. Calculate the expected future value of the
call option with the help of probability
Cu*p+[cd*(1-p)]
5. Calculate the present value of the call
Future value/(1+r)n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valuationofoptions-210510054909/75/Valuation-of-options-44-2048.jpg)














