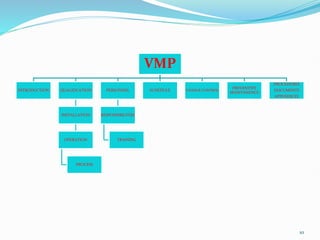
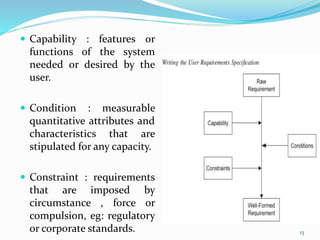
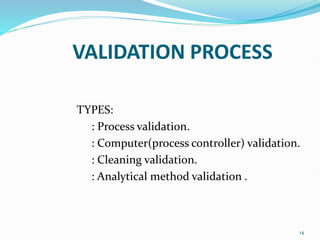
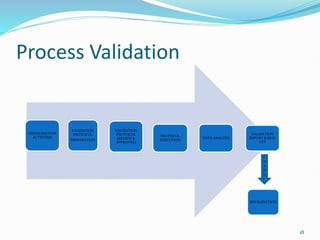
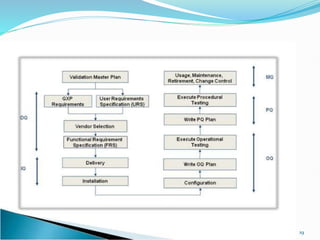
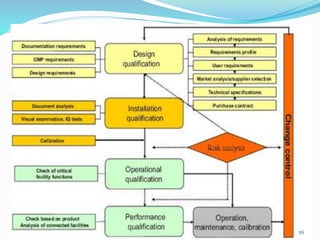
The document outlines the concepts of validation and qualification, emphasizing their roles in ensuring processes and equipment meet quality standards in manufacturing. It details the validation master plan, types of validations (such as process and cleaning validation), and the steps involved in the validation process, including user requirement specifications and various qualifications. The advantages of validation, including compliance with regulations and reduced defect costs, are also highlighted.