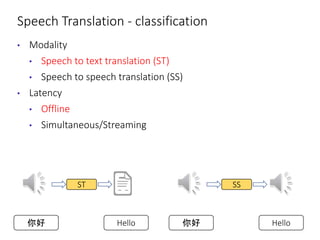
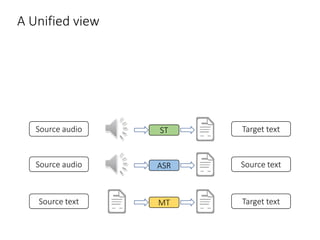
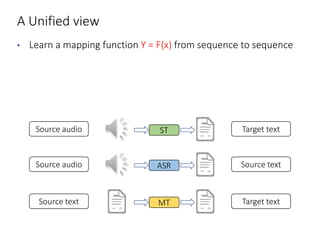
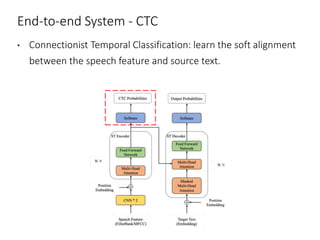
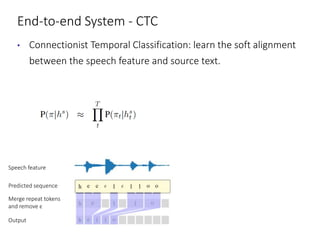
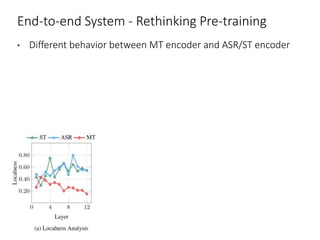
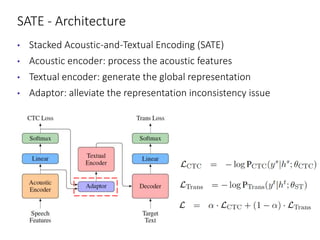
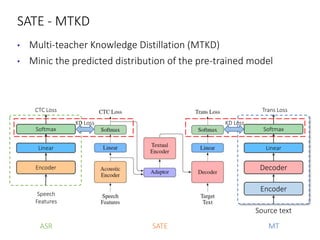
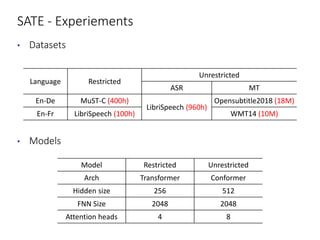
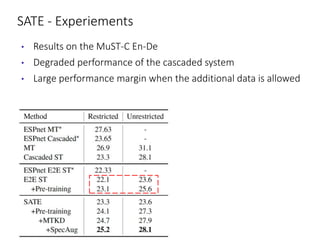
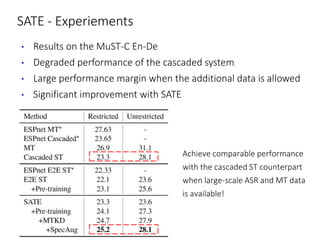
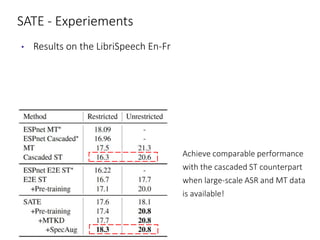
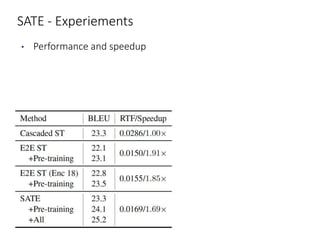
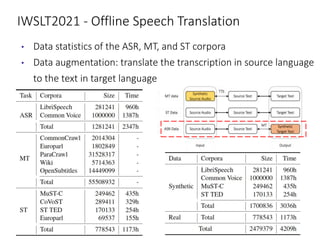
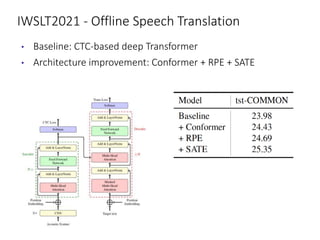
The document discusses utilizing pre-trained models for end-to-end speech translation. It describes how cascaded and end-to-end speech translation systems work, and the advantages and disadvantages of each. It then presents the stacked acoustic-and-textual encoding (SATE) approach which uses a pre-trained acoustic encoder and textual encoder with an adaptor to alleviate representation inconsistencies. Experimental results on the MuST-C dataset show SATE achieves comparable performance to cascaded systems when large pre-trained ASR and MT models are available. The document also discusses the offline speech translation task at IWSLT2021 where ensemble models using SATE outperformed baselines.