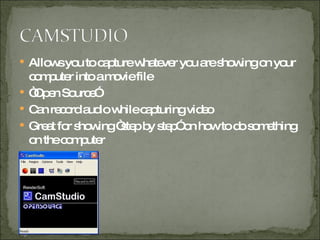
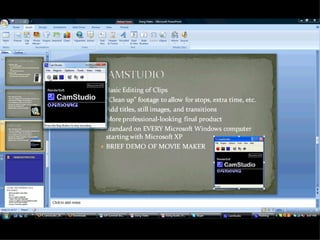
The Burrell School District in-service on February 16, 2009, focused on utilizing video recordings in the classroom to enhance learning experiences. Participants learned about various video editing tools and platforms, including Microsoft Movie Maker, Discovery Streaming, TeacherTube, and YouTube, along with best practices for filming and editing. The session emphasized the importance of incorporating differentiated instruction and student choice in video projects, while also providing support materials and resources for effective implementation.