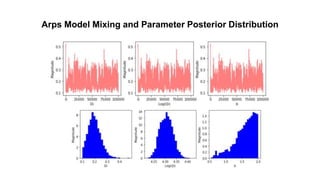
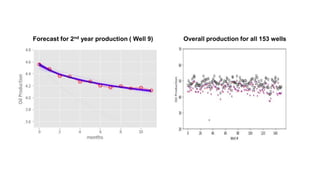
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are used to estimate parameters for decline curve analysis (DCA) production forecasting models. Accurate production forecasts are important for operational decisions, planning, transactions, and regulatory proceedings. The commonly used Arps model is formulated, with non-informative prior distributions proposed for each parameter. MCMC is used to obtain the posterior distributions of the parameters by calculating acceptance ratios at each step. Forecasts are generated for individual wells and overall production across 153 wells. Future work could involve detecting and removing anomalous data, and using more complex hierarchical models instead of the Arps model.


![Model Formulation: Arps Model
Arps Model, Empirical
Model
𝒒𝒕 = 𝒒𝒊(𝟏 + 𝒃𝑫𝒊 𝒕)
−
𝟏
𝒃
Proposed Distribution
𝒒𝒊,𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒐𝒔𝒆~ 𝑵 (𝒒𝒊, 𝟏)
𝑫𝒊,𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒐𝒔𝒆~ 𝑵 (𝑫𝒊, 𝟎. 𝟏)
𝒃 𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒐𝒔𝒆~ 𝑵 (𝒃,, 𝟎. 𝟏)
Parameters
Uniform Prior [0.1, 1,000,000]
𝑫𝒊 Uniform Prior [0.1, 50]
𝒃 Uniform Prior [0, 2]
Acceptance Ratio
𝜶 = 𝑴𝒊𝒏 𝟏,
𝒇(𝒒|𝜽 𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒐𝒔𝒂𝒍)
𝒇(𝒒|𝜽 𝒏−𝟏)
𝒒𝒊
non-informative prior distribution for each of the parameter normal distribution is proposed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/disi-190516172801/85/Using-MCMC-sampling-technique-for-Well-production-forecasting-4-320.jpg)