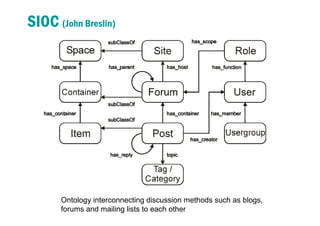
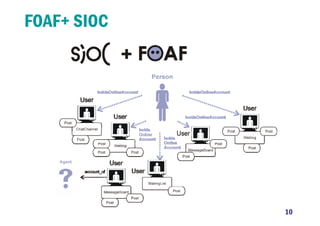
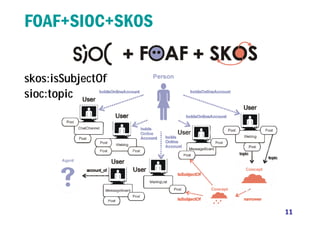
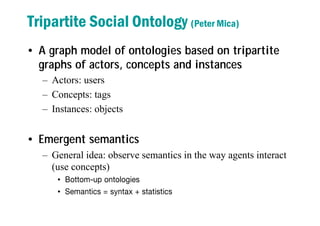
1) The document discusses modeling user interactions in online social networks to solve real problems. It analyzes data from Twitter and Me2day to measure differences in strength of user interactions.
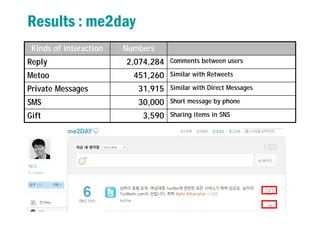
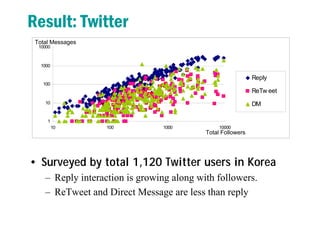
2) It finds that interactions like replies are more common than retweets or direct messages on Twitter, while interactions like comments are more common than "metoos" on Me2day.
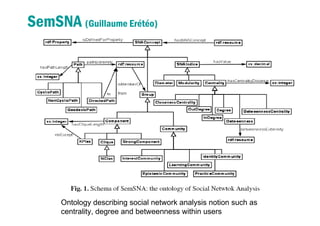
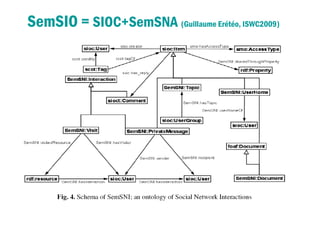
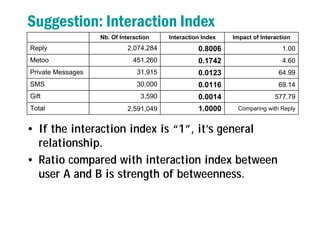
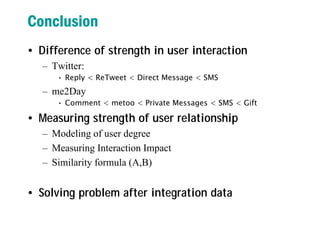
3) It proposes developing an interaction index and formulas to measure strength of relationships between users based on analyzing types and amounts of interactions over time. This could help solve problems like identifying disconnected friends or recommending experts to follow.