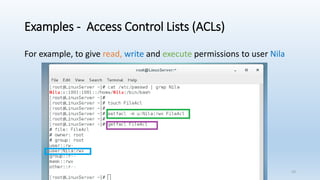
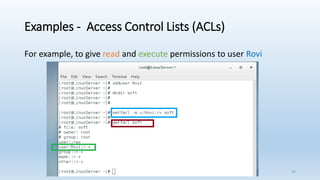
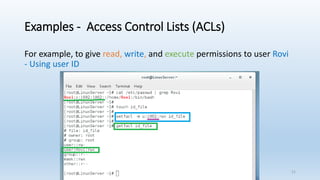
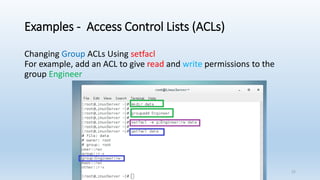
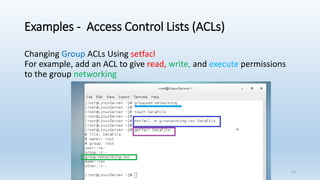
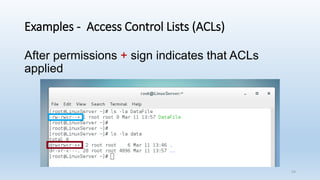
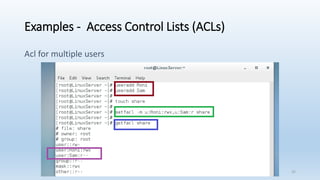
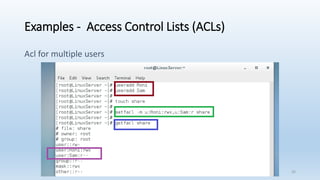
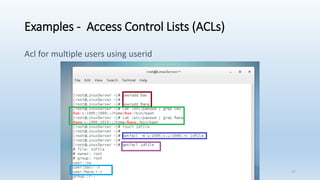
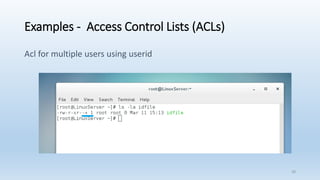
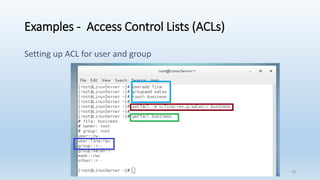
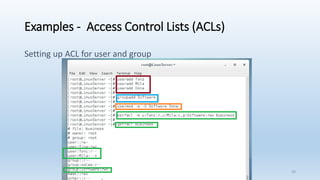
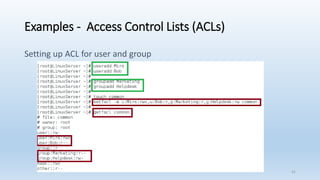
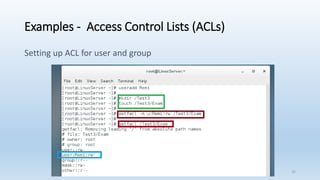
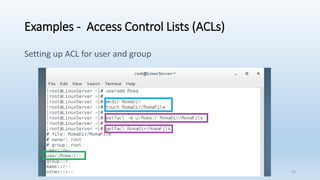
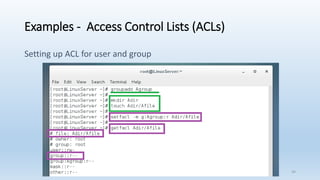
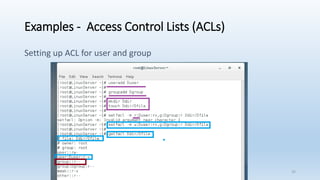
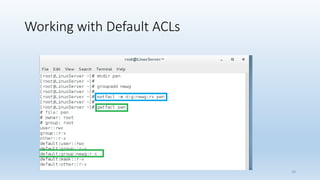
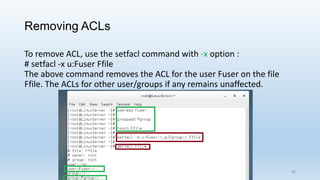
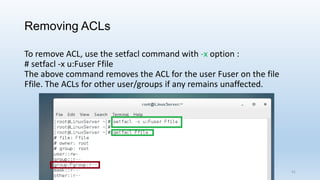
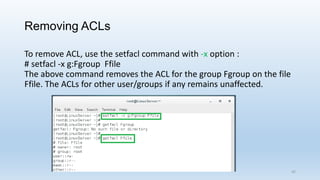
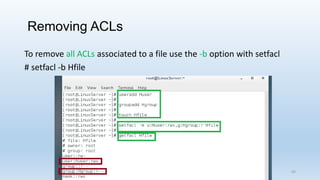
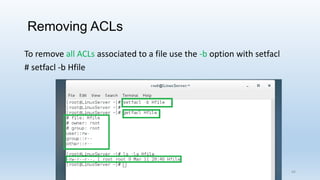
The document discusses Linux Access Control Lists (ACLs), providing a flexible mechanism for managing file and directory permissions beyond traditional Unix/Linux permissions. It details how to set, modify, and remove ACLs using the setfacl command, as well as describing the differences between access and default ACLs. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of ACLs, including the ability to give permissions to multiple users or groups and enabling inheritance for new items in a directory.