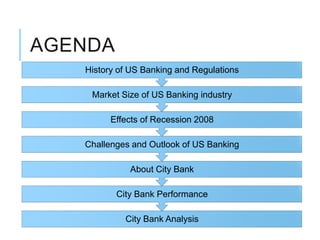
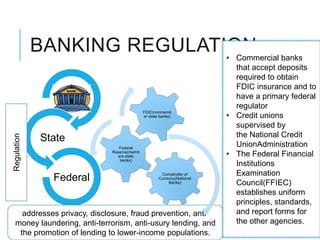
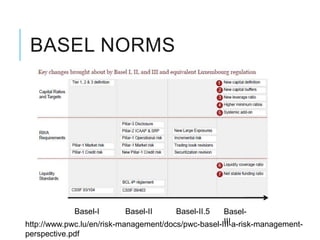
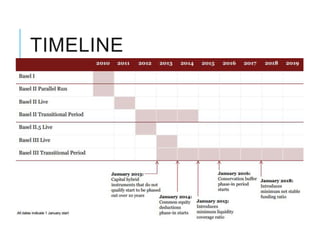
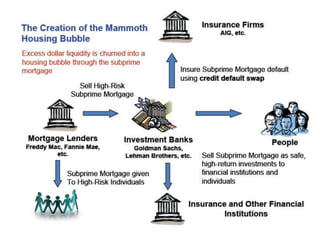
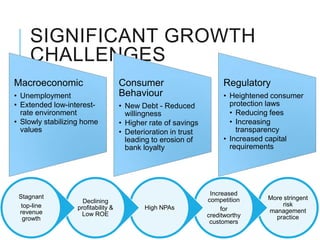
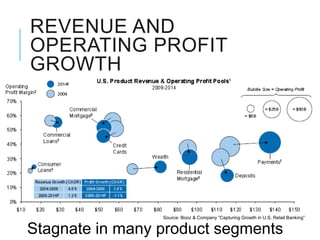
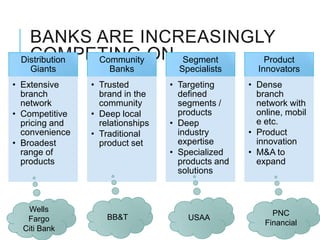
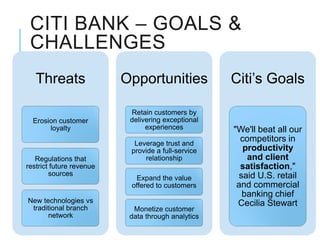
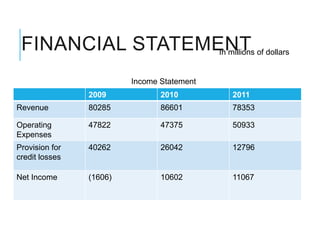
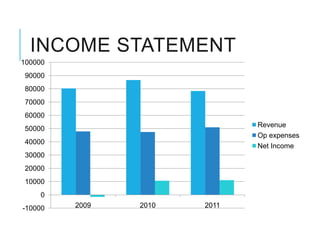
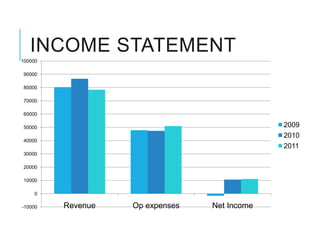
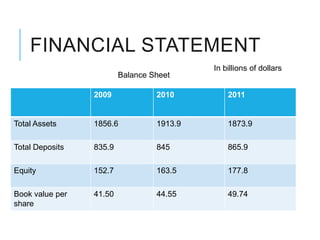
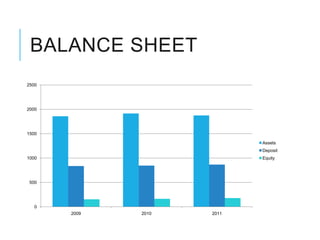
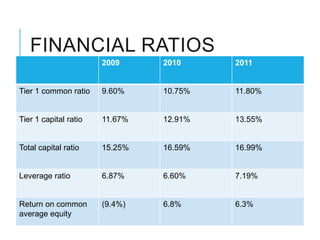
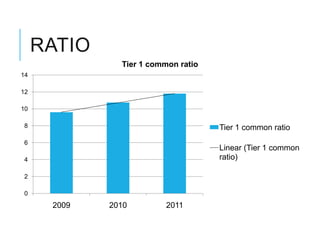
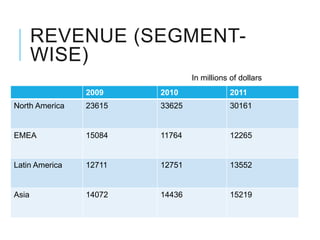
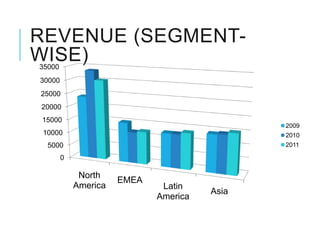
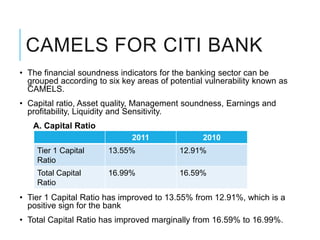
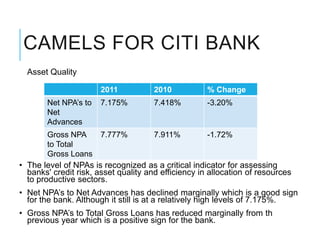
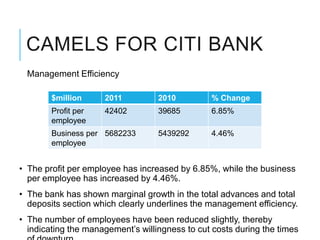
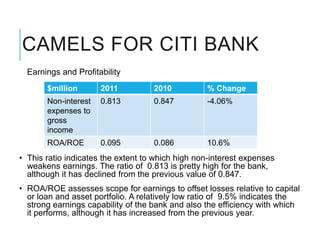
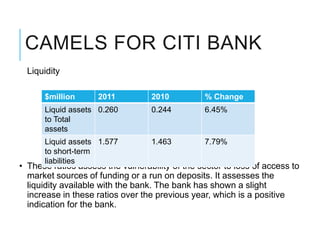
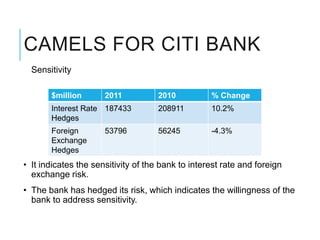
Citibank is one of the largest international banks, with retail banking operations in over 160 countries. During the 2008 recession, Citibank lost billions from the subprime mortgage crisis and was forced to cut staff, relocate employees, and seek federal financing to avoid collapse. Currently, Citibank faces threats like eroding customer trust and stagnant revenue growth. However, opportunities exist to retain customers through improved digital offerings and gain market share through strategic acquisitions. Citibank's goals are to regain customer trust, boost top-line revenue, and strengthen risk management practices.