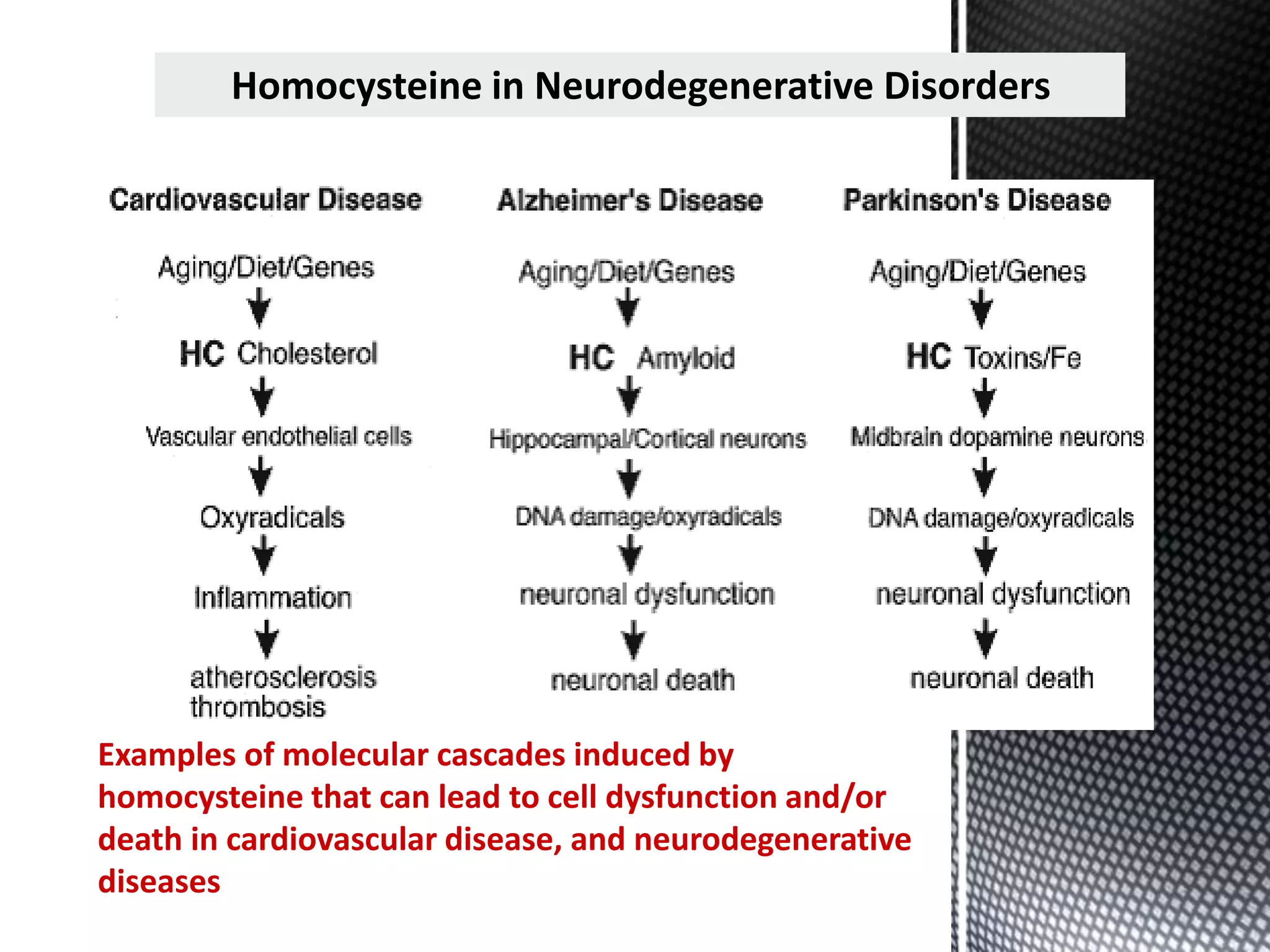
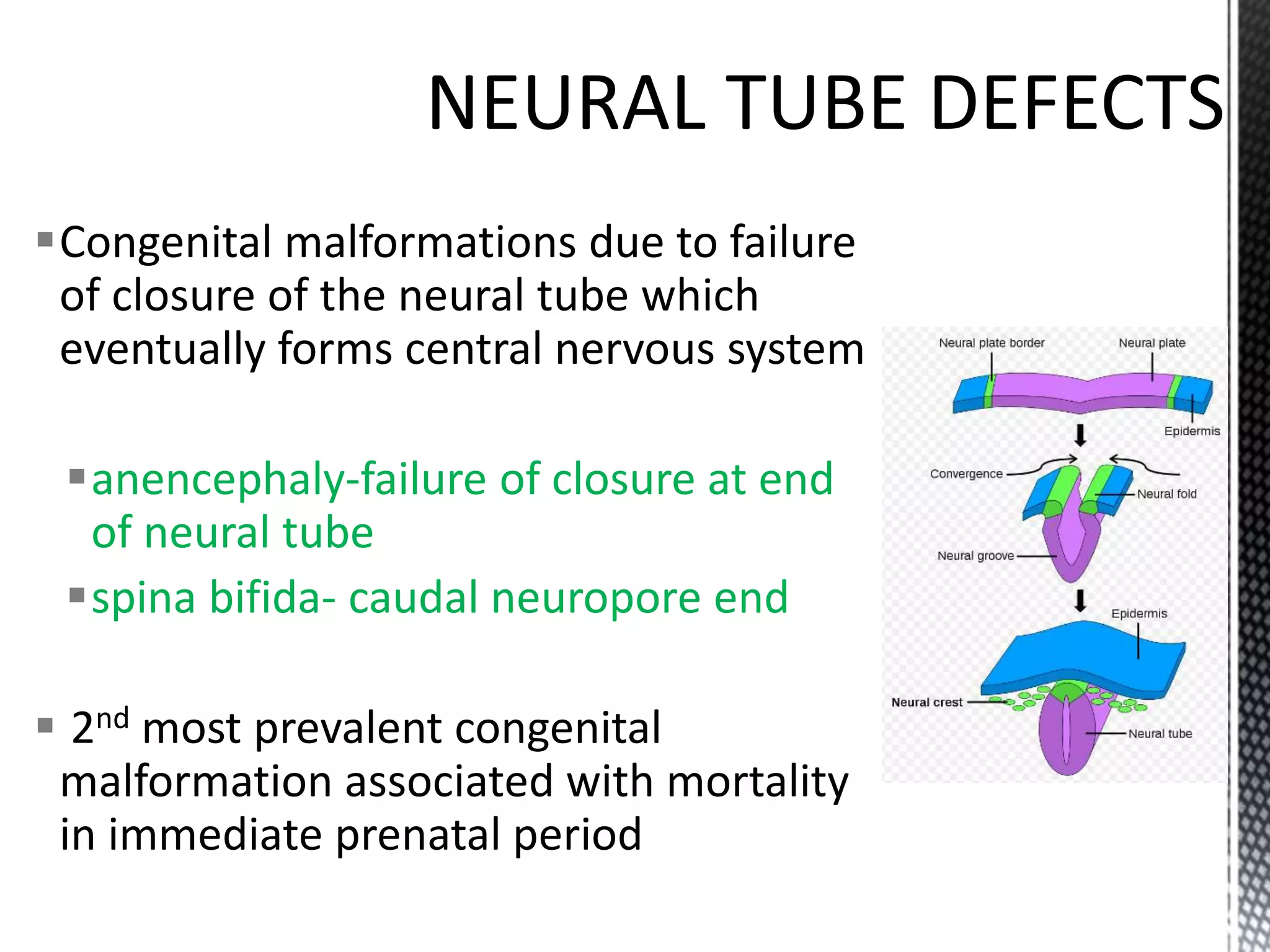
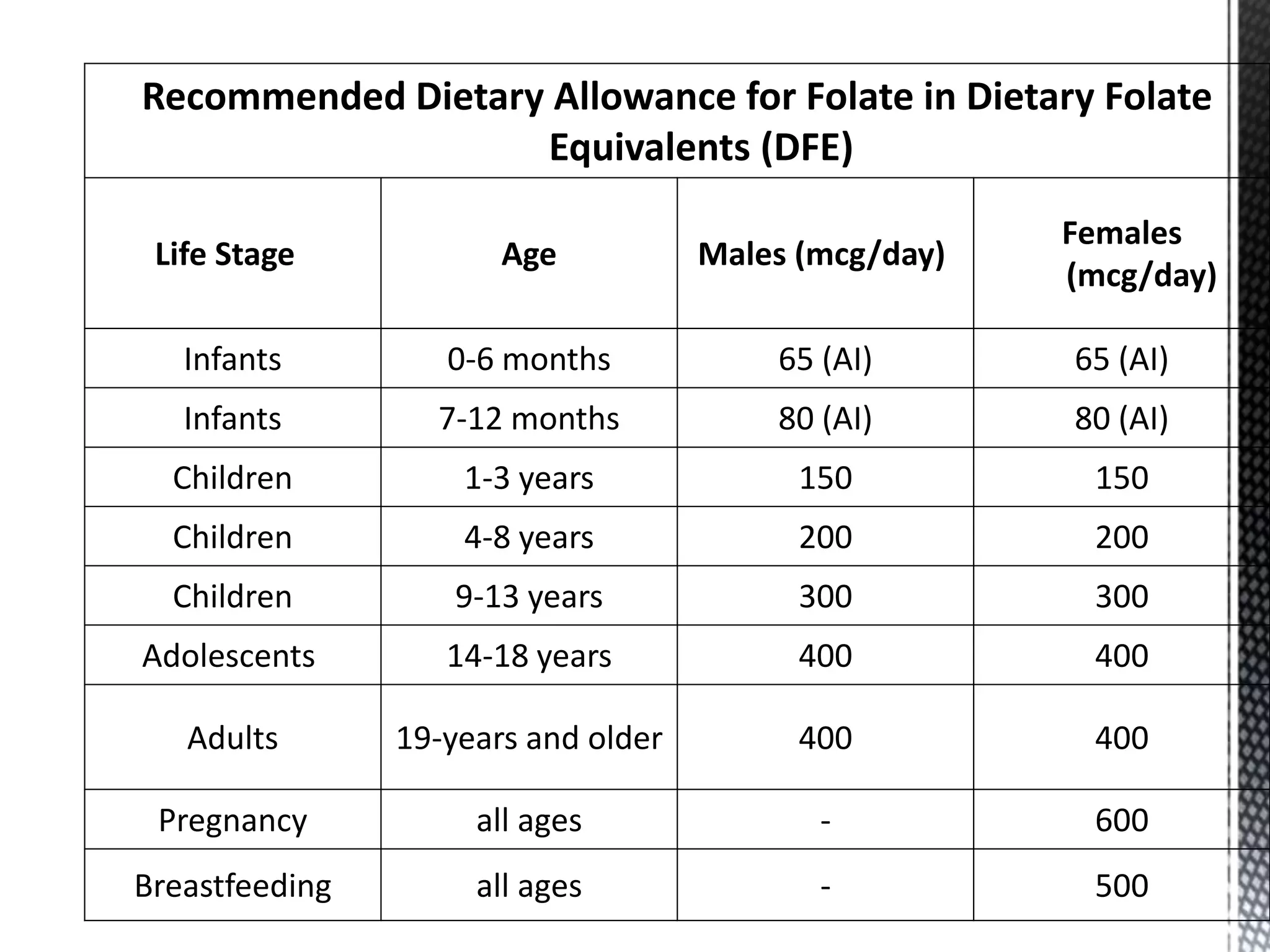
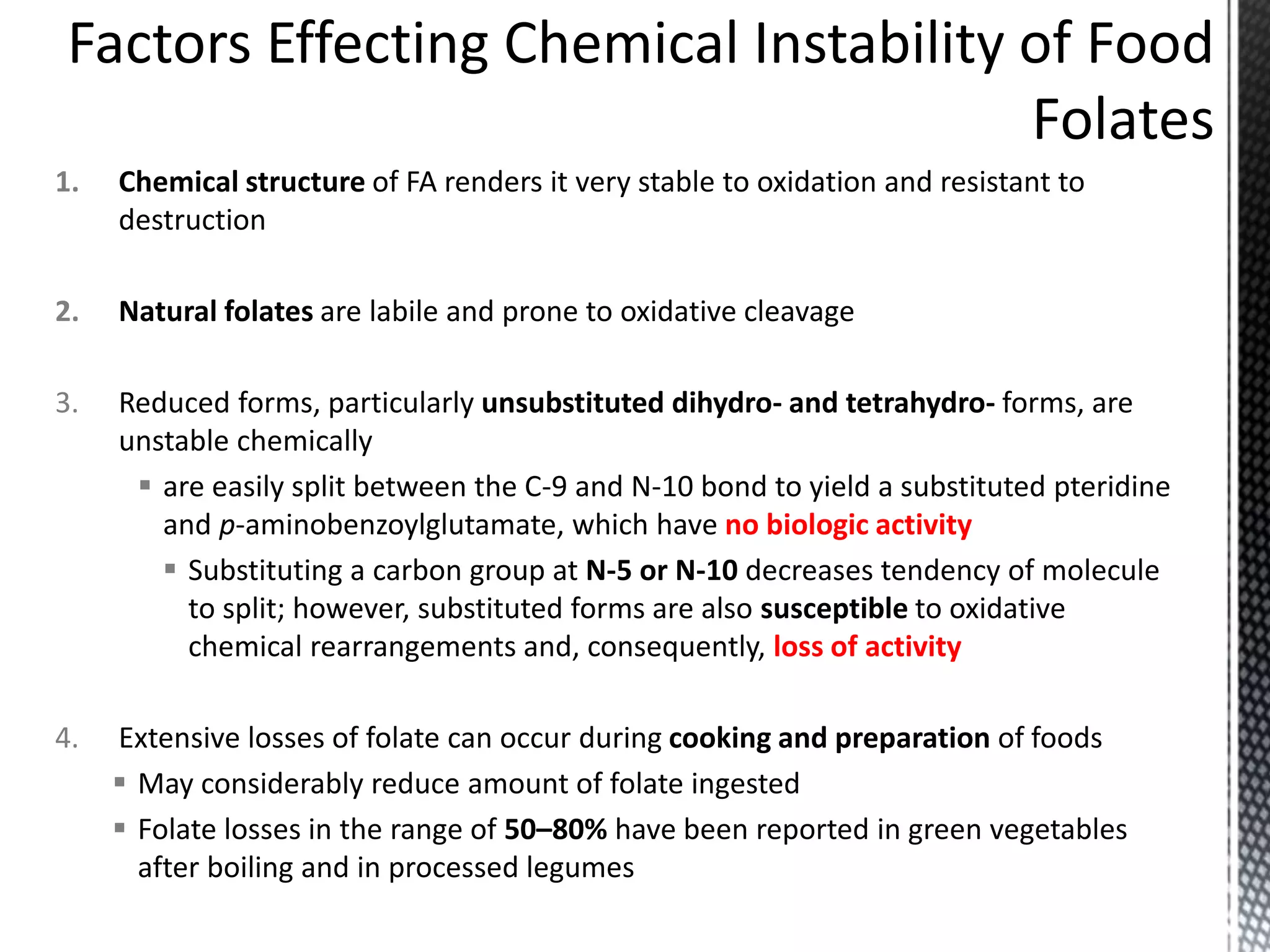
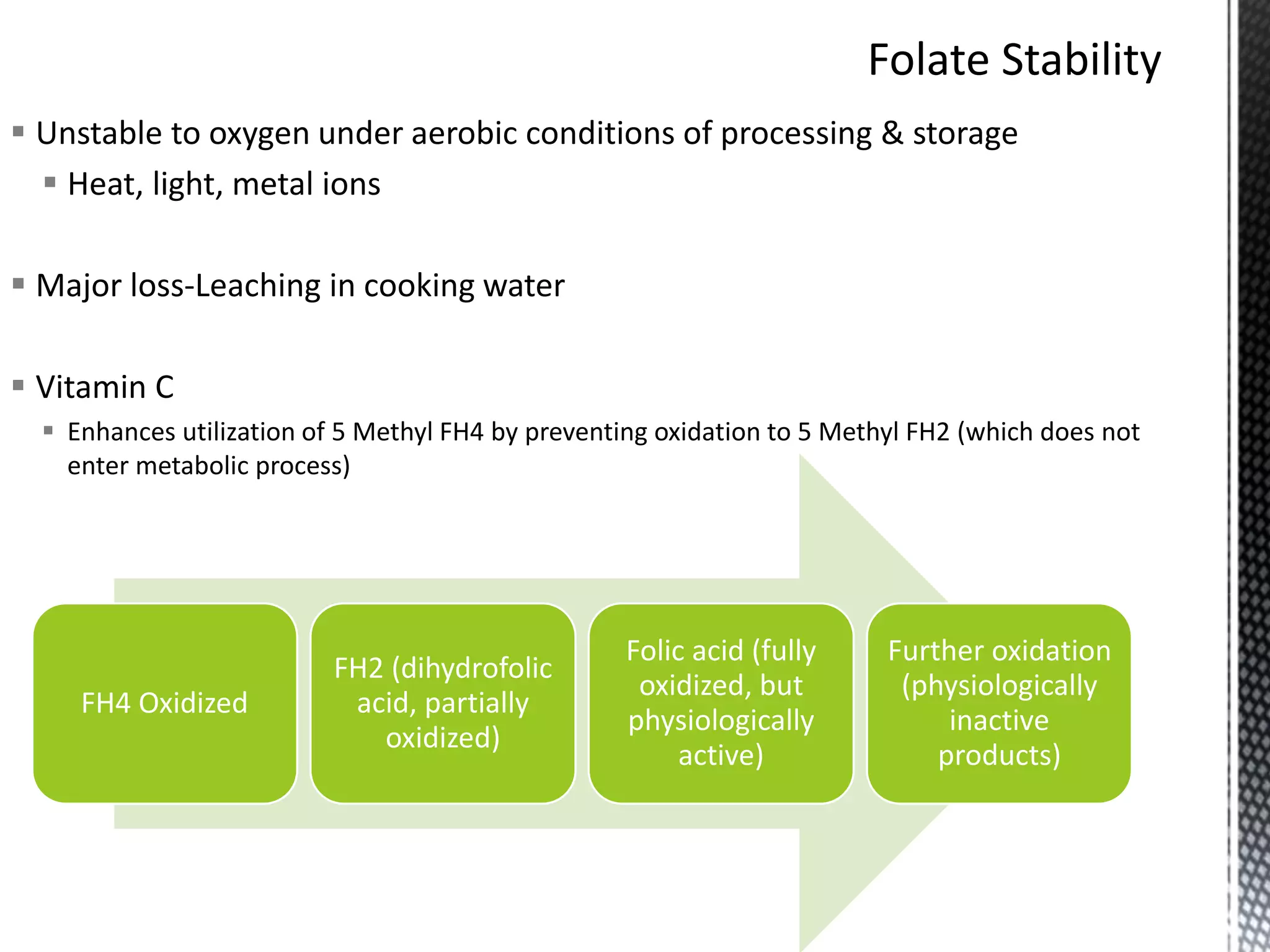
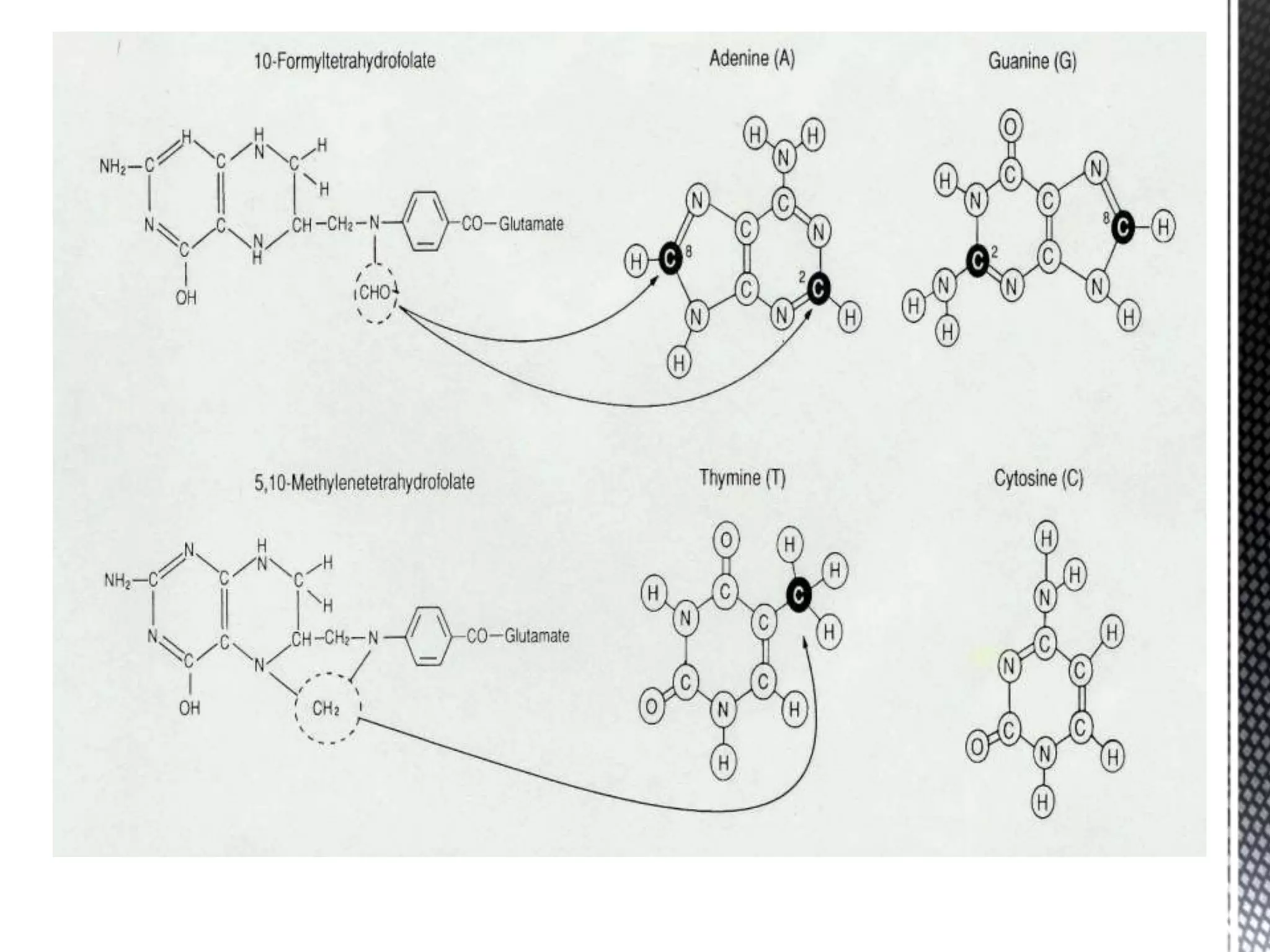
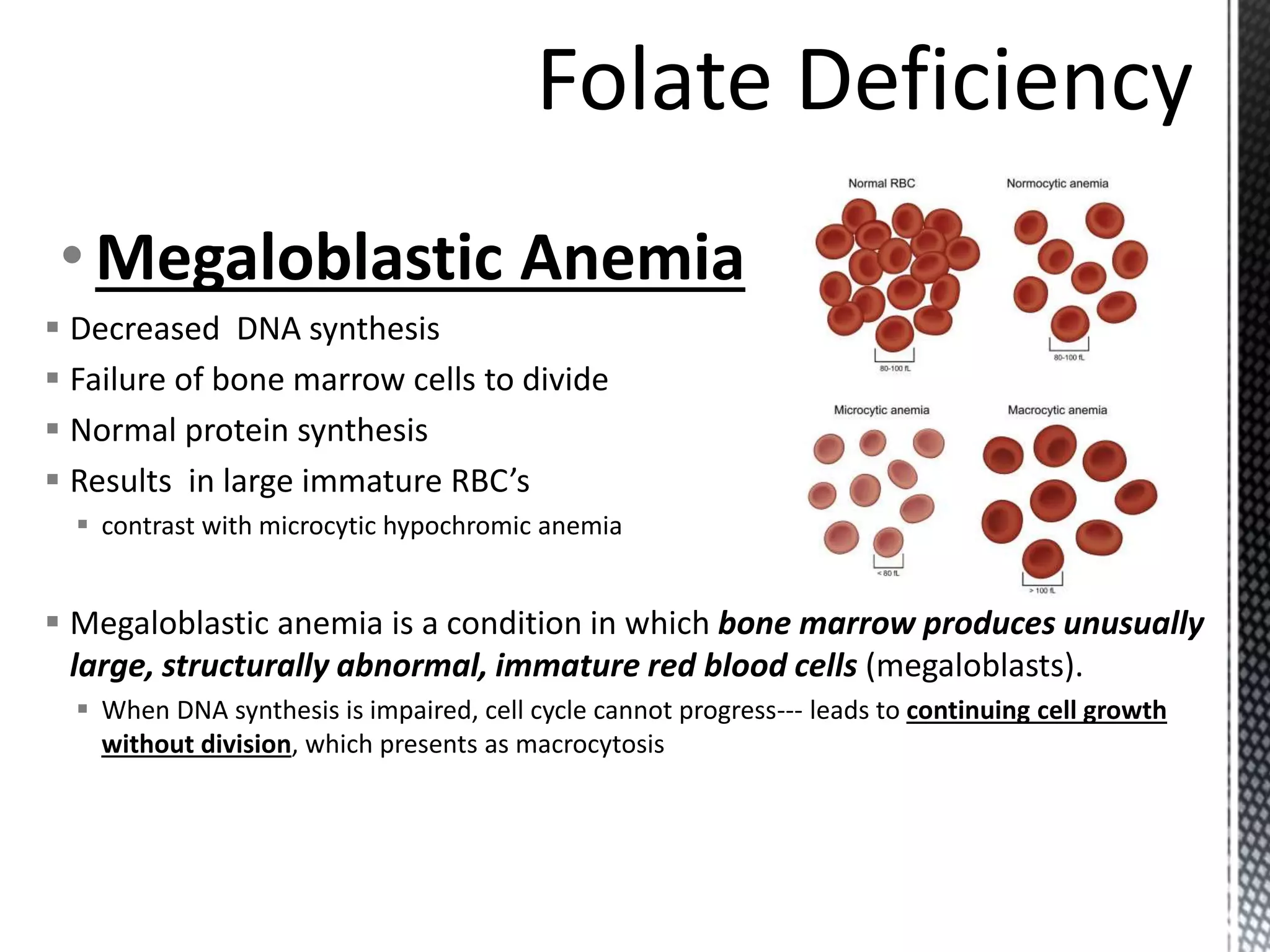
Folic acid is a B vitamin that plays important roles in DNA synthesis and preventing neural tube defects. It was discovered in the 1930s and is found naturally in foods like leafy greens, beans, and oranges. Folic acid supplementation and food fortification has reduced neural tube defects by 60-100% by ensuring adequate intake early in pregnancy. A deficiency can cause megaloblastic anemia and elevated homocysteine levels, increasing heart disease risk. The synthetic form folic acid is more bioavailable than natural folate and is used in supplements and fortified foods.









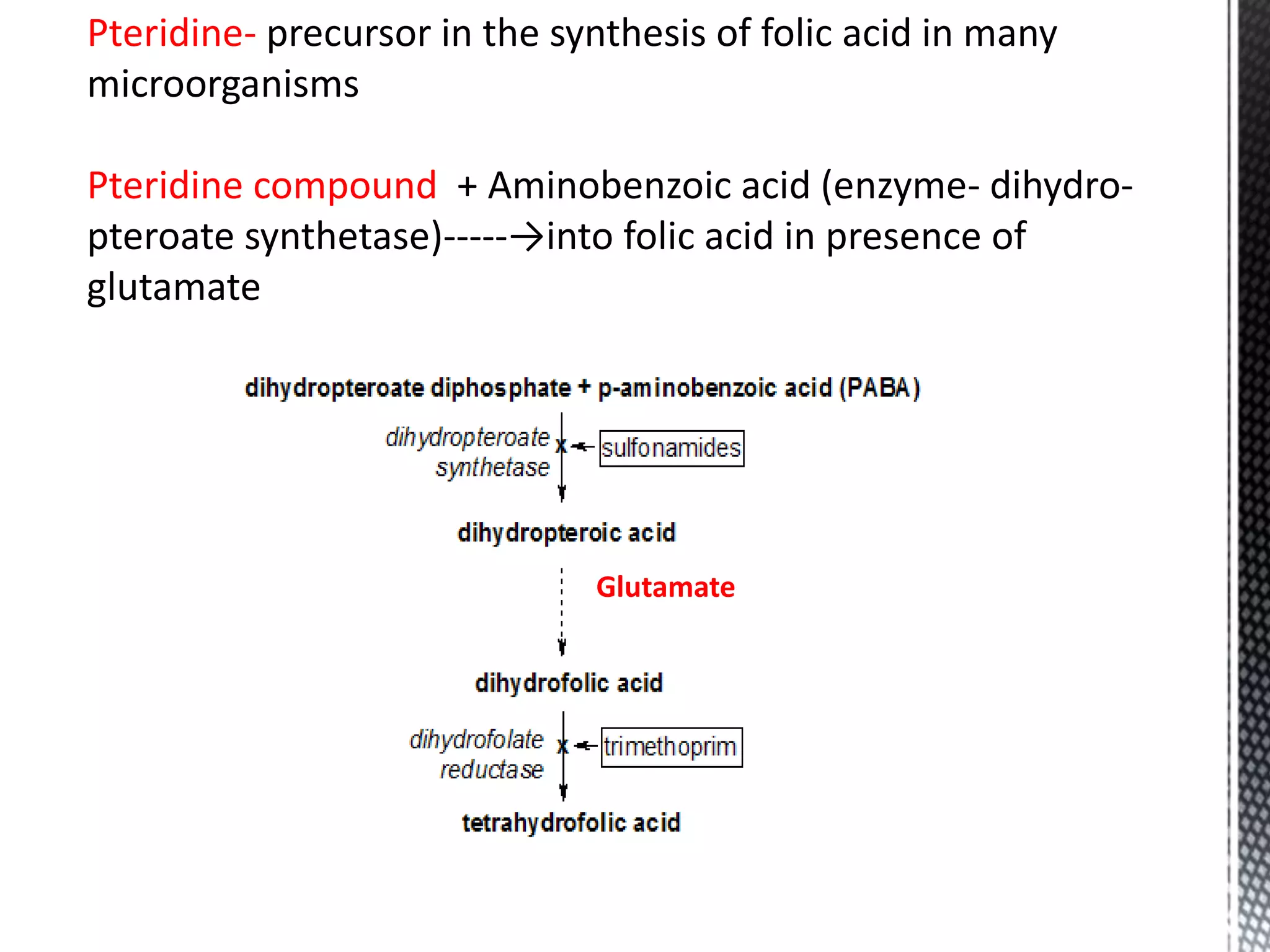

















![• Homocysteine
–Coronary Heart Disease risk factor
genetic homocystinuria - premature CHD
high [homocys] related to high CHD risk
low [folate, B-12, B-6] related to high CHD risk
low intake of B-vit related to high CHD risk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/updatedfolicacid-230915083348-dcb06b7e/75/Updated-Folic-Acid-ppt-36-2048.jpg)