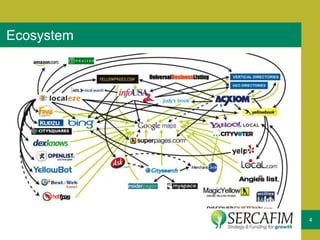
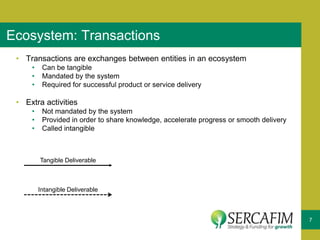
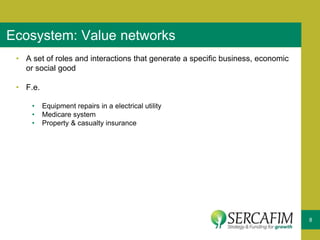
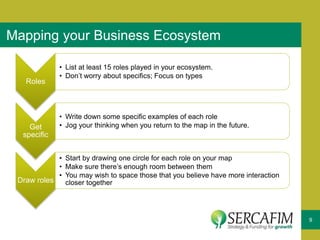
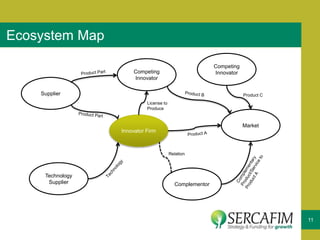
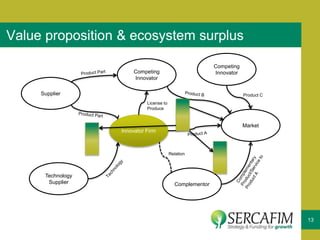
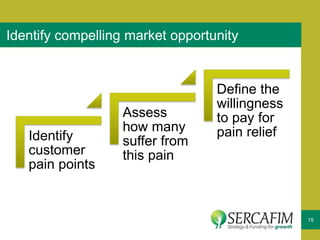
The document discusses the concept of business ecosystems, emphasizing the dynamic relationships among interconnected organizations that contribute to mutual survival. It outlines the importance of mapping these ecosystems, identifying roles and transactions, and analyzing interactions to uncover business opportunities and customer pain points. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of developing a business model that maximizes value creation and capture within the ecosystem.