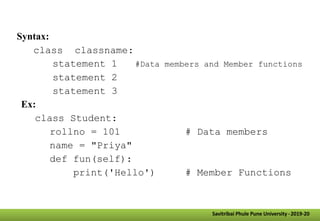
- The document discusses various object-oriented programming concepts including classes, objects, methods, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction.
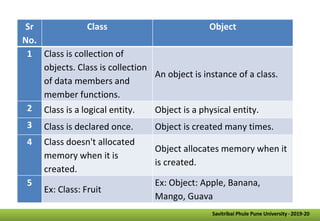
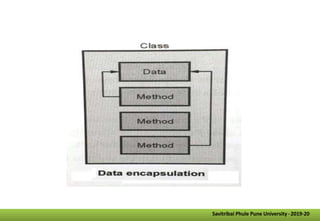
- It defines classes as collections of objects that contain data members and methods, and objects as instances of classes. Methods are functions associated with objects.
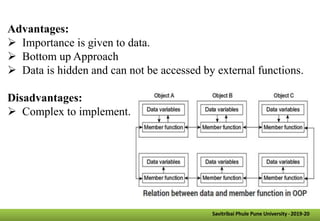
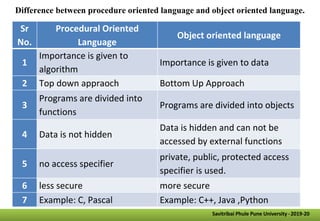
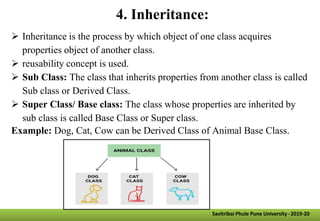
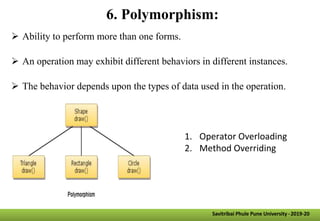
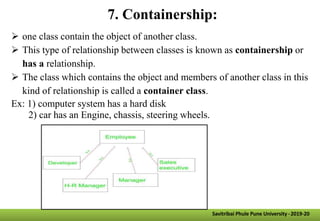
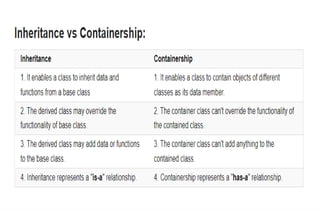
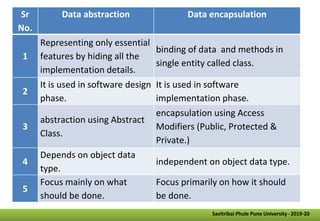
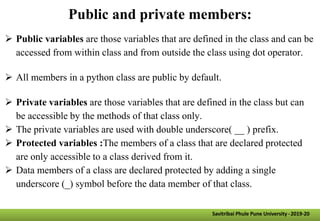
- Other key concepts covered are inheritance, which allows classes to acquire properties from other classes; polymorphism which allows operations to exhibit different behaviors depending on the data types used; and encapsulation which hides data implementation from users.






















![Savitribai Phule Pune University -2019-20
Write a program in python to Create class EMPLOYEE for storing details (Name,
Designation, gender, Date of Joining and Salary). Define function members to display all
EMPLOYEE details.
class Employee:
name = []
designation = []
gender = []
doj = []
salary = []
def __init__(self):
for i in range(3):
self.name.append(input("Enter the name:"))
self.designation.append(input("Enter the Designation:"))
self.gender.append(input("Enter the gender:"))
self.doj.append(input("Enter the doj:"))
self.salary.append(int(input("Enter the salary:")))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-v-220913061129-026884d4/85/Unit-V-pptx-38-320.jpg)
![Savitribai Phule Pune University -2019-20
def display(self):
print("-------------Details of Employee-----------------")
print(" NamettDesignationtGenderttDate of
JoiningttSalary ")
print("-------------------------------------------------")
for i in range(3):
print(self.name[i],"tt",self.designation[i],"t",
self.gender[i],"tt",self.doj[i],"tt",self.salary[i] )
e = Employee()
e.display()
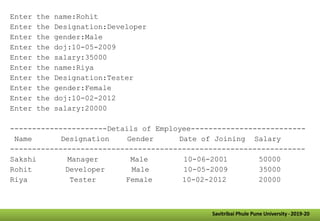
Output:
Enter the name:Sakshi
Enter the Designation:Manager
Enter the gender:Male
Enter the doj:10-06-2001
Enter the salary:50000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-v-220913061129-026884d4/85/Unit-V-pptx-39-320.jpg)