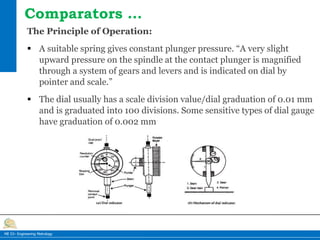
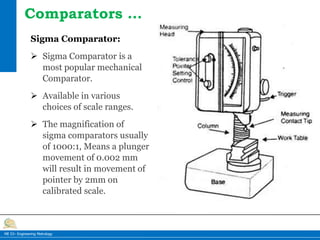
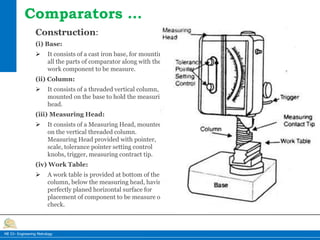
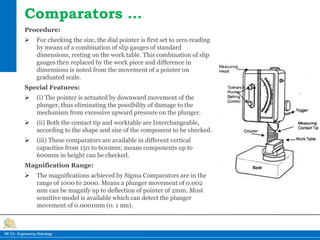
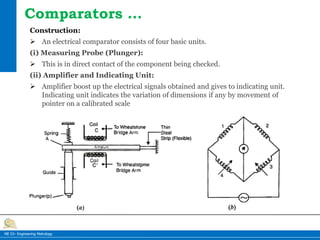
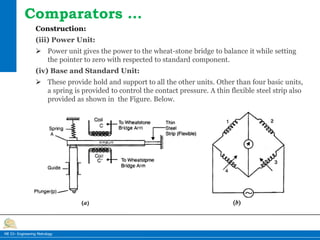
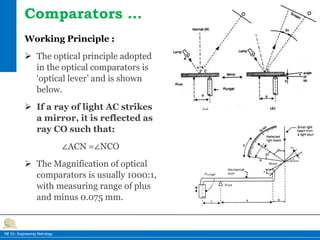
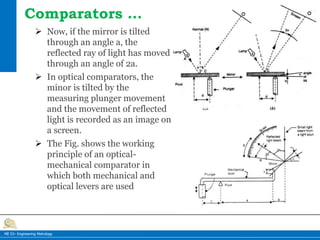
This document provides information on different types of comparators used in engineering metrology. It describes mechanical comparators, which use lever systems or gears to magnify measurements, as well as dial indicators. Electrical comparators are also discussed, which convert plunger movements into electrical signals that are amplified and shown on a calibrated display. Specific mechanical comparators described in detail include lever comparators, sigma comparators, and dial indicators. The working principles, components, uses, advantages, and disadvantages of different comparator types are summarized.