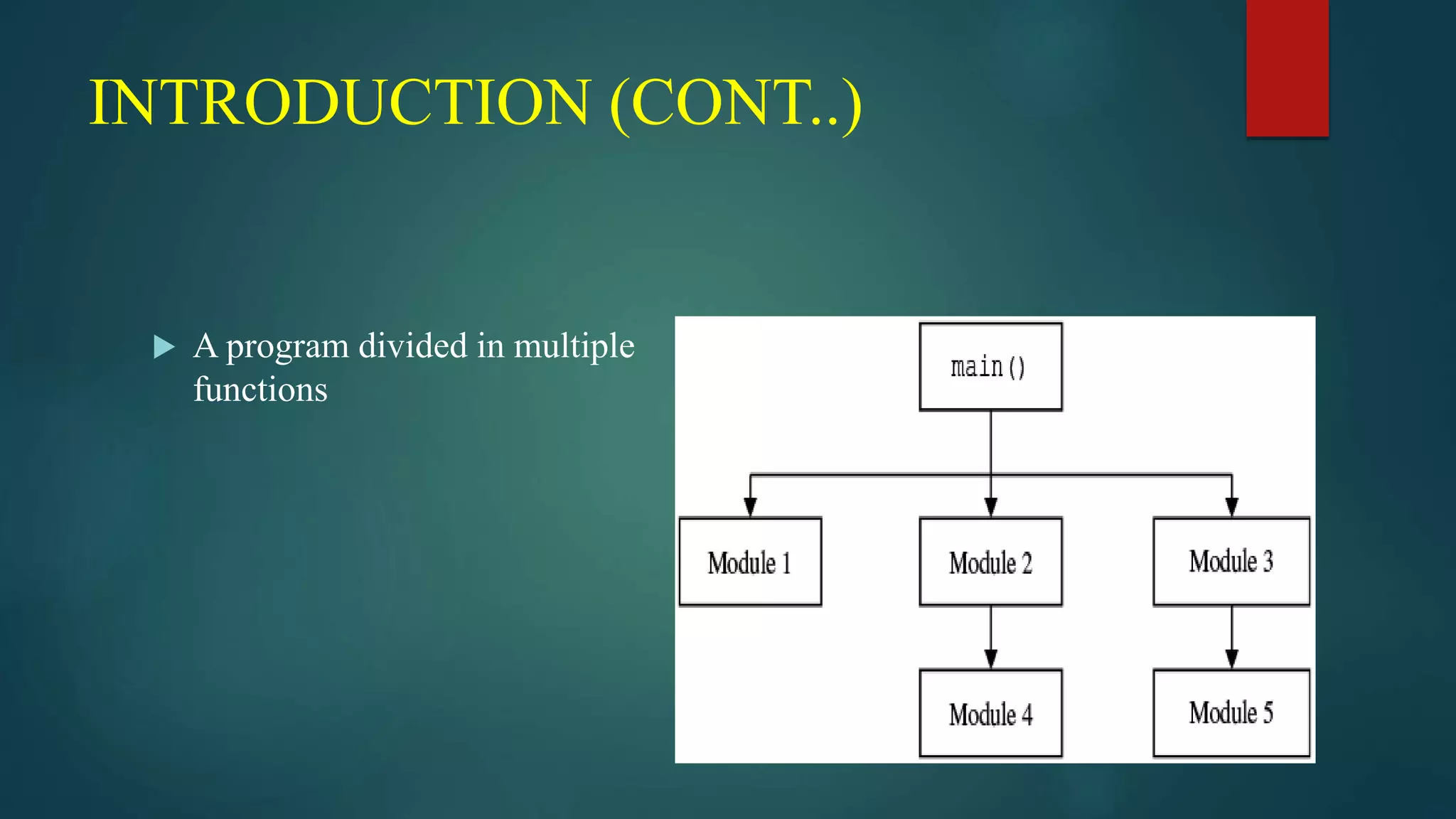
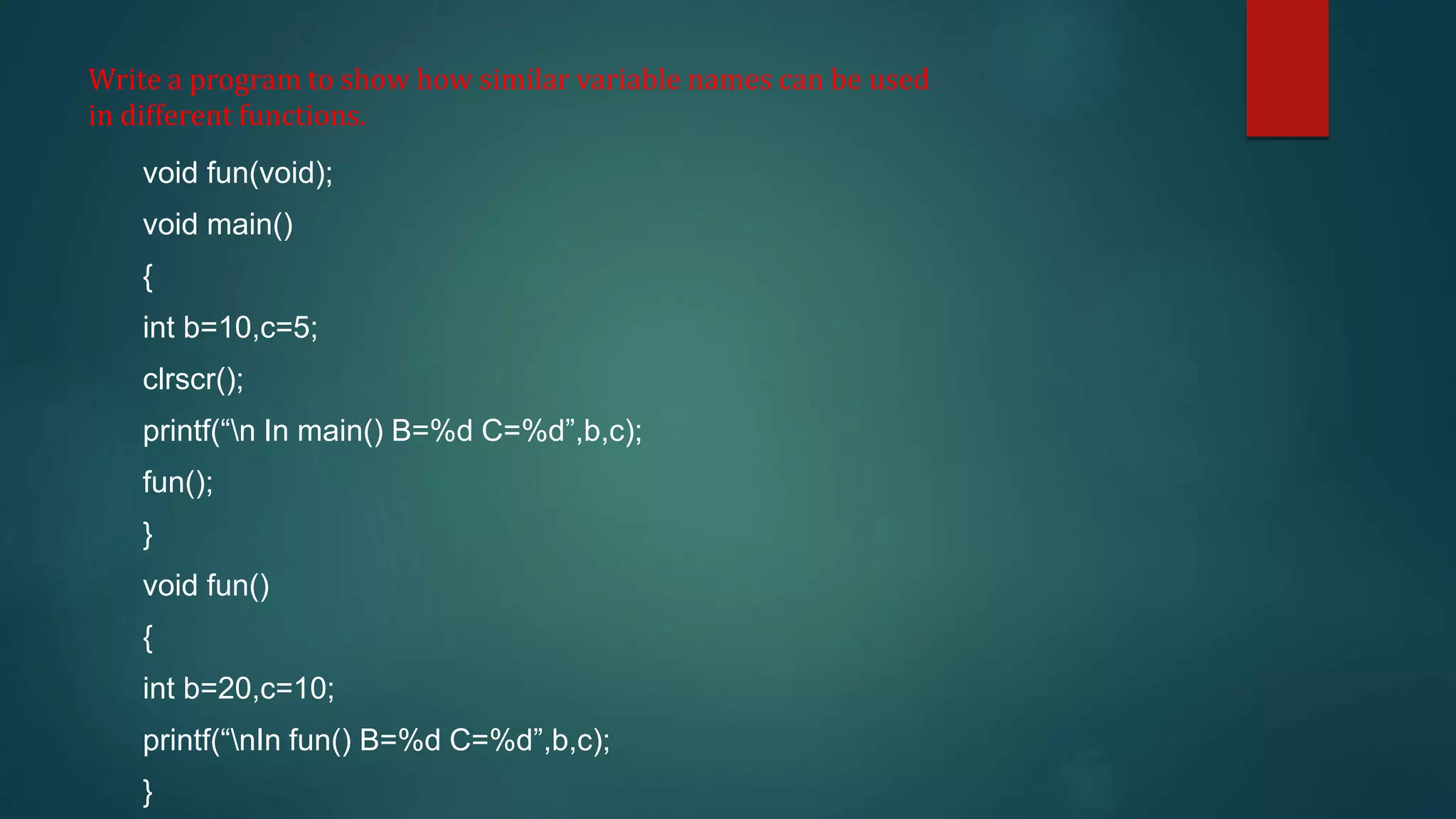
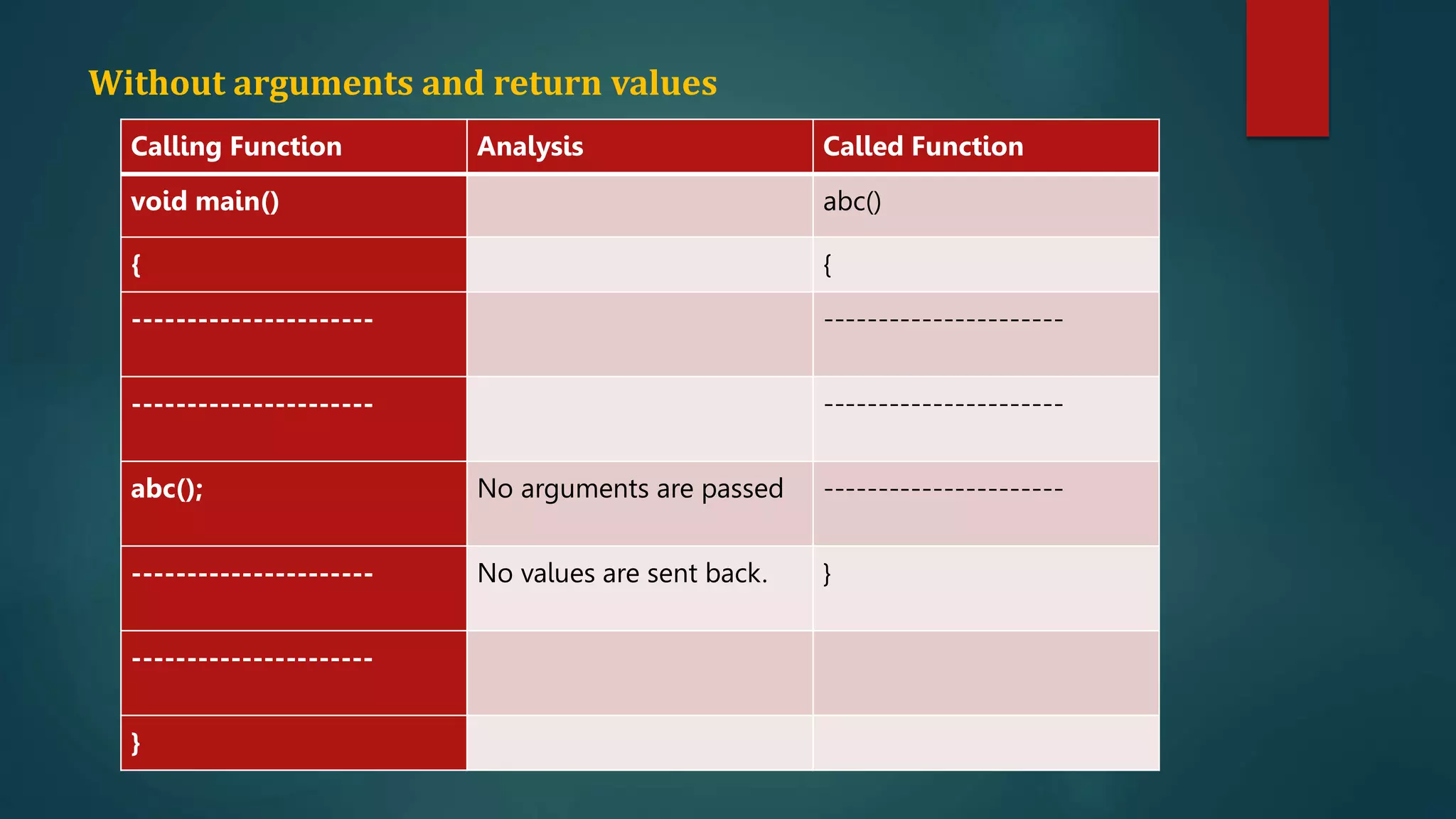
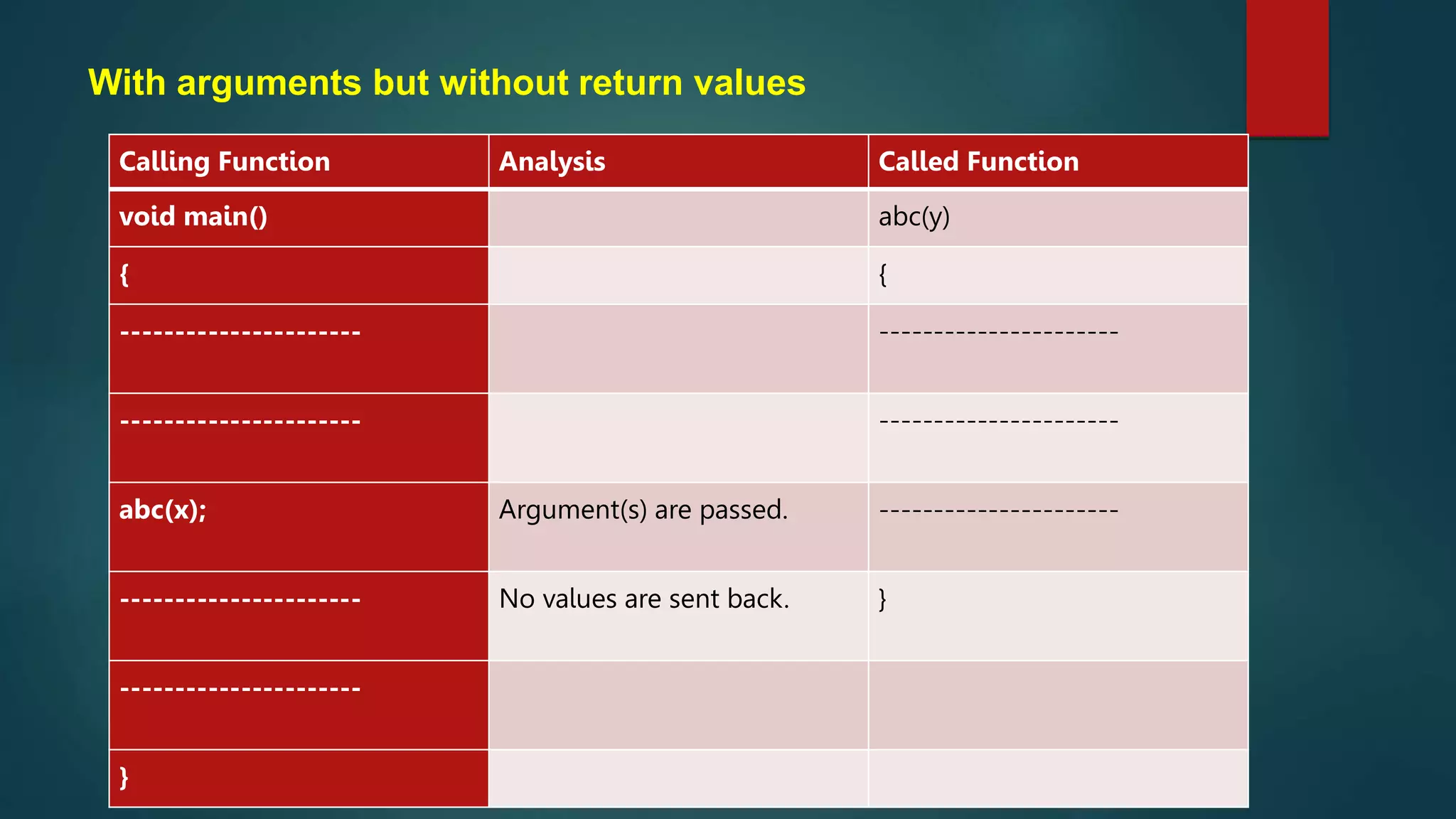
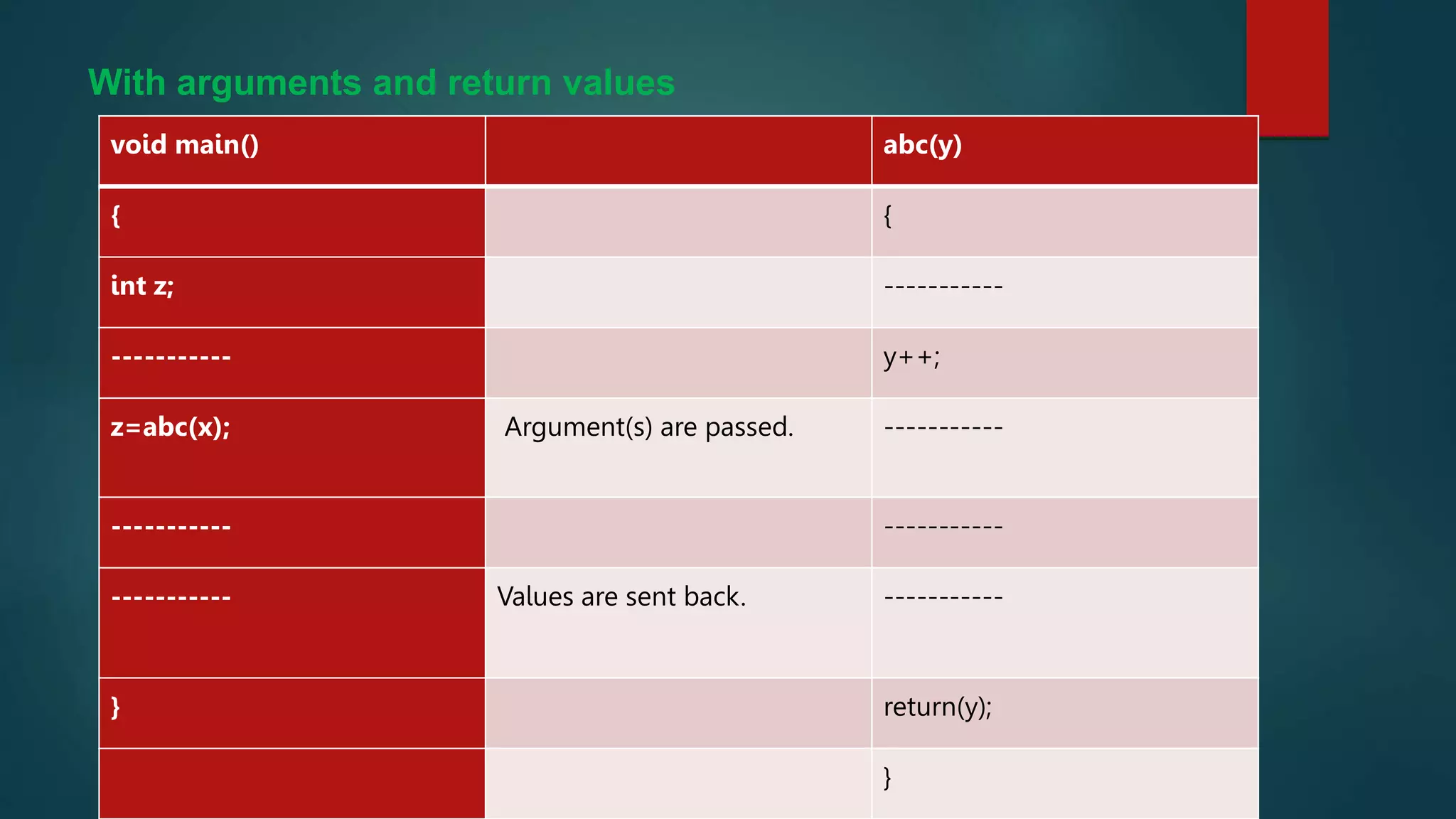
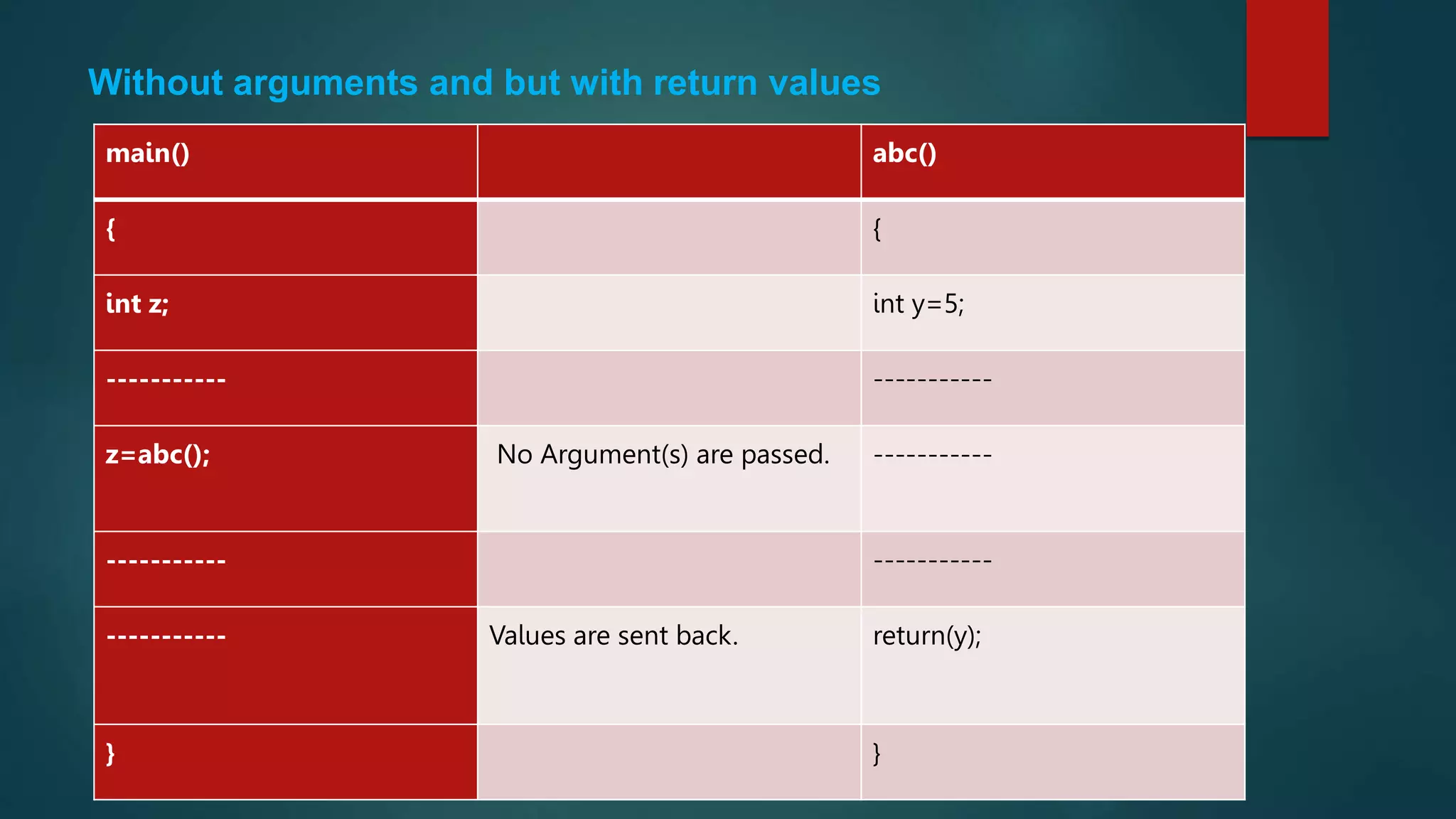
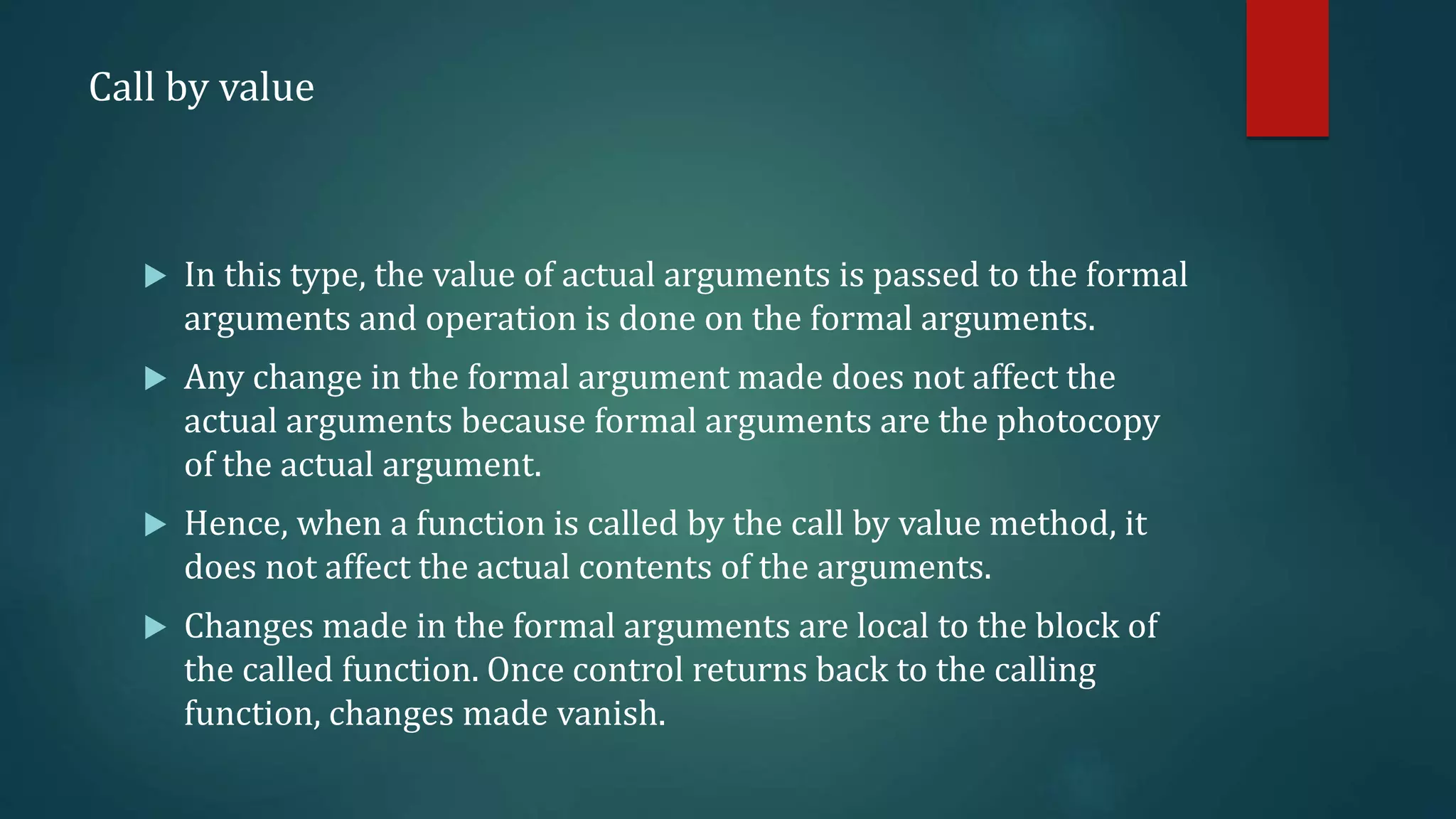
This document discusses functions in C programming. It begins by explaining why programs should be divided into smaller subprograms or functions for manageability. There are two types of functions: library functions which are pre-defined and cannot be modified, and user-defined functions which are created by the user. Every C program must contain a main() function. Functions allow code reusability and modularity. Parameters are used to pass data between functions. The return statement returns data from a function. Local variables are only accessible within their own function.