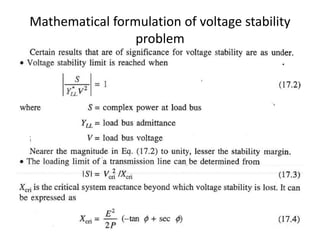
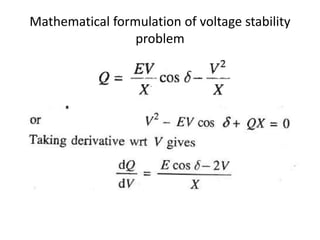
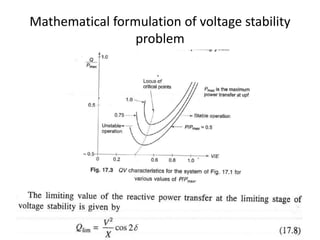
The document discusses voltage stability in power systems, focusing on the ability to maintain steady-state voltages during disturbances. It covers various aspects such as reactive power flow, mathematical formulation of stability problems, and methods to prevent voltage collapse. Key strategies include voltage analysis, reactive power compensation, and control mechanisms to avoid voltage instability.