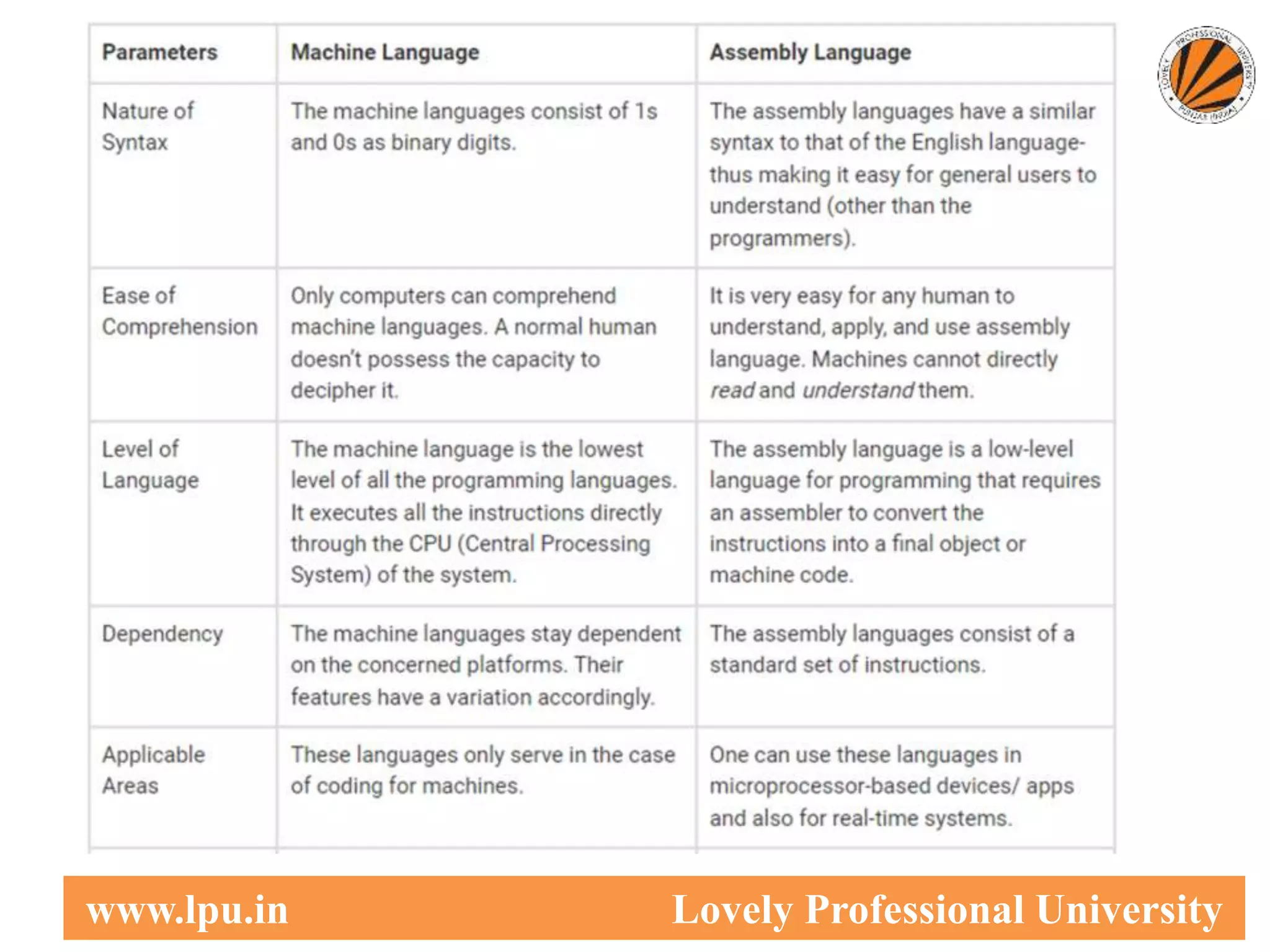
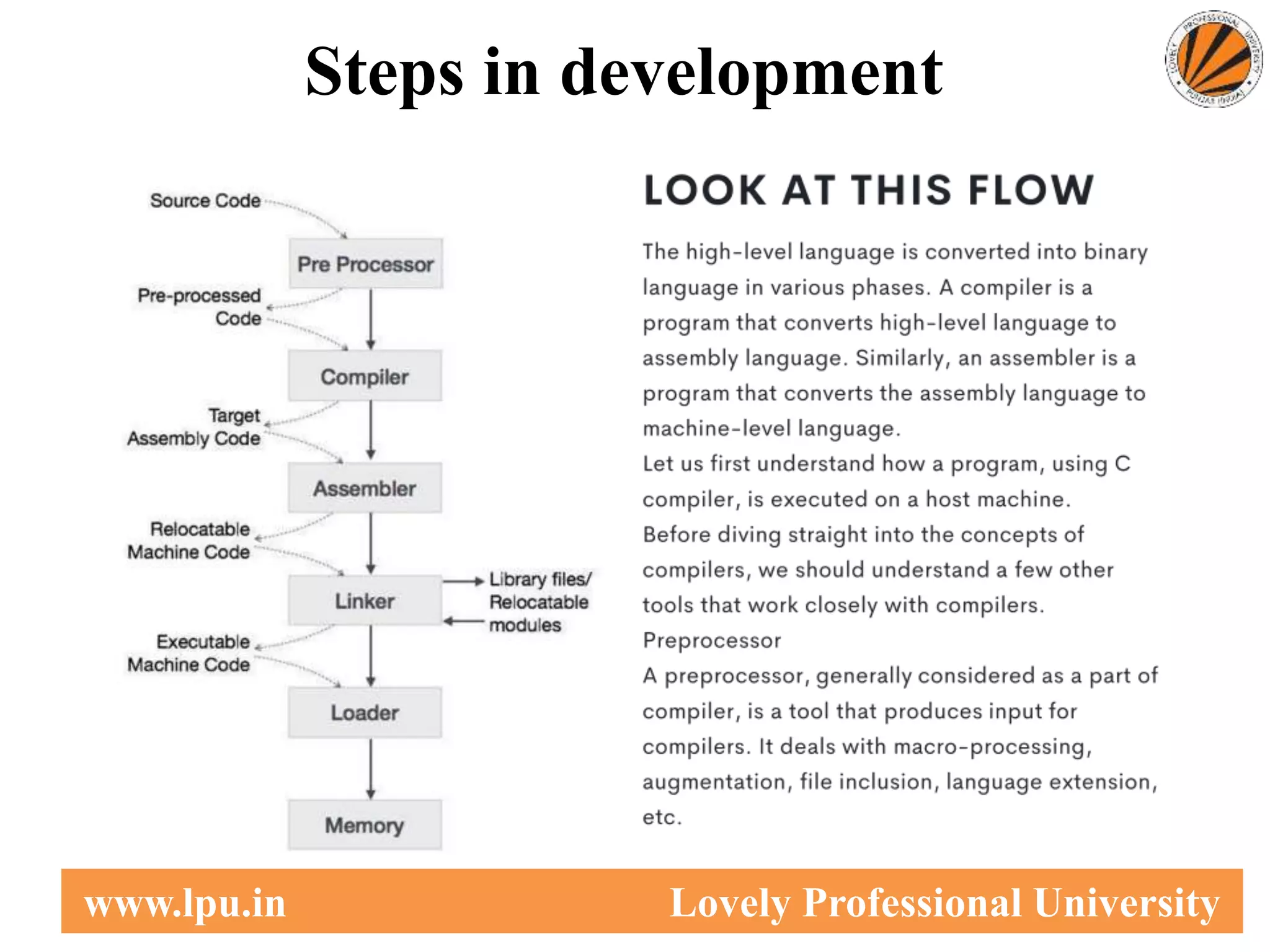
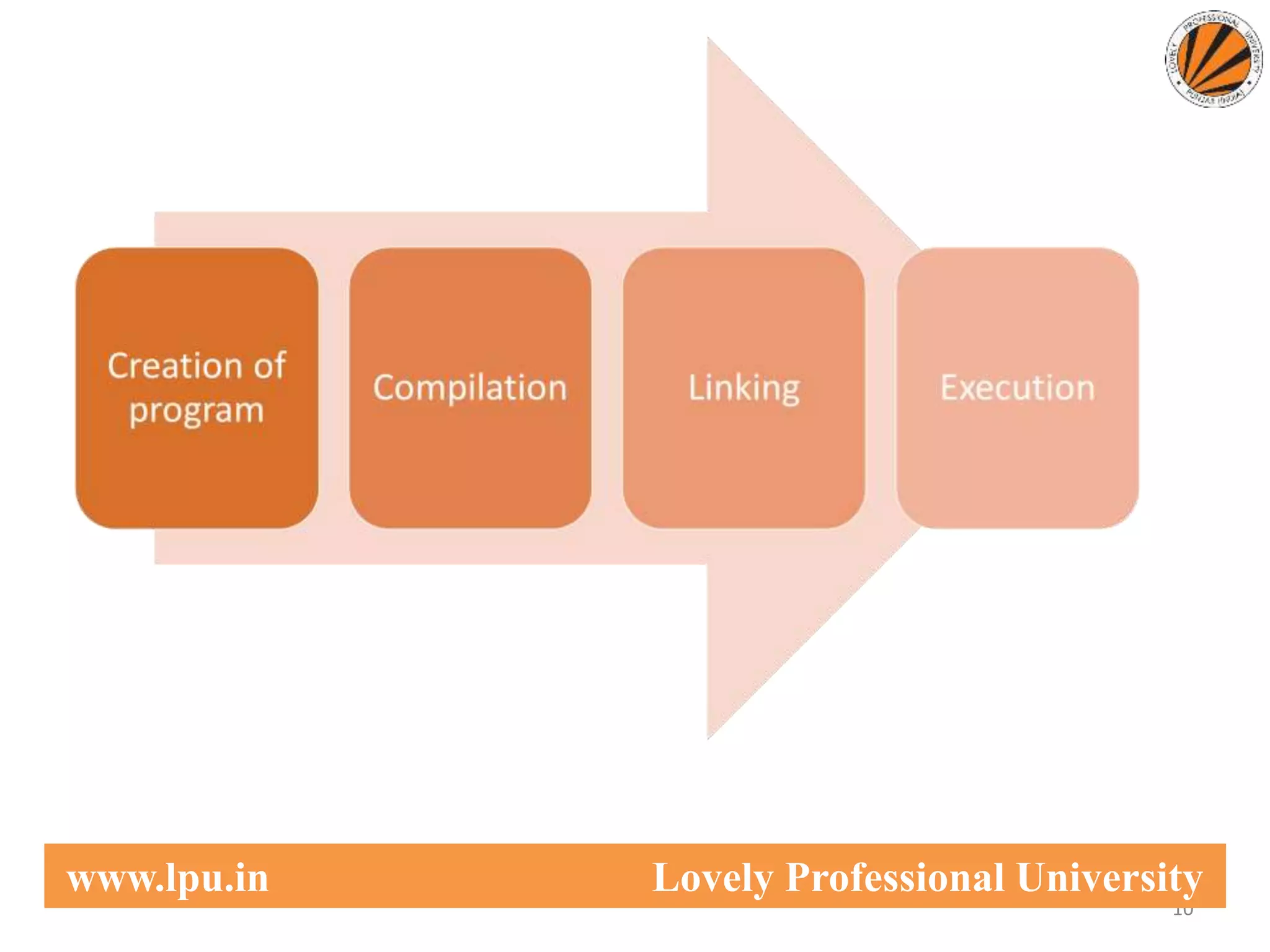
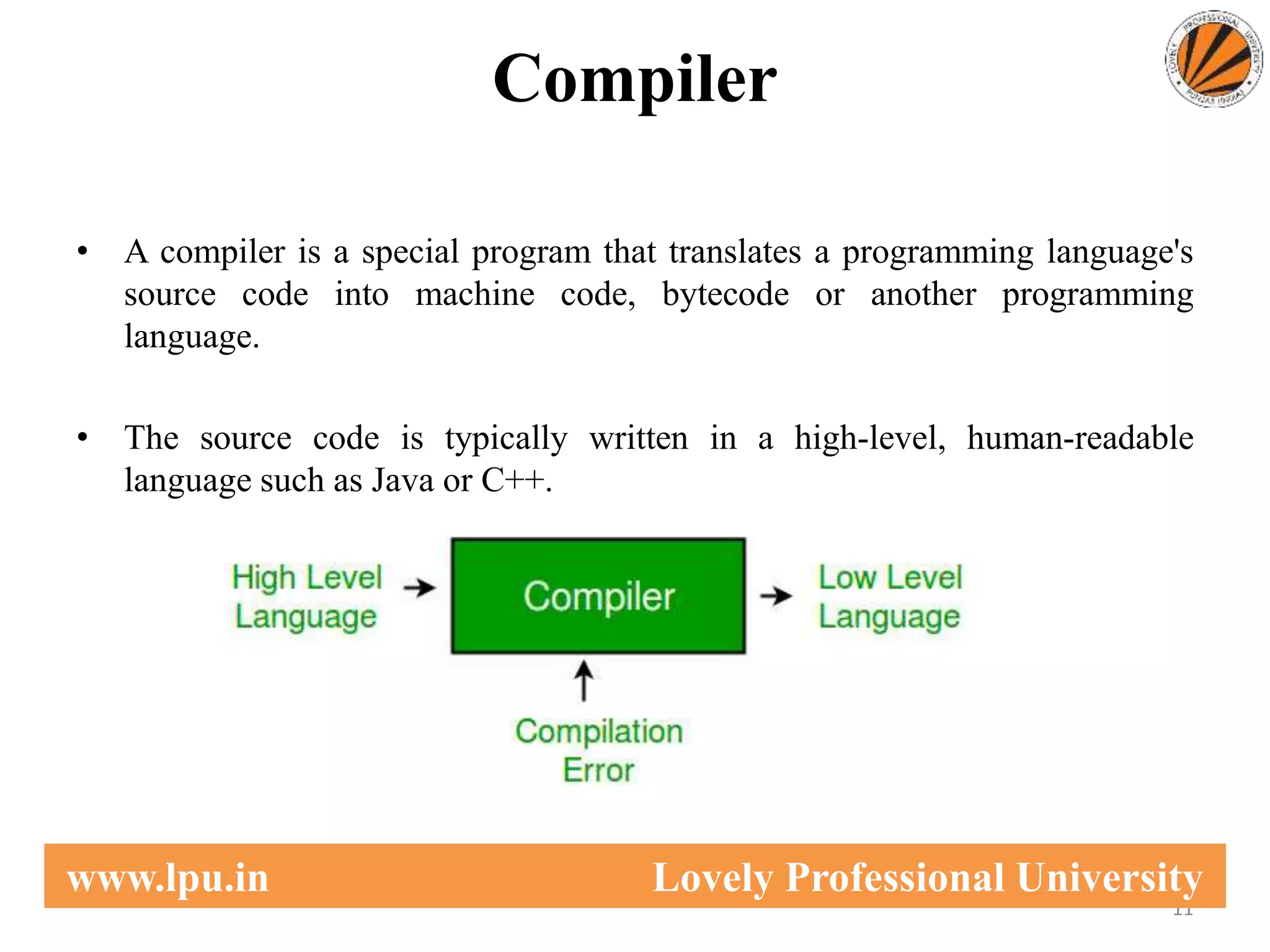
This document provides an overview of computer languages, including machine language, assembly language, and high-level languages. It discusses the steps involved in developing a program from writing source code to execution. Key aspects covered include compilers translating source code to machine code, interpreters translating statements sequentially, and assemblers translating assembly language to machine code.