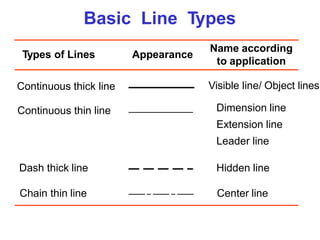
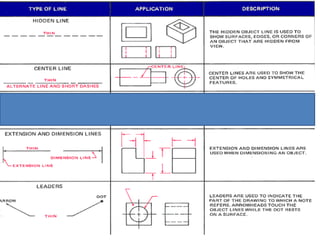
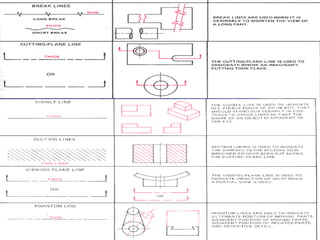
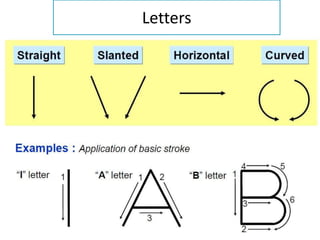
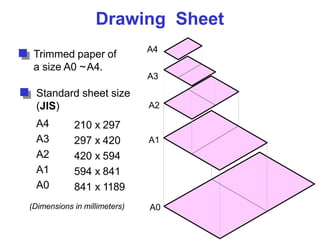
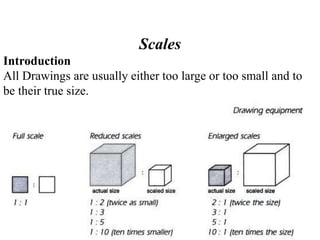
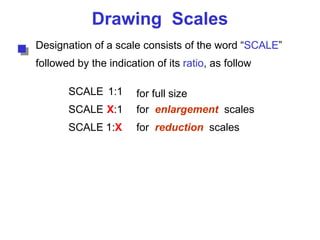
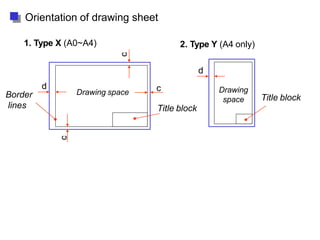
This document discusses the alphabet of lines, which are different types of lines used in technical drawings to convey specific meanings. It explains that drawings use lines similar to how written language uses letters, with lines like object lines, hidden lines, and section lines serving as the "alphabet." The document also provides examples of common line types and their appearances, and background on drawing scales and sheet sizes.