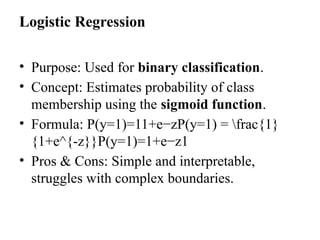
This unit introduces the basic concepts and principles of machine learning, a key branch of artificial intelligence that enables systems to learn from data and improve performance without explicit programming. It explains different types of learning methods such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.