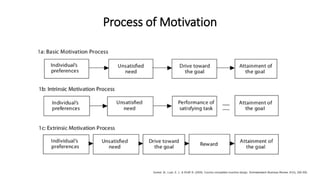
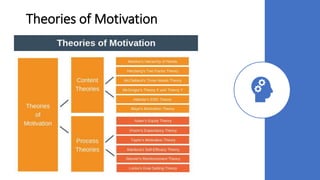
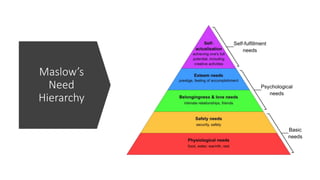
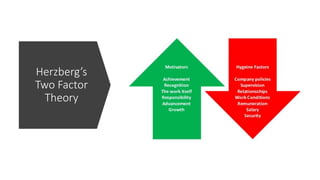
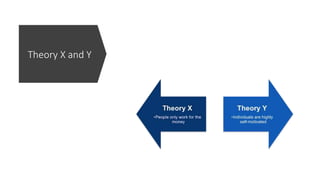
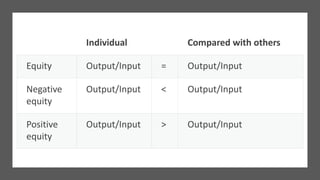
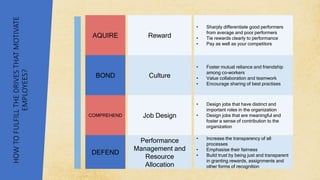
This document discusses various theories and aspects of employee motivation. It describes intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and defines them. It also outlines several motivation theories including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, McGregor's Theory X and Y, goal setting theory, equity theory, and expectancy theory. Each theory is summarized briefly. Additionally, the document discusses strategies for motivating creative employees and how managers can fulfill the key drives that motivate employees through reward systems, organizational culture, job design, and performance management.