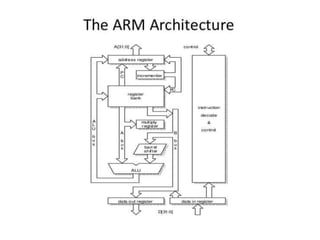
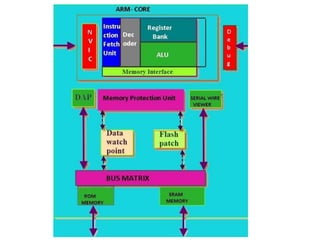
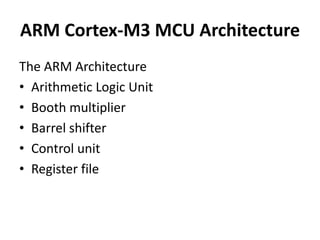
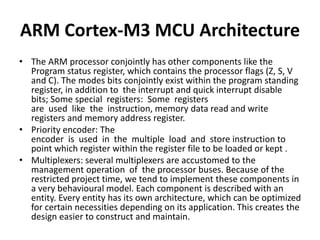
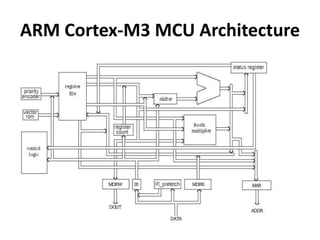
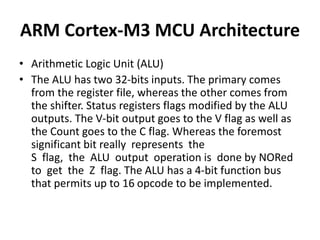
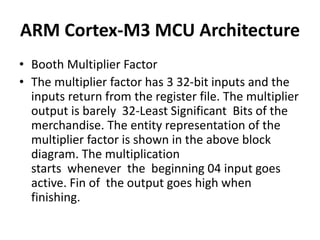
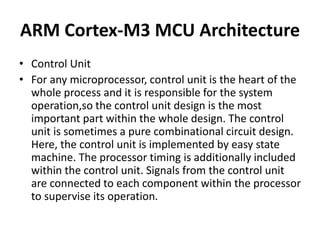
The document discusses the ARM Cortex architecture. It describes the ARM Cortex as a 32-bit RISC microcontroller introduced in 1987. It discusses the main ARM Cortex families (Ax, Rx, Mx series) and focuses on the Cortex-M3 architecture. The Cortex-M3 uses a Harvard architecture and has a 3-stage pipeline. It includes components like the ALU, multiplier, barrel shifter, registers, priority encoder, and control unit to manage instruction execution and system operation.