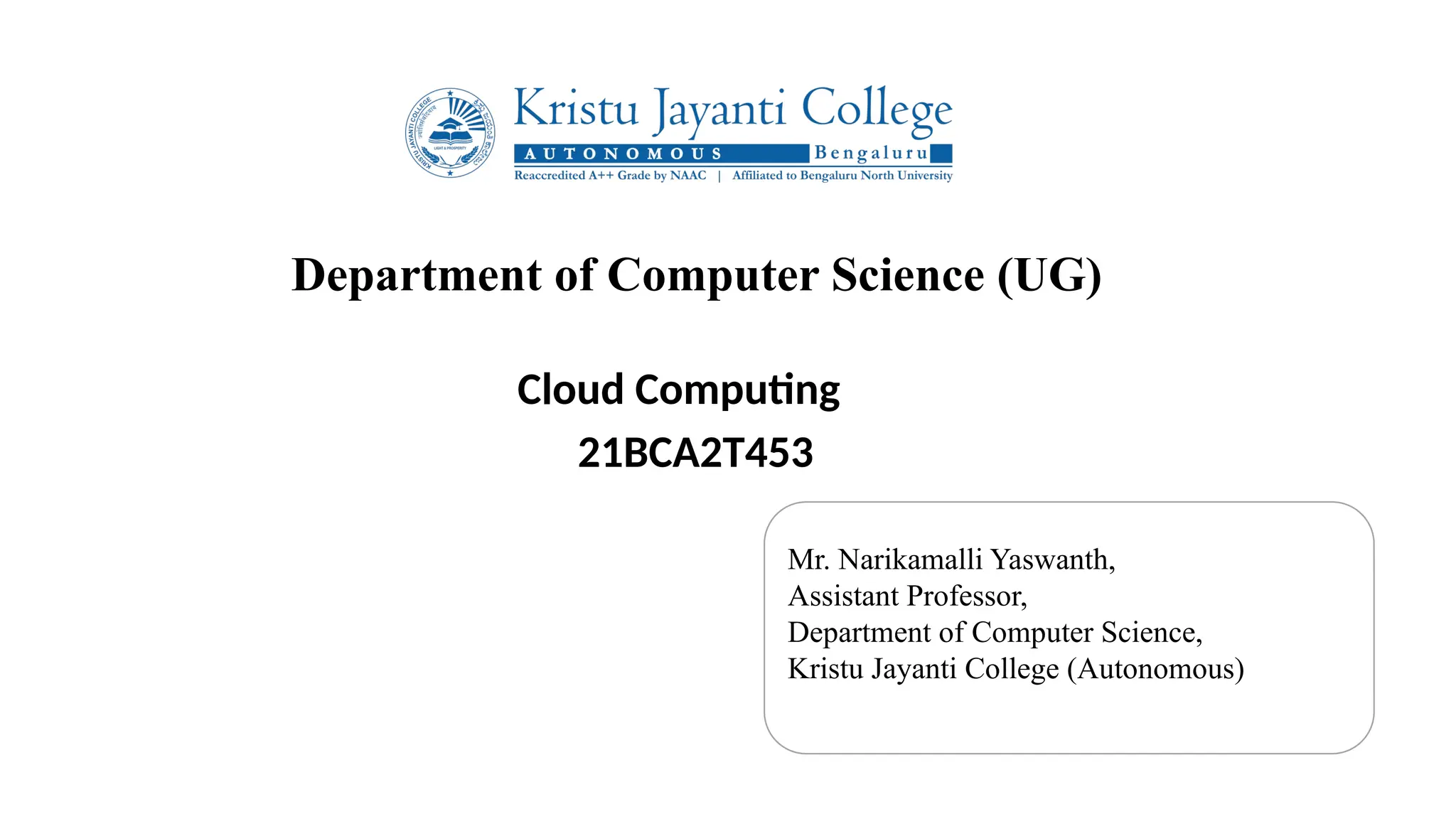
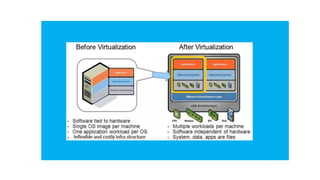
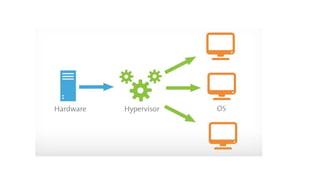
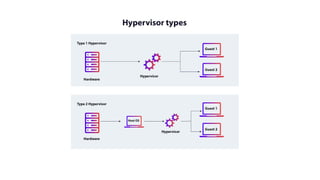
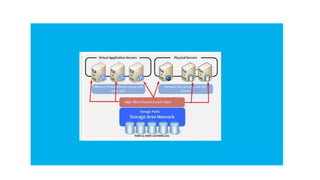
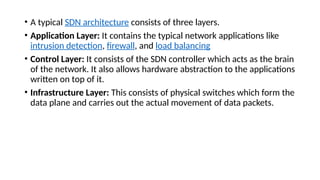
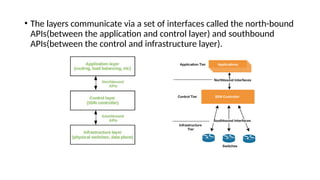
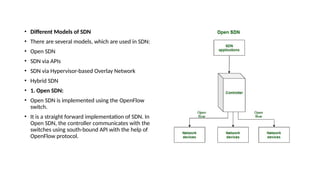
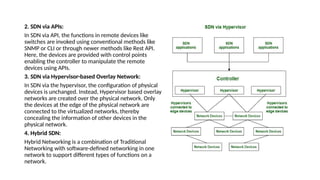
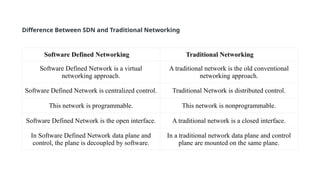
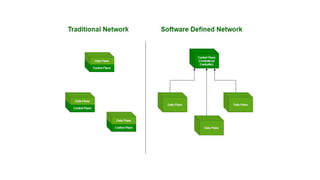
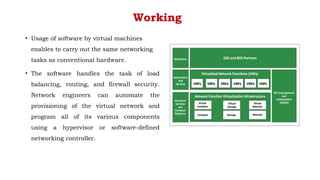
The document provides an in-depth overview of cloud computing, focusing on virtualization technologies, including hypervisors and types of virtualization such as hardware, operating system, and server virtualization. It elaborates on software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV), explaining their importance, architecture, benefits, and use cases in managing and deploying network services efficiently. Key components, advantages, and disadvantages of SDN and NFV are highlighted to illustrate the evolution and modernization of networking paradigms.