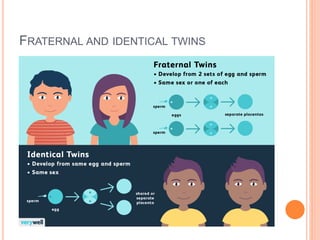
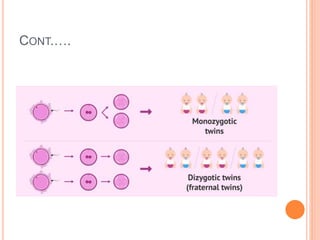
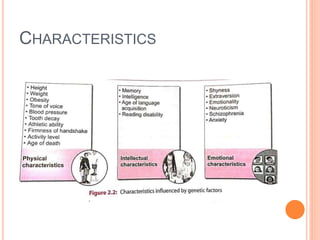
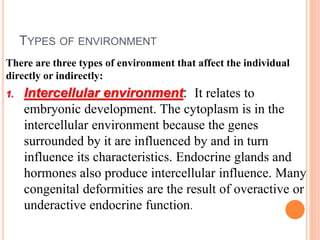
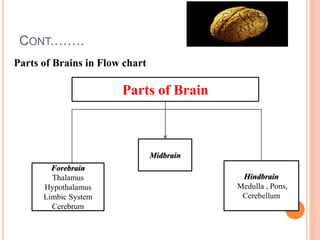
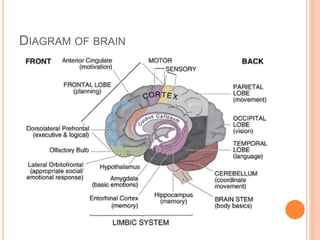
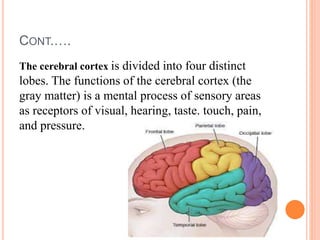
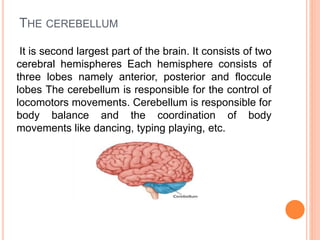
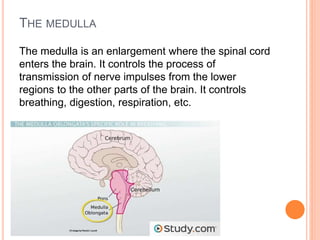
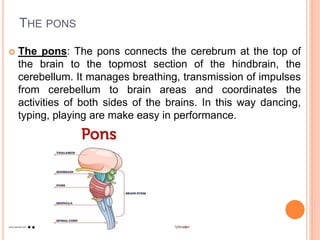
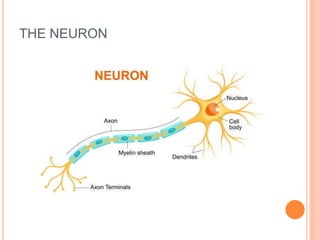
The document discusses heredity and the mechanisms of heredity including genes, chromosomes, and genetic combinations that determine traits. It also discusses the different types of environment that influence development from the intercellular and intrauterine environments to the external physical, biological, and psychosocial environments. The brain and nervous system are described as controlling behavior through neurons, synapses, and different parts of the brain like the forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, cerebrum, and hemispheres.