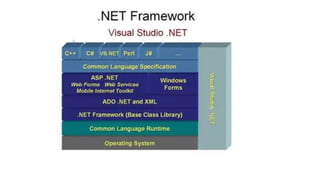
Introduction to Visual Programming
Visual programming is a method of creating software applications using graphical elements rather than writing code in textual form. In visual programming, developers can drag and drop components, connect them using visual representations of logic, and design applications in a more intuitive way. This approach emphasizes what the program should do rather than focusing on the syntax of programming languages.
Key Features:
Uses visual elements like buttons, forms, and icons.
Often employs flowcharts or block diagrams to represent logic.
Simplifies programming for beginners and non-programmers.
Enables rapid application development (RAD).


































![Defining Sub Procedures
The Sub statement is used to declare the name, parameter and the body of a sub procedure. The syntax
for the Sub statement is −
[Modifiers] Sub SubName [(ParameterList)]
[Statements]
End Sub
Where,
Modifiers − specify the access level of the procedure; possible values are - Public, Private,
Protected, Friend, Protected Friend
SubName − indicates the name of the Sub
ParameterList − specifies the list of the parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1visualprogrammingbca-part1-251001012029-f2ae123e/85/Unit-1_Visual-Programming-BCA-Part-1-pdf-43-320.jpg)





![Saving Visual Basic Application
1. Click on File → Save All.
2. This saves:
○ Your form design (e.g., Form1.vb)
○ Your code (e.g., Form1.vb [Design])
○ The full project and solution files
3. Your project is saved as:
○ .sln file (Solution)
○ .vbproj file (Project)
○ .vb files (Code)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1visualprogrammingbca-part1-251001012029-f2ae123e/85/Unit-1_Visual-Programming-BCA-Part-1-pdf-49-320.jpg)





