Embed presentation
Download to read offline


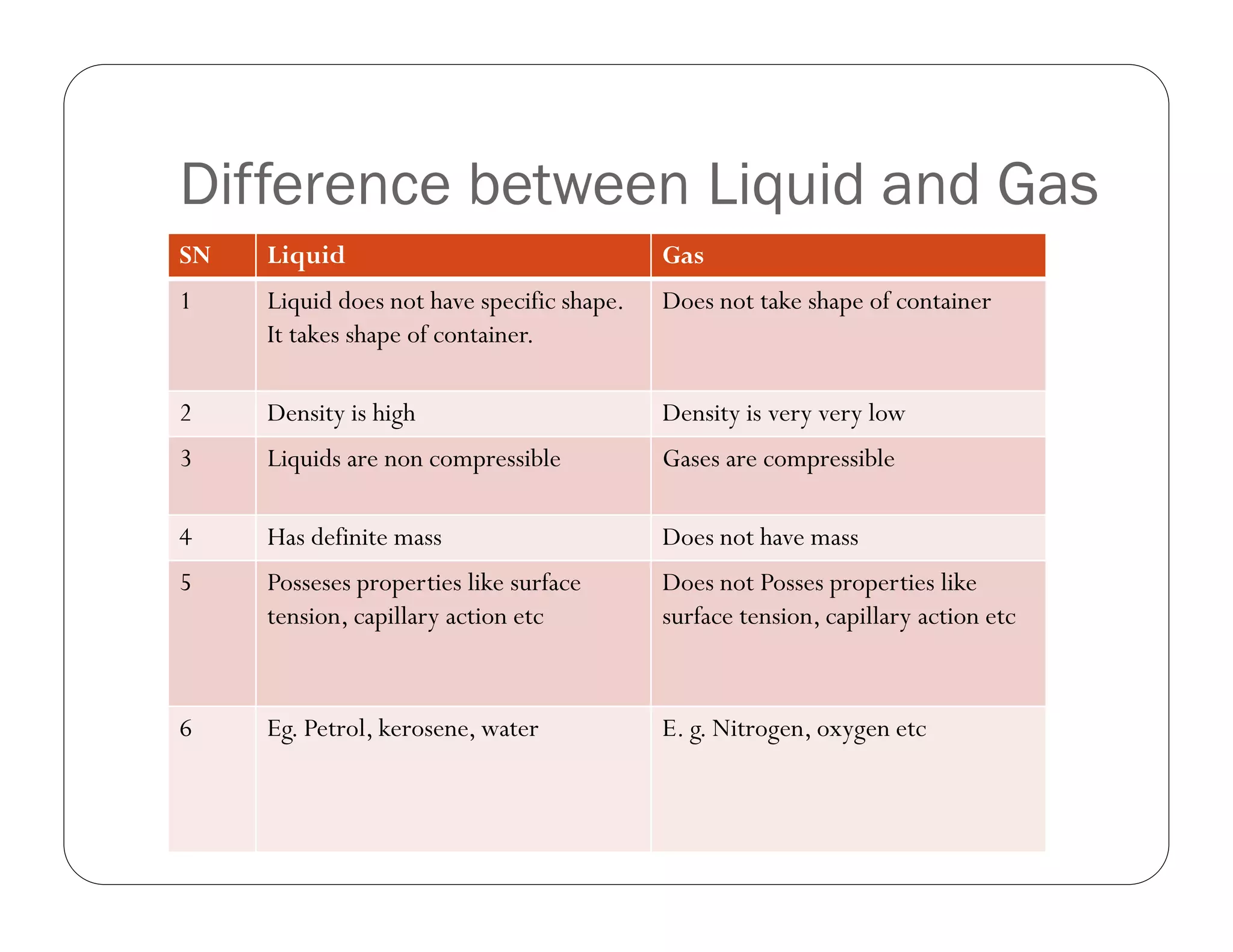


Fluid mechanics deals with fluids like liquids and gases. Liquids take the shape of their container but do not have a definite shape, while gases do not take the shape of any container. Liquids are denser and non-compressible compared to gases, which are less dense and compressible. Common examples of fluids in daily life include air conditioning, water, fuels for vehicles, and fluids involved in refrigeration and food. Water is the most widely used fluid in civil engineering projects like dams, canals, and concrete construction due to its abundance on Earth. Fluids can also be categorized as compressible or non-compressible, ideal or real, and Newtonian or non-Newtonian.





