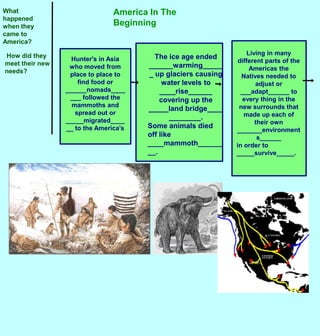
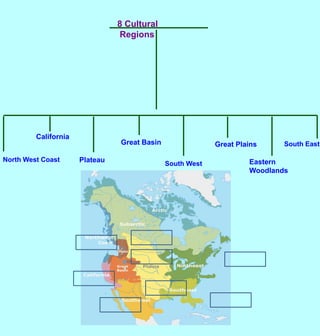
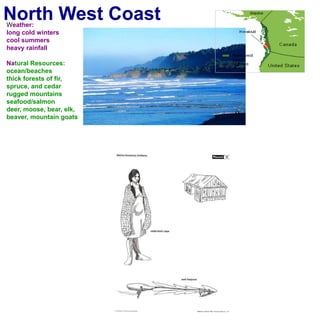
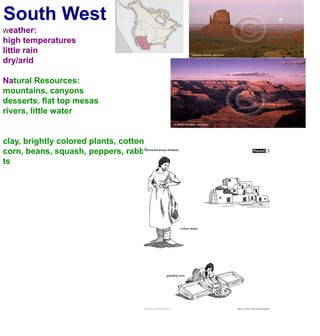
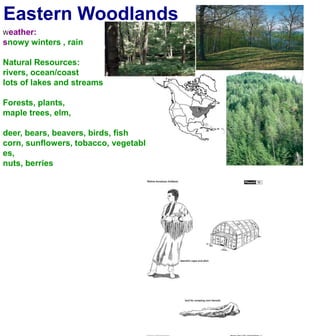
The first Americans crossed into North America from Asia over a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska during the last ice age approximately 30,000 years ago. As the climate warmed, glaciers melted and sea levels rose, covering the land bridge. Some animal species like mammoths died off during this period of climate change. Native Americans adapted to their new environments across North America by developing different cultures, languages, tools and ways of life suited to the varied natural resources of places like the Northwest Coast, Great Plains, California and Eastern Woodlands. They shared some common traits like believing nature had spirits, not owning land, only using needed resources, and participating in trade.