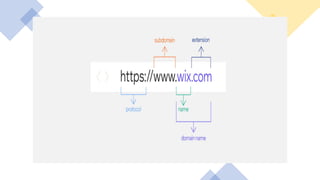
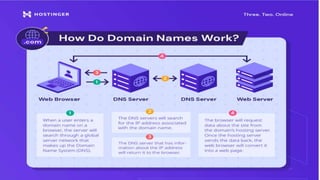
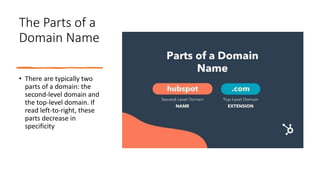
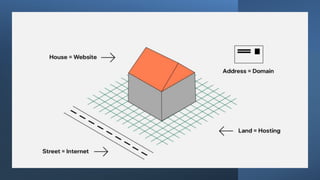
This document explains domain names and web hosting, detailing their importance and differences. A domain name serves as a memorable address for a website, while web hosting provides the necessary space on a server for the website's files. The document also outlines the components of a domain, the process of purchasing a domain name, and the relationship between a domain and hosting.