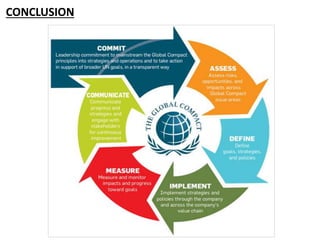
The document discusses the United Nations Global Compact (UNGC), a voluntary initiative for businesses to implement sustainable and socially responsible policies. It outlines key drivers for UNGC including market liberalization, globalization, and NGO activism putting pressure on companies. While UNGC can help fill governance gaps and mitigate risks, it is ultimately voluntary with no enforcement, and some argue it acts more to protect companies from regulation rather than enforce accountability.