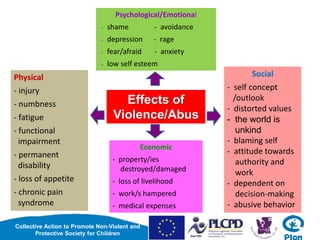
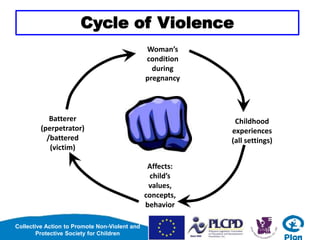
This document discusses violence and its effects. It defines violence as acts intended to hurt people, and lists different forms like physical, verbal, emotional, sexual, and economic abuse. It notes that violence can be perpetrated by individuals, groups, states, or the environment. The effects of violence are psychological/emotional like depression or fear, physical like injury, and social like distorted values. The document also discusses how violence is often intergenerationally transmitted as children who witness abuse learn that it is a normal way to resolve conflicts. It concludes that breaking this cycle requires practicing non-violent child discipline.