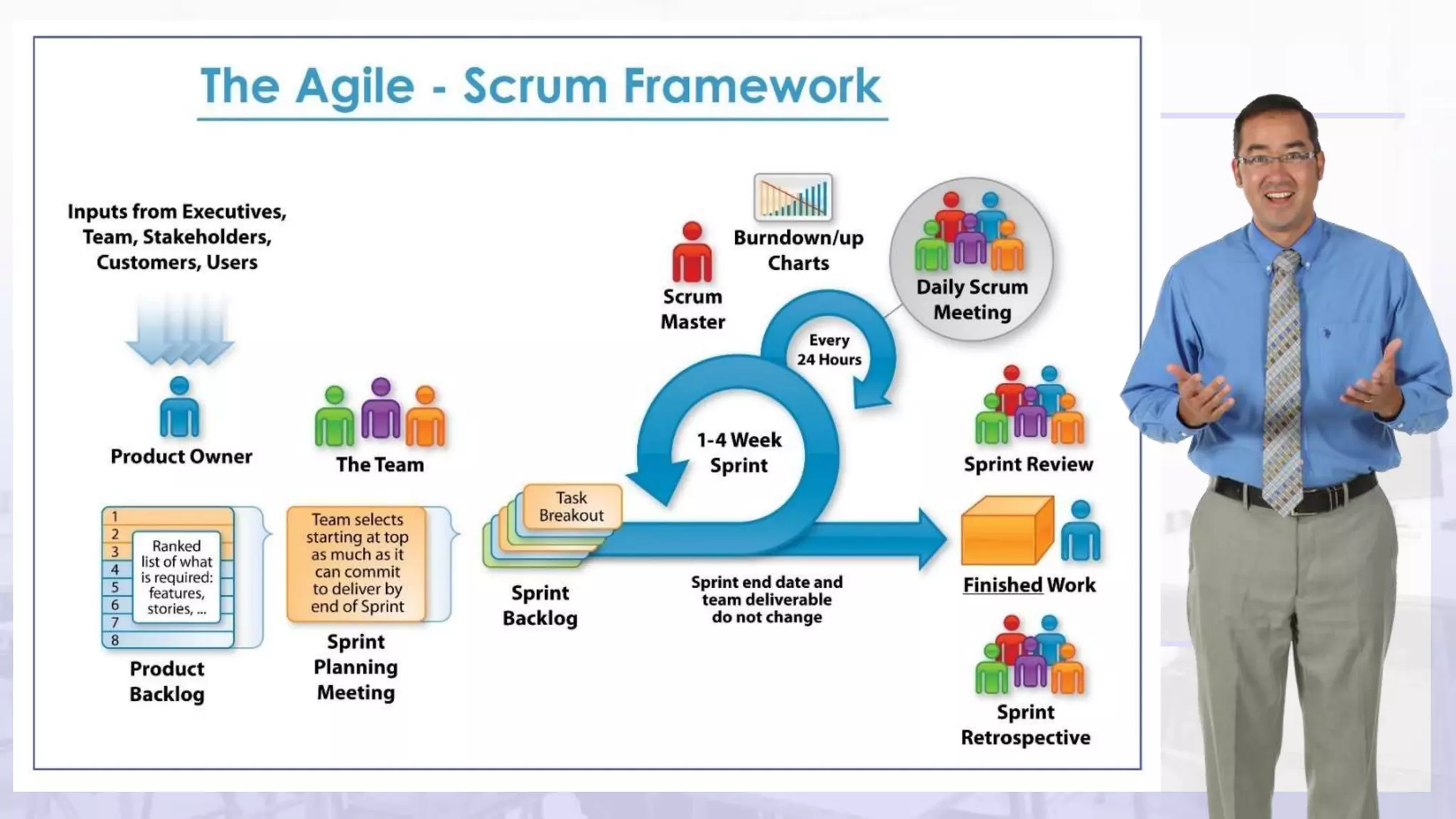
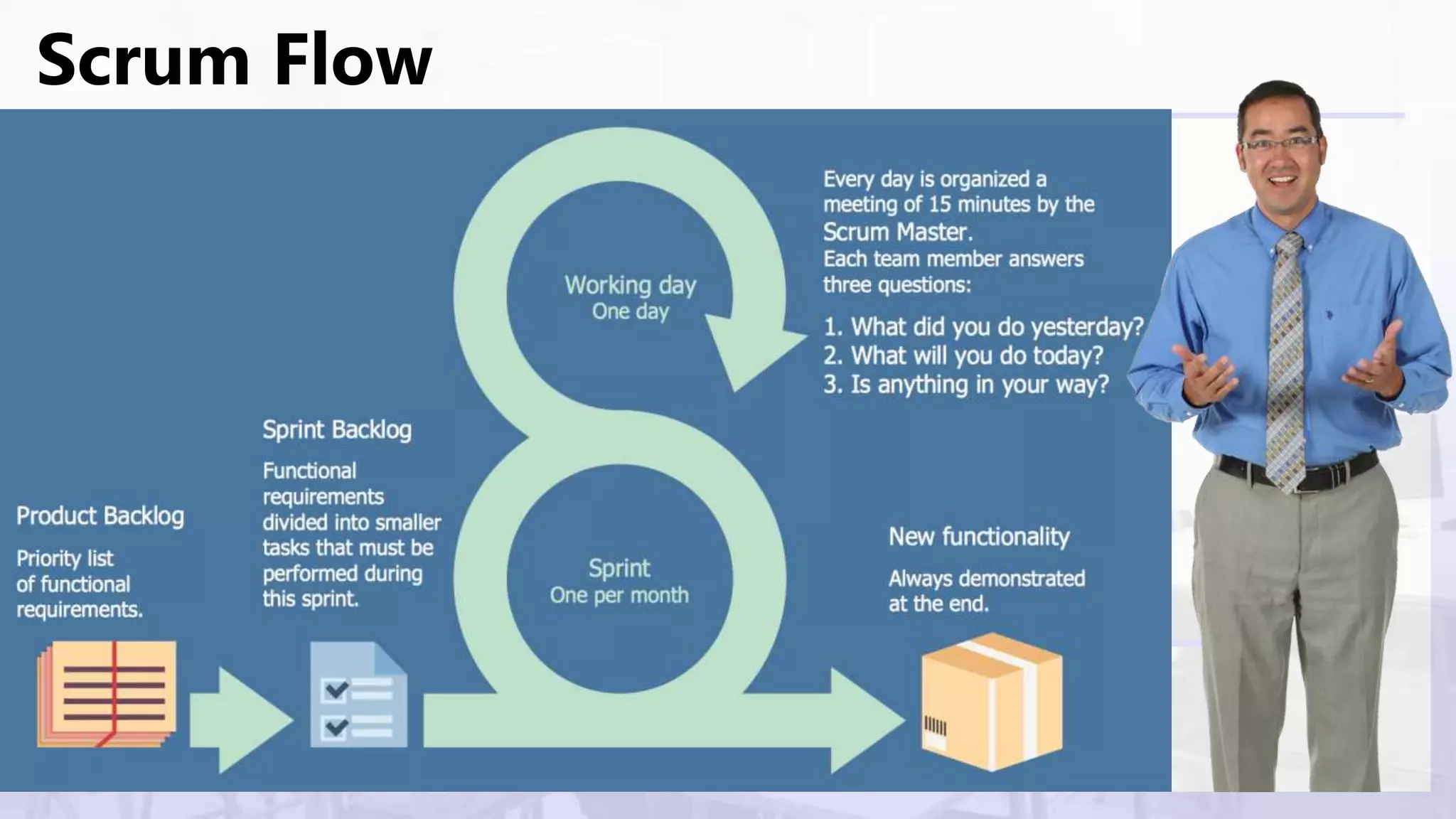
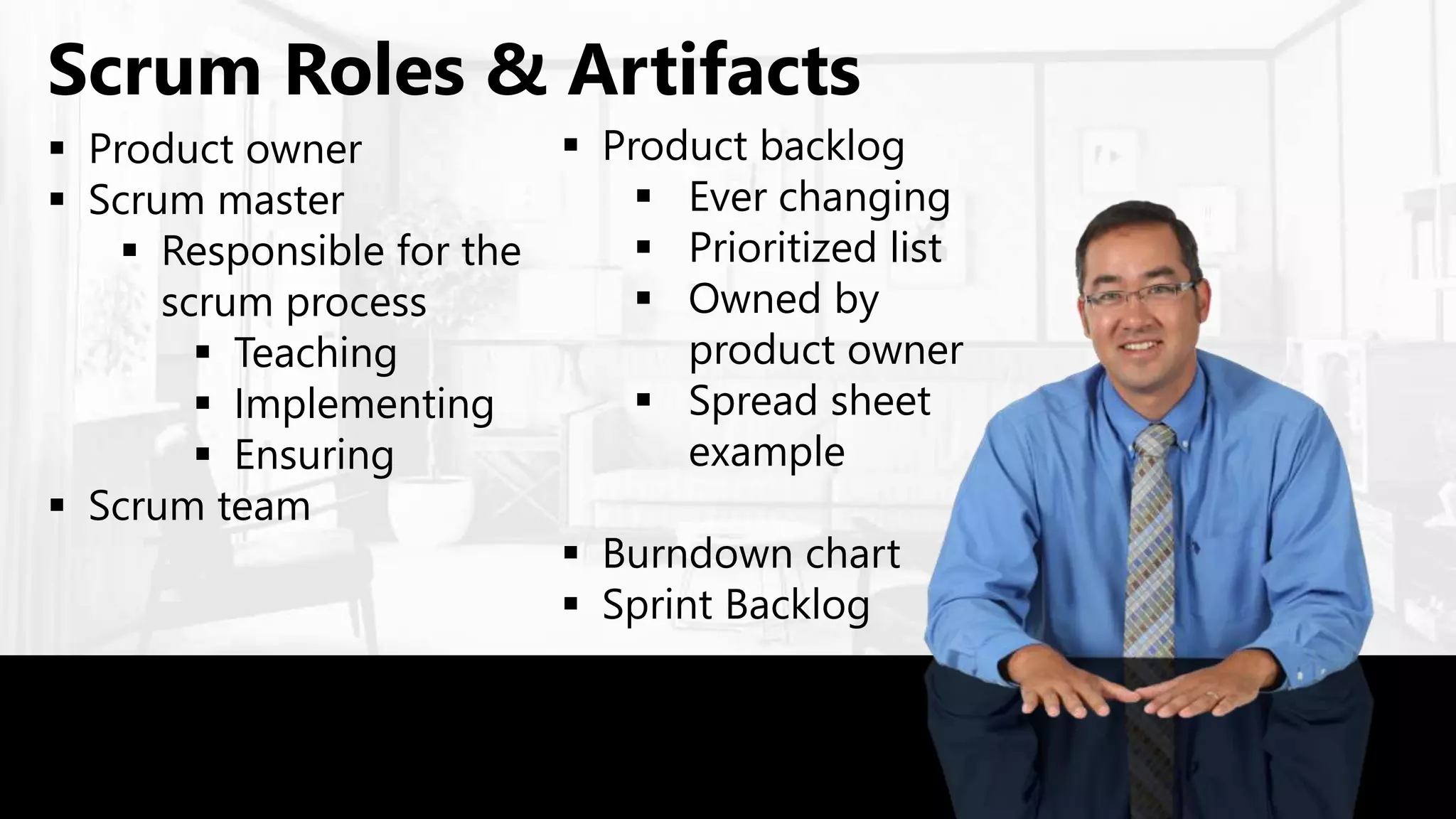
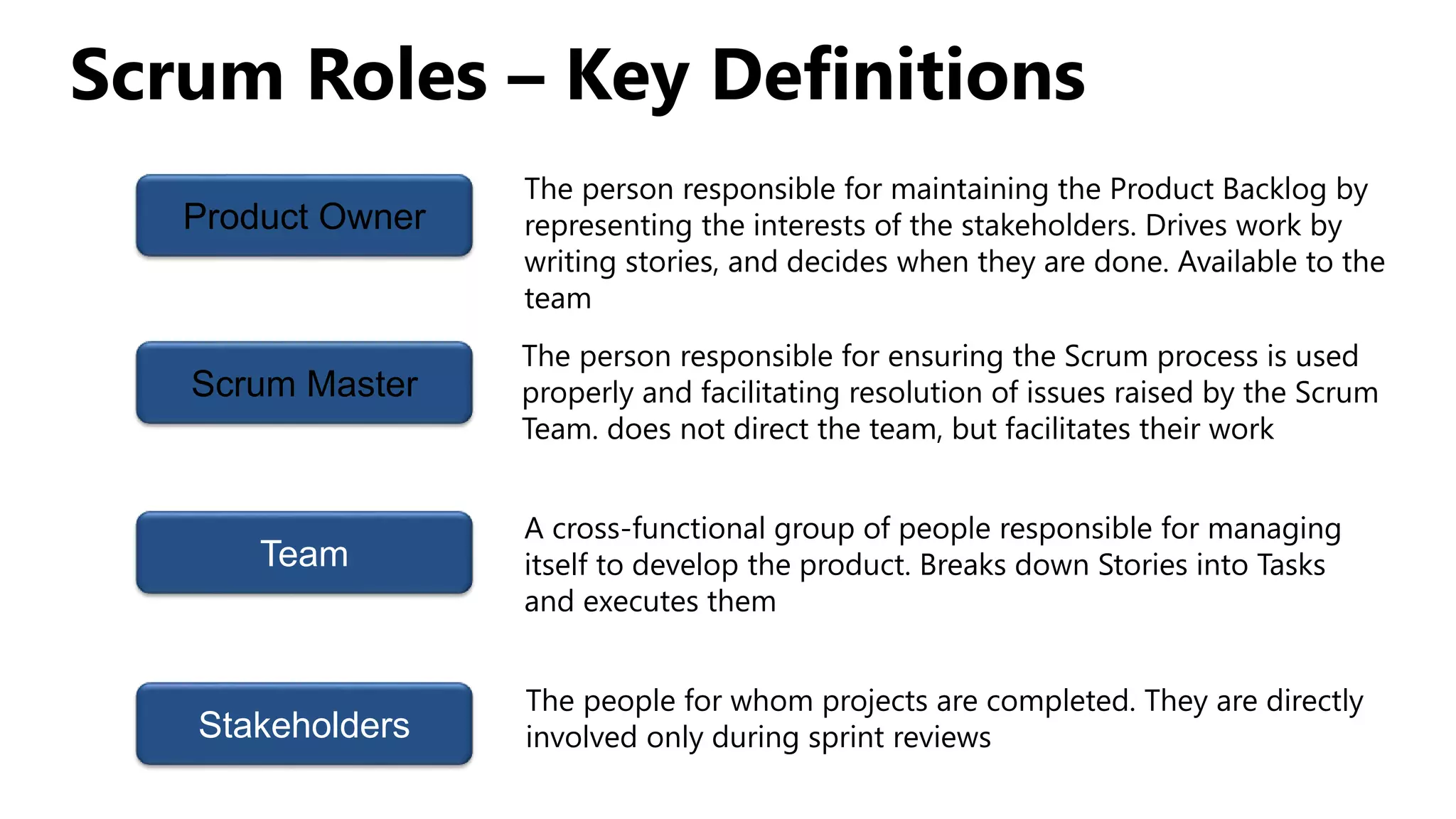
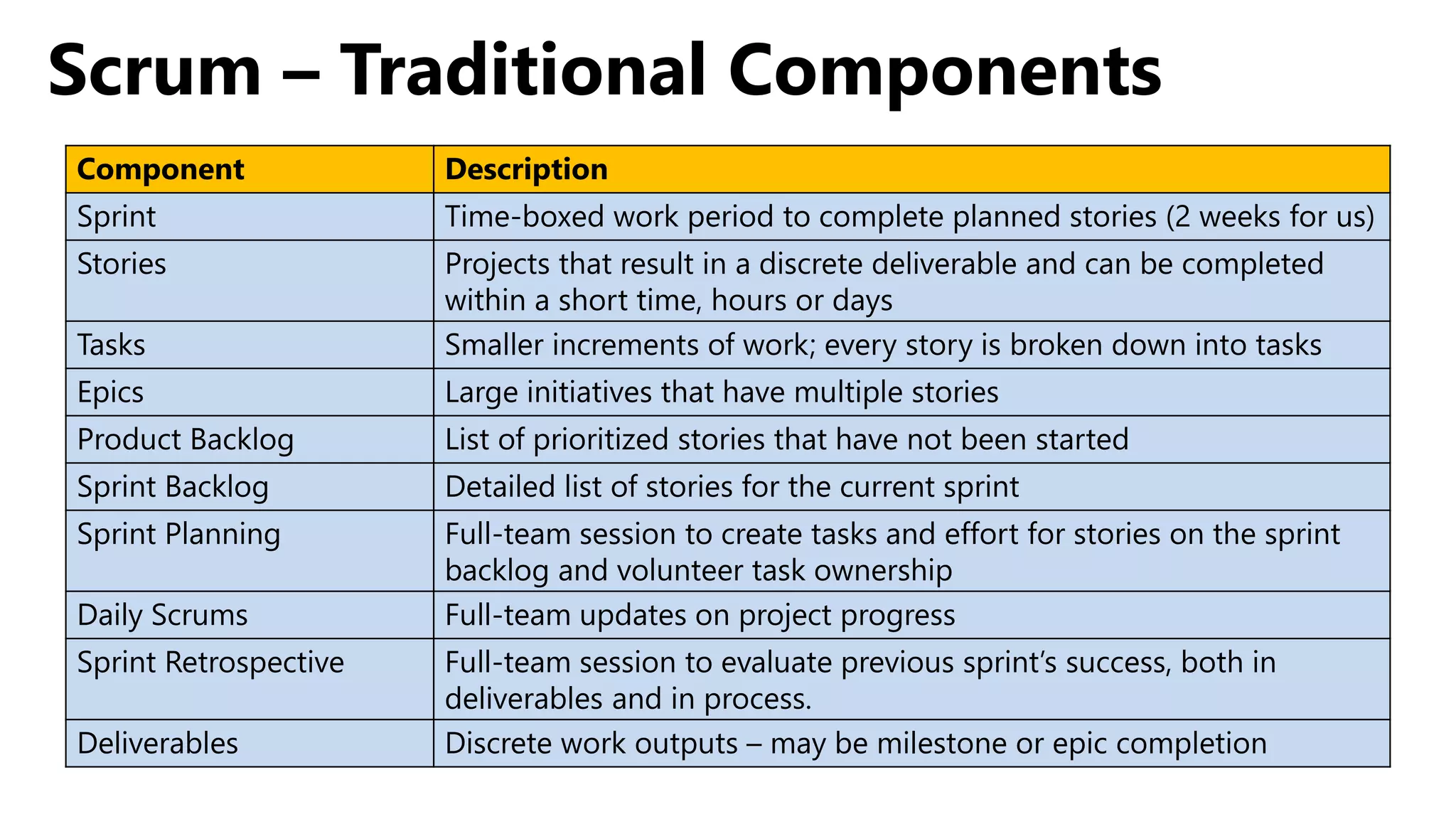
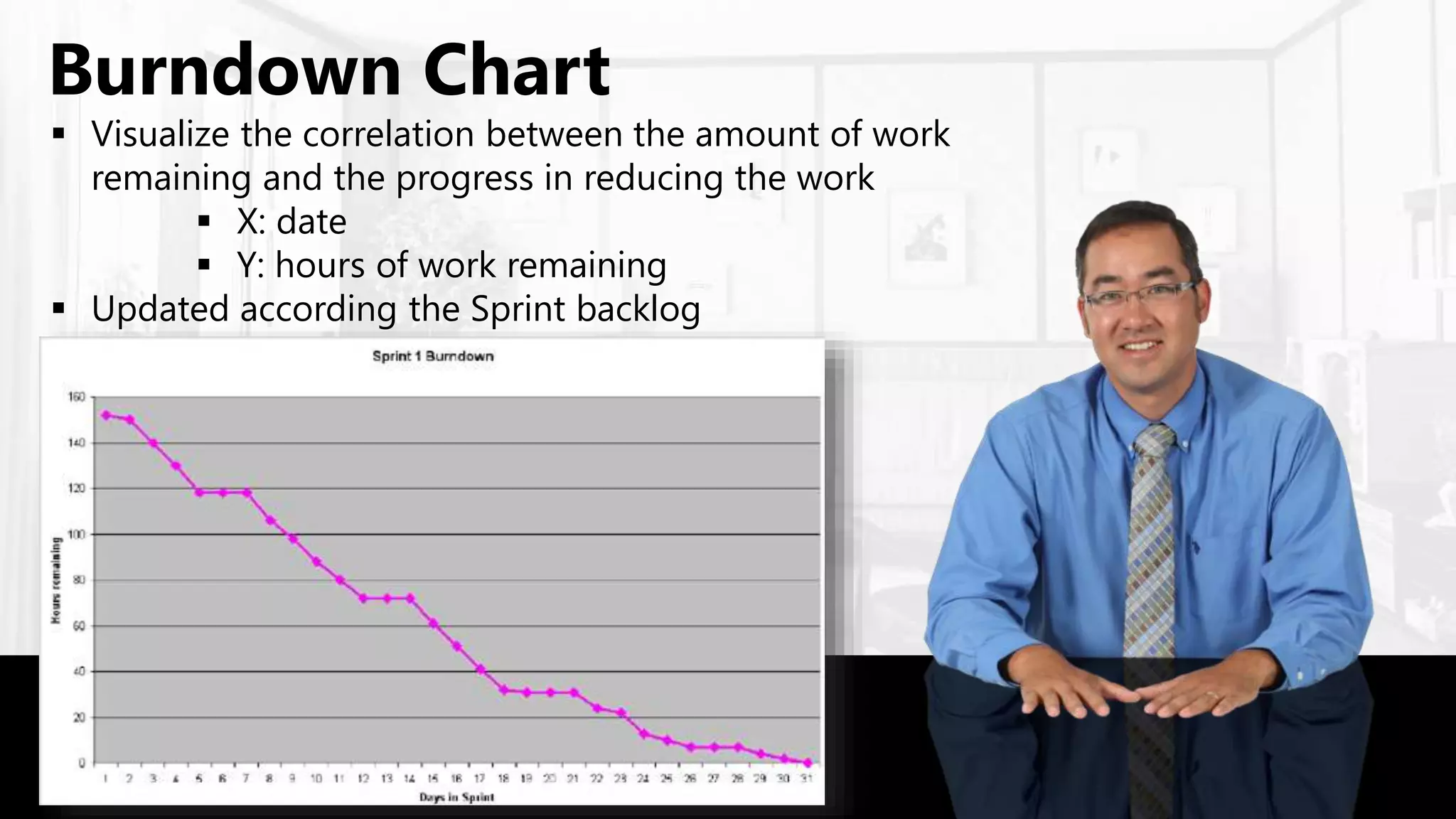
Scrum is an agile project management framework used for software development projects. It aims to deliver new software capabilities every 2-4 weeks. Key roles in Scrum include the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Scrum Team. The Product Owner maintains a prioritized Product Backlog of stories. The Scrum Master ensures the Scrum process is followed. The Scrum Team works in sprints to complete stories from the Product Backlog. The Sprint Backlog defines tasks for a sprint. A Burndown Chart visualizes work remaining over time.