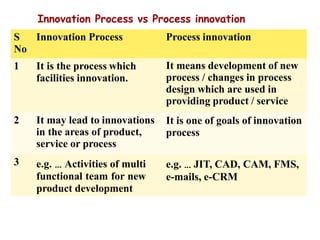
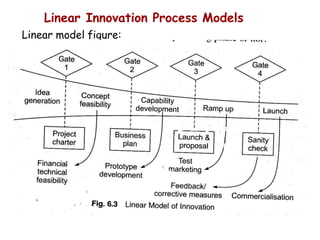
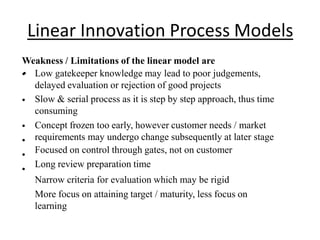
The document discusses different models of the innovation process. It describes the innovation process as involving search, exploration, cycles of divergent and convergent thinking, and needing support at the national, enterprise, and individual levels. It then contrasts linear models of innovation, like technology push and market pull models, with more flexible models where phases can overlap and ideas can emerge at any stage. Flexible models attempt to better reflect the complexity of real-world innovation.