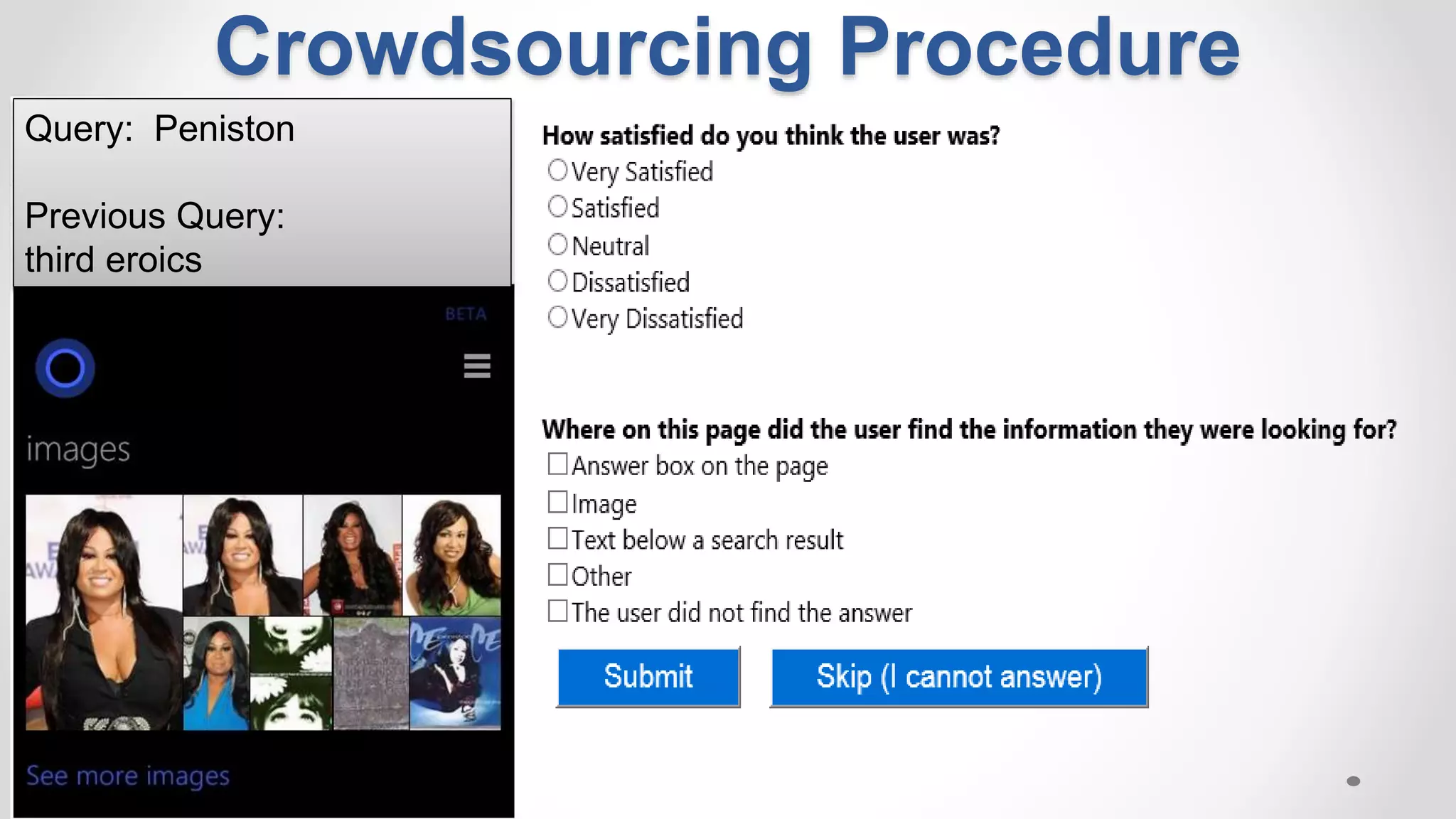
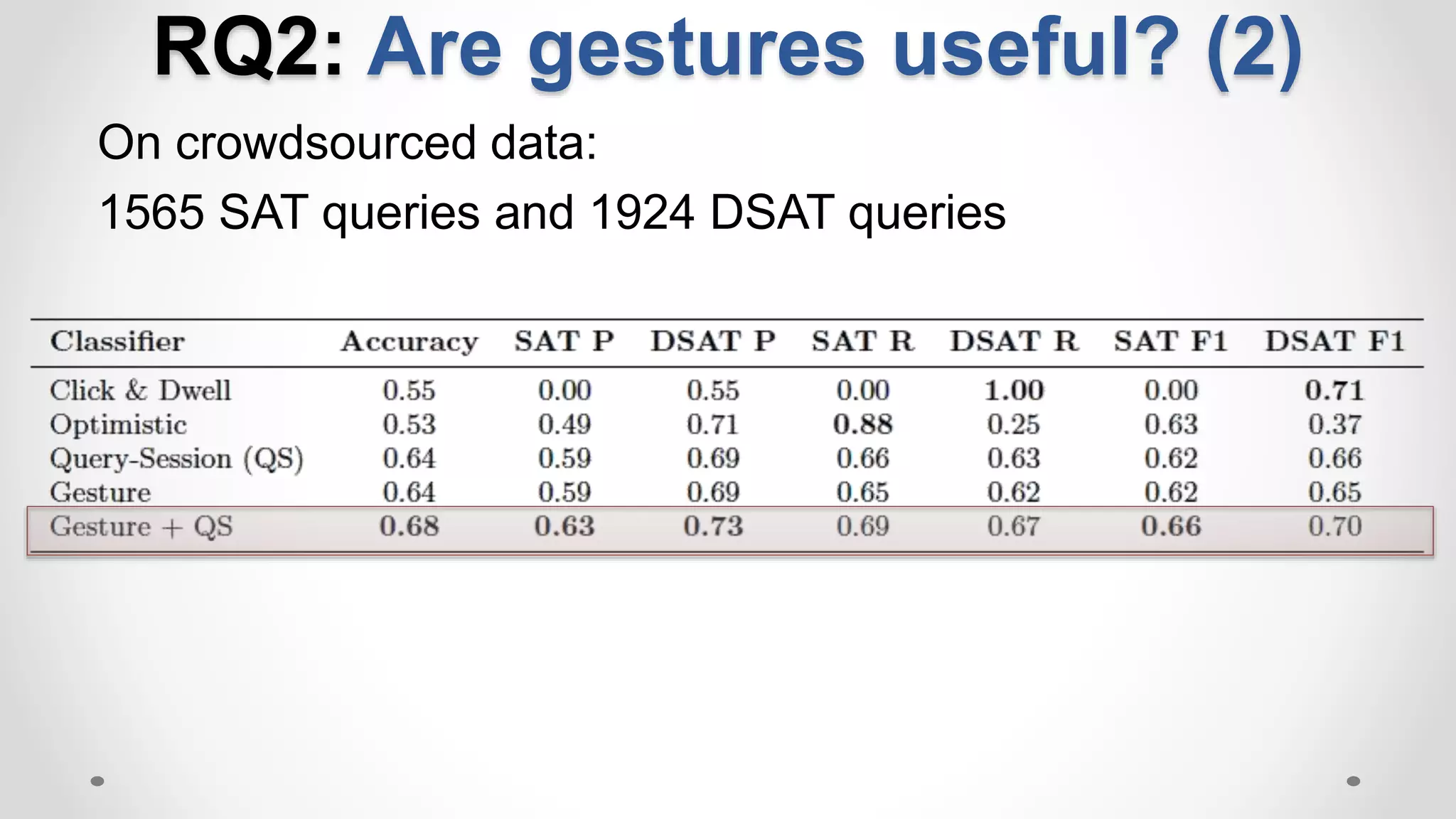
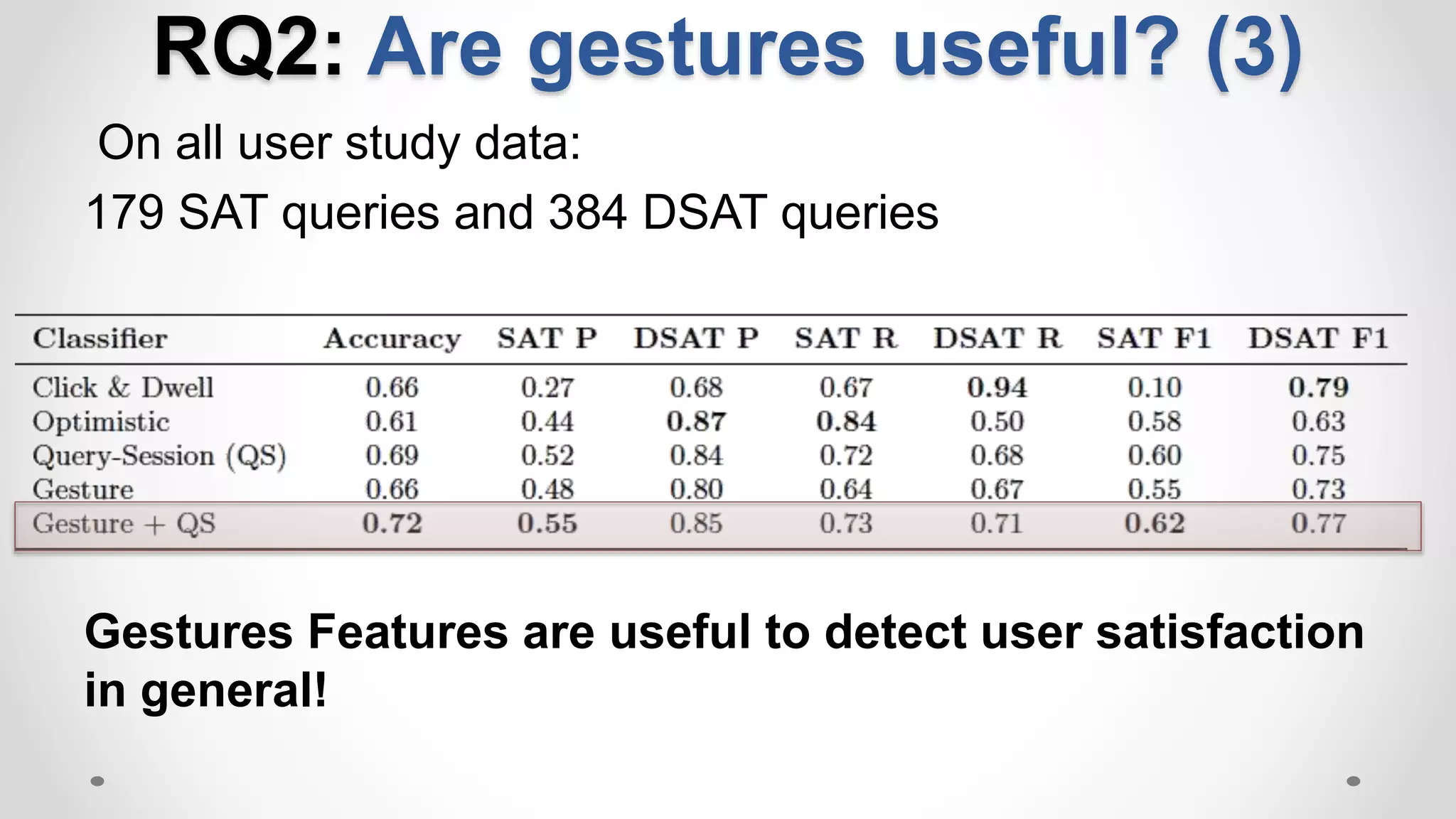
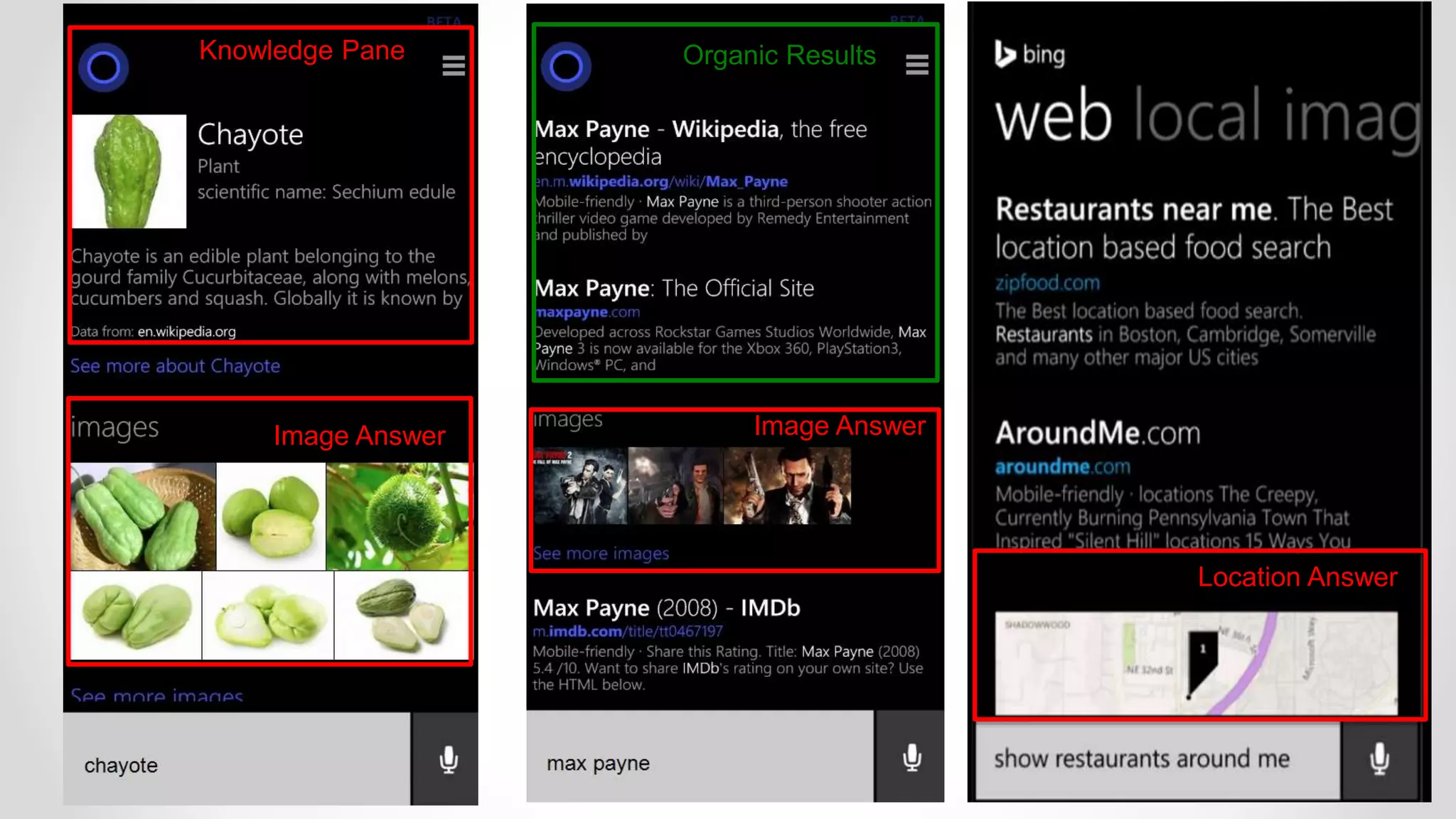
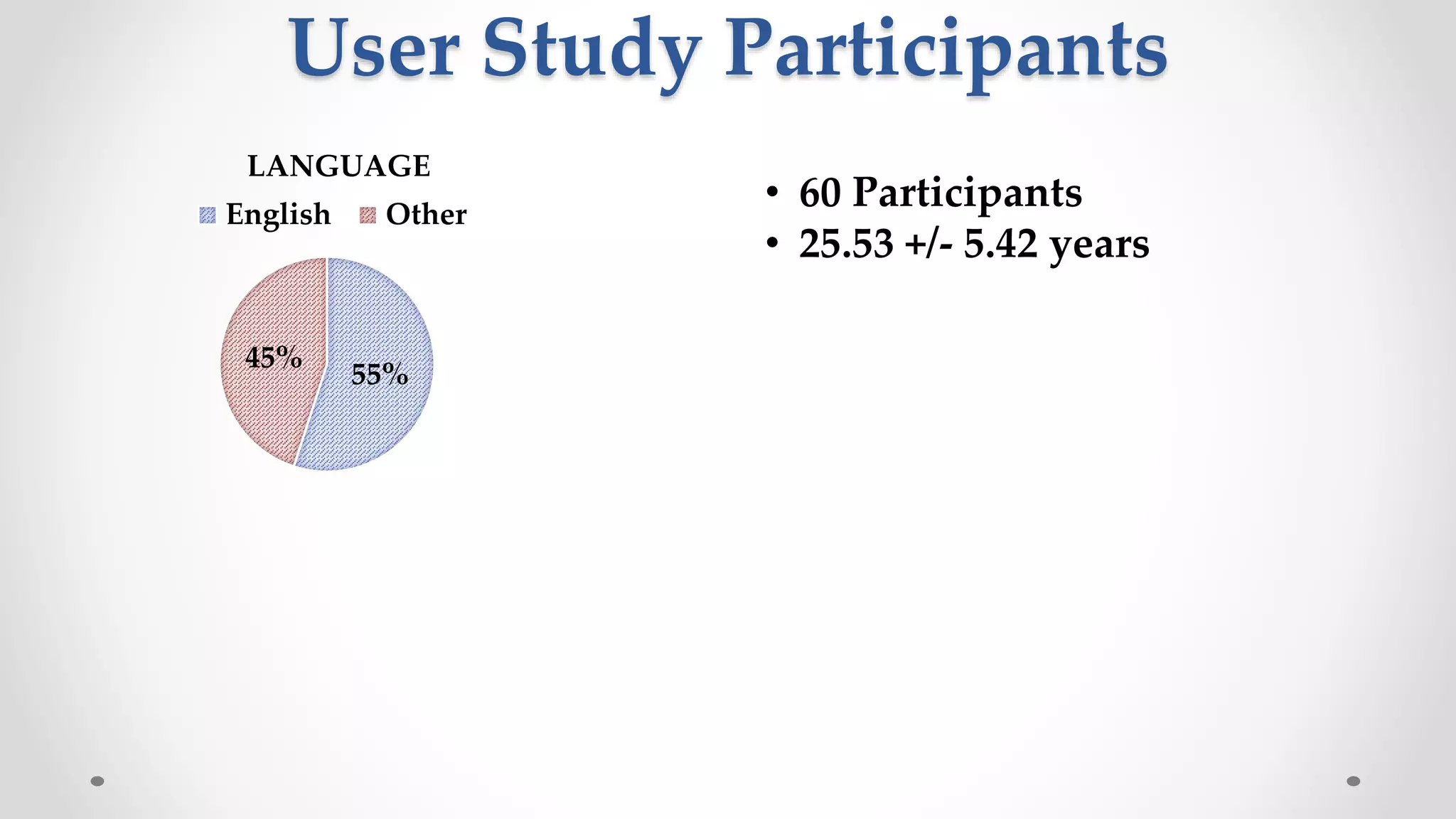
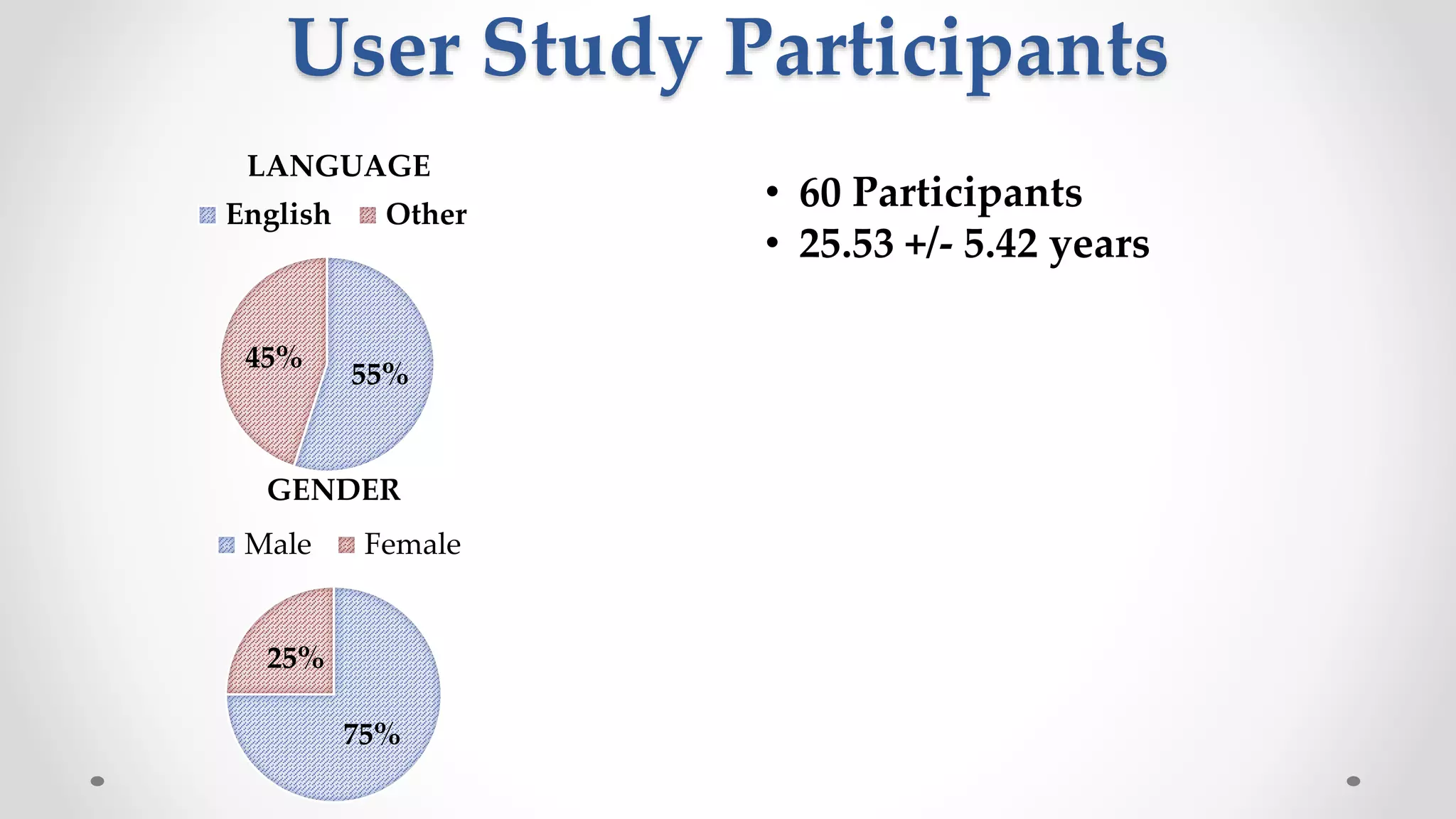
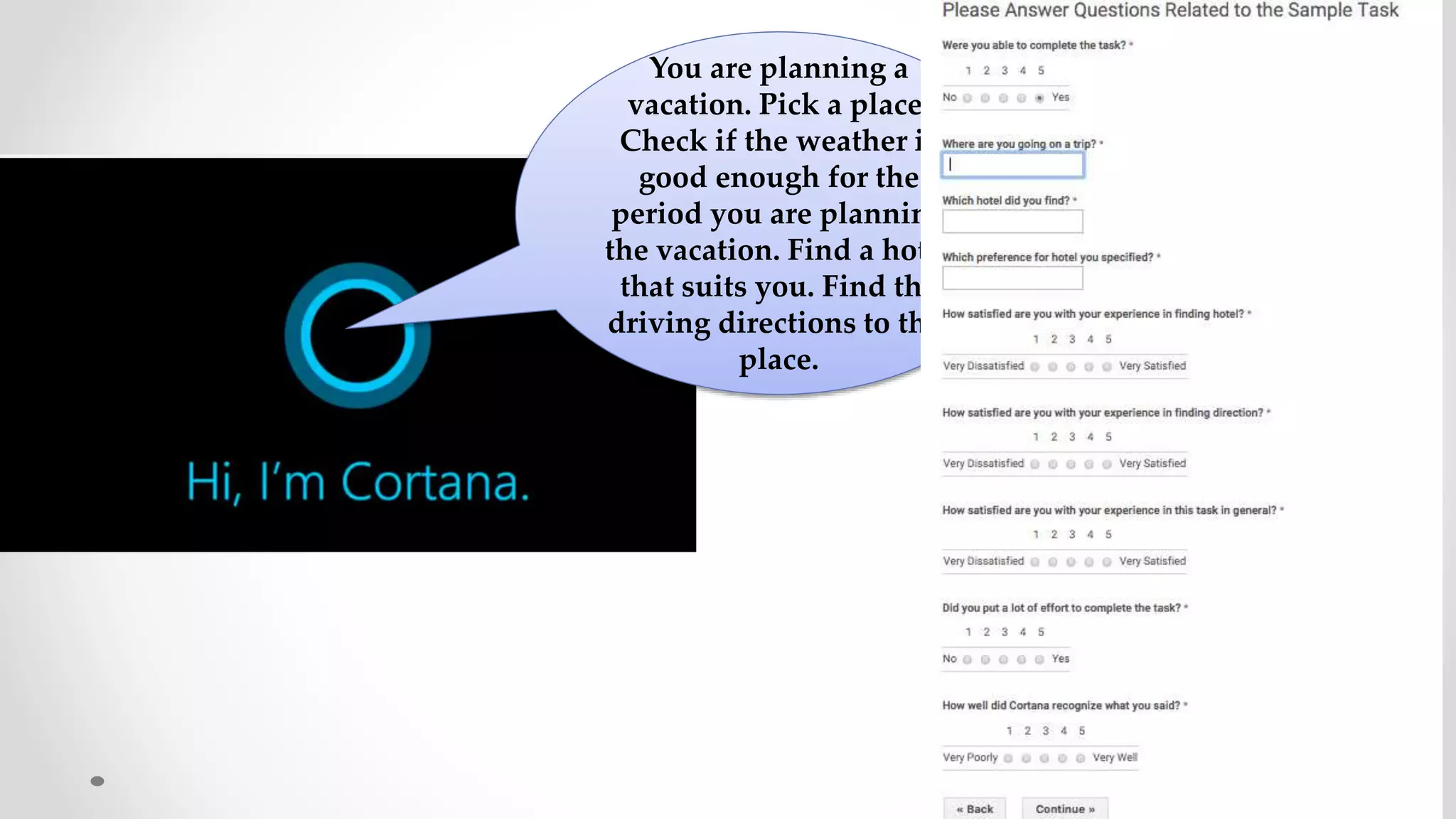
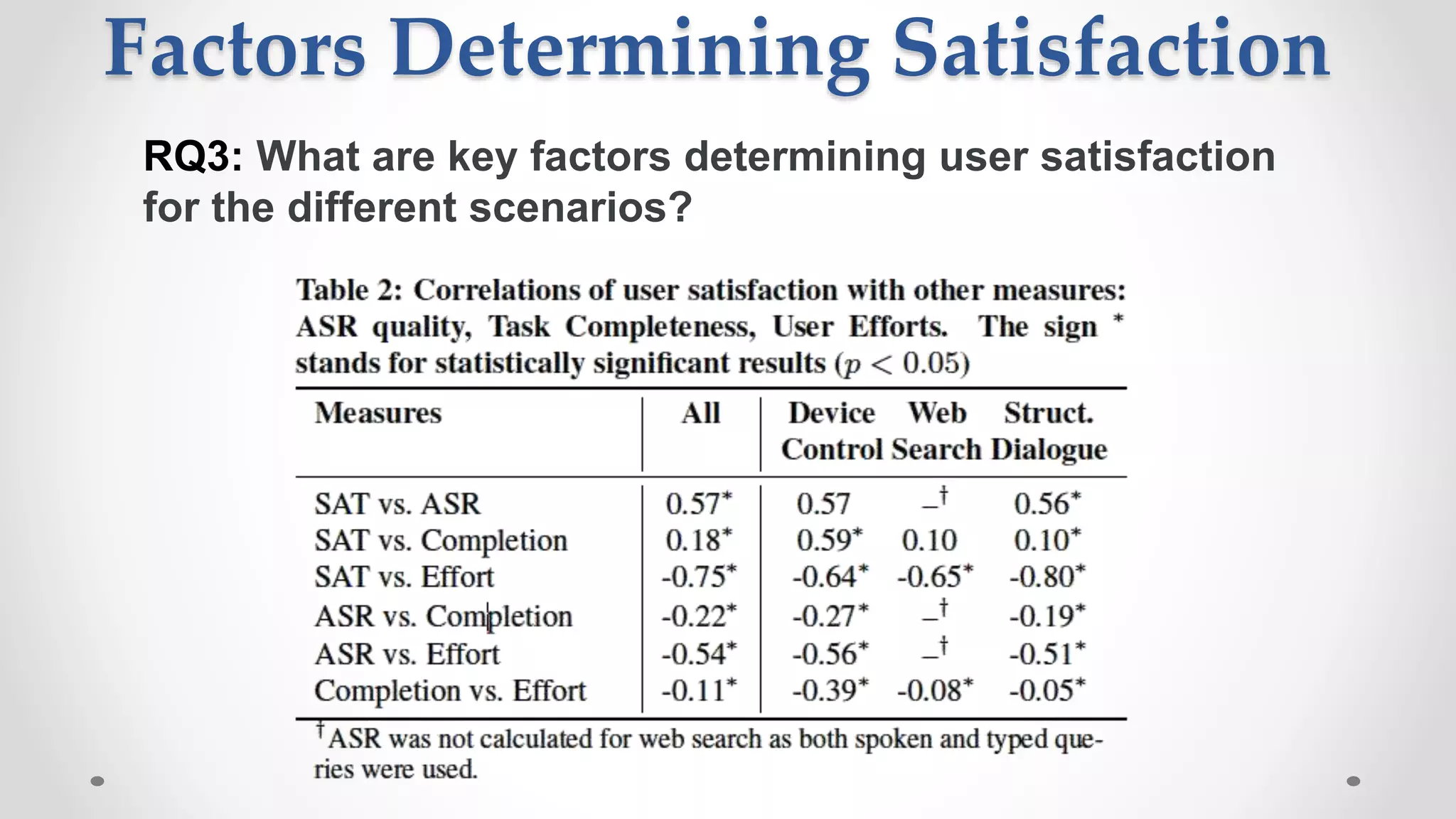
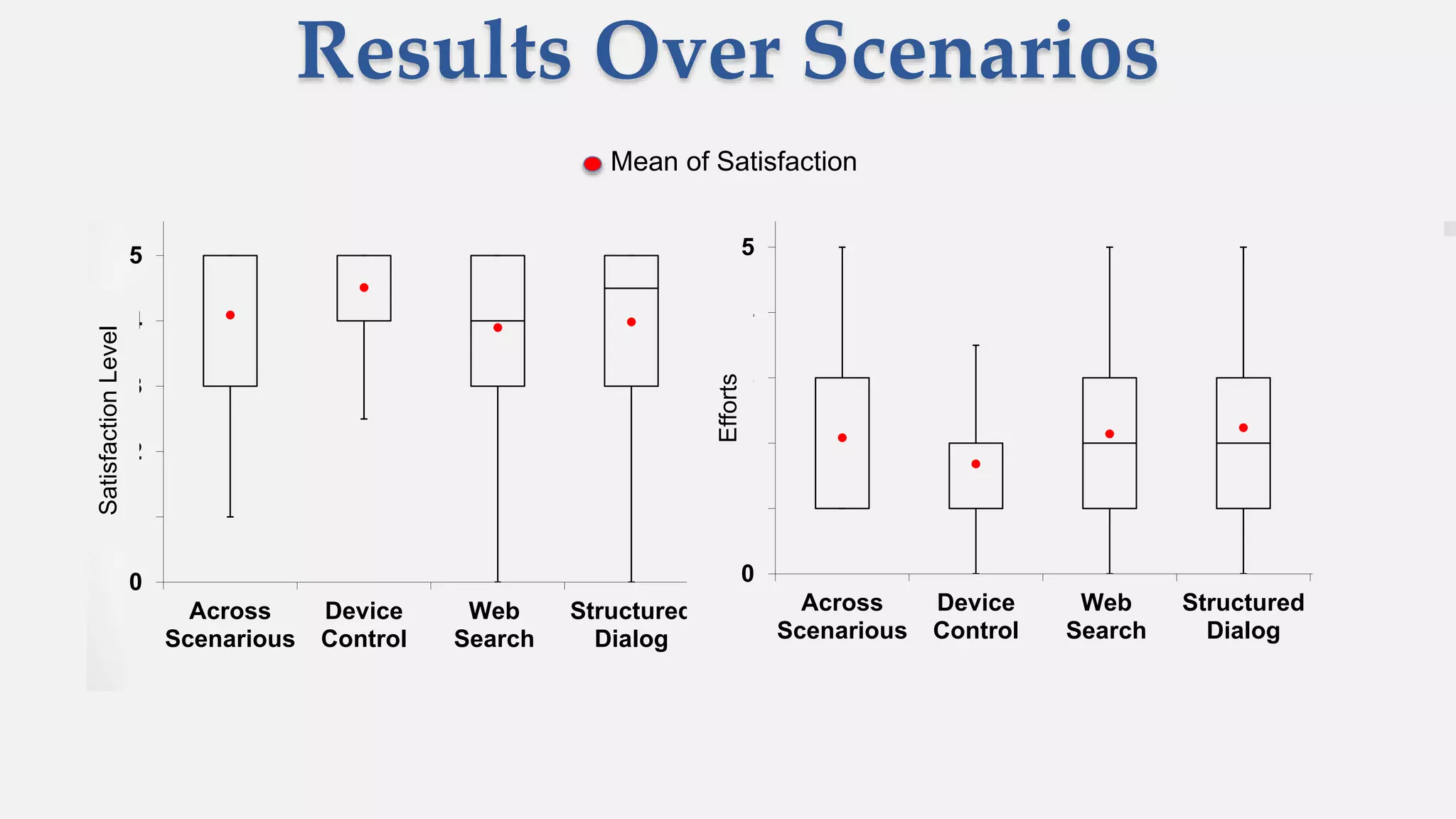
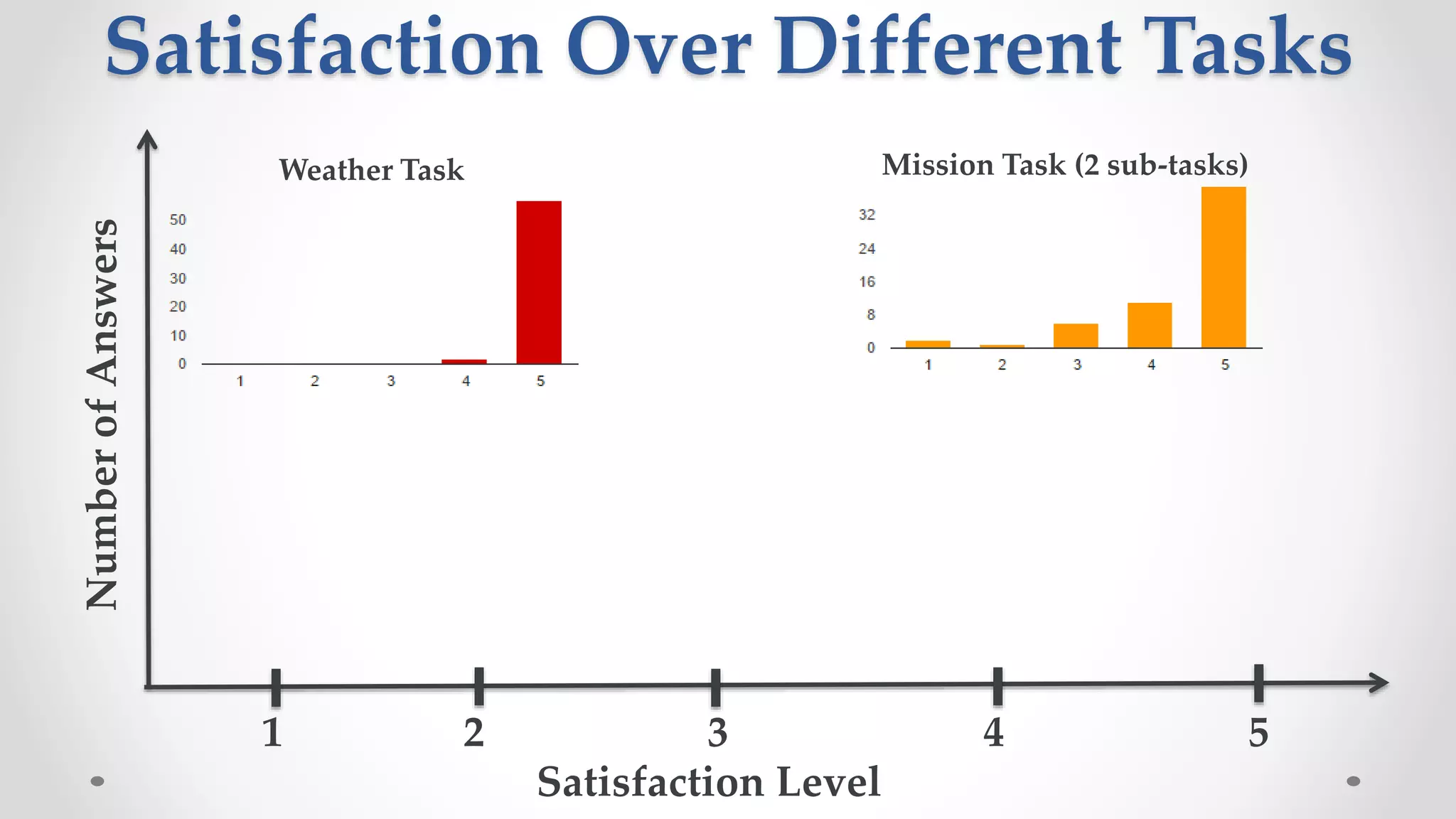
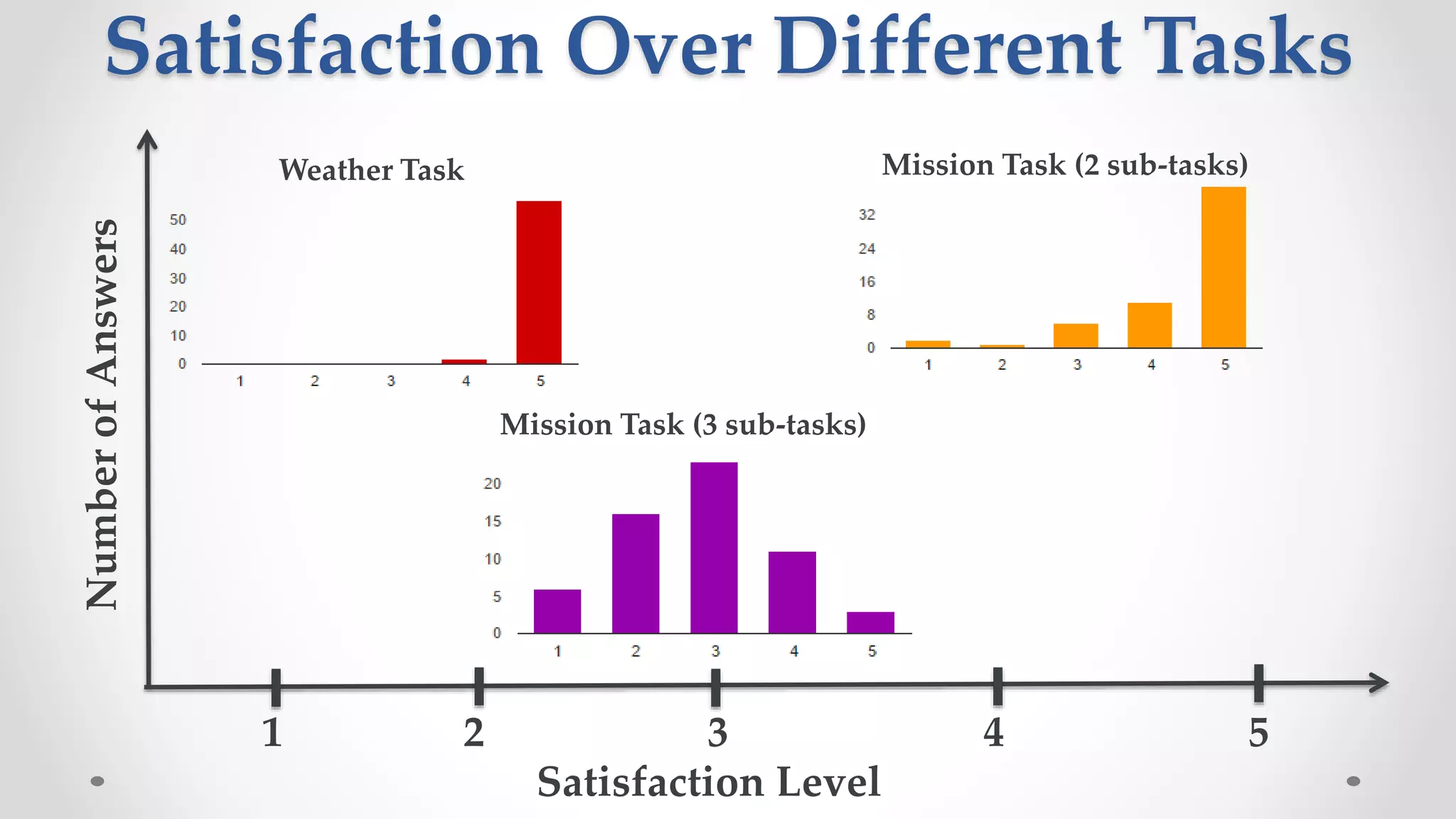
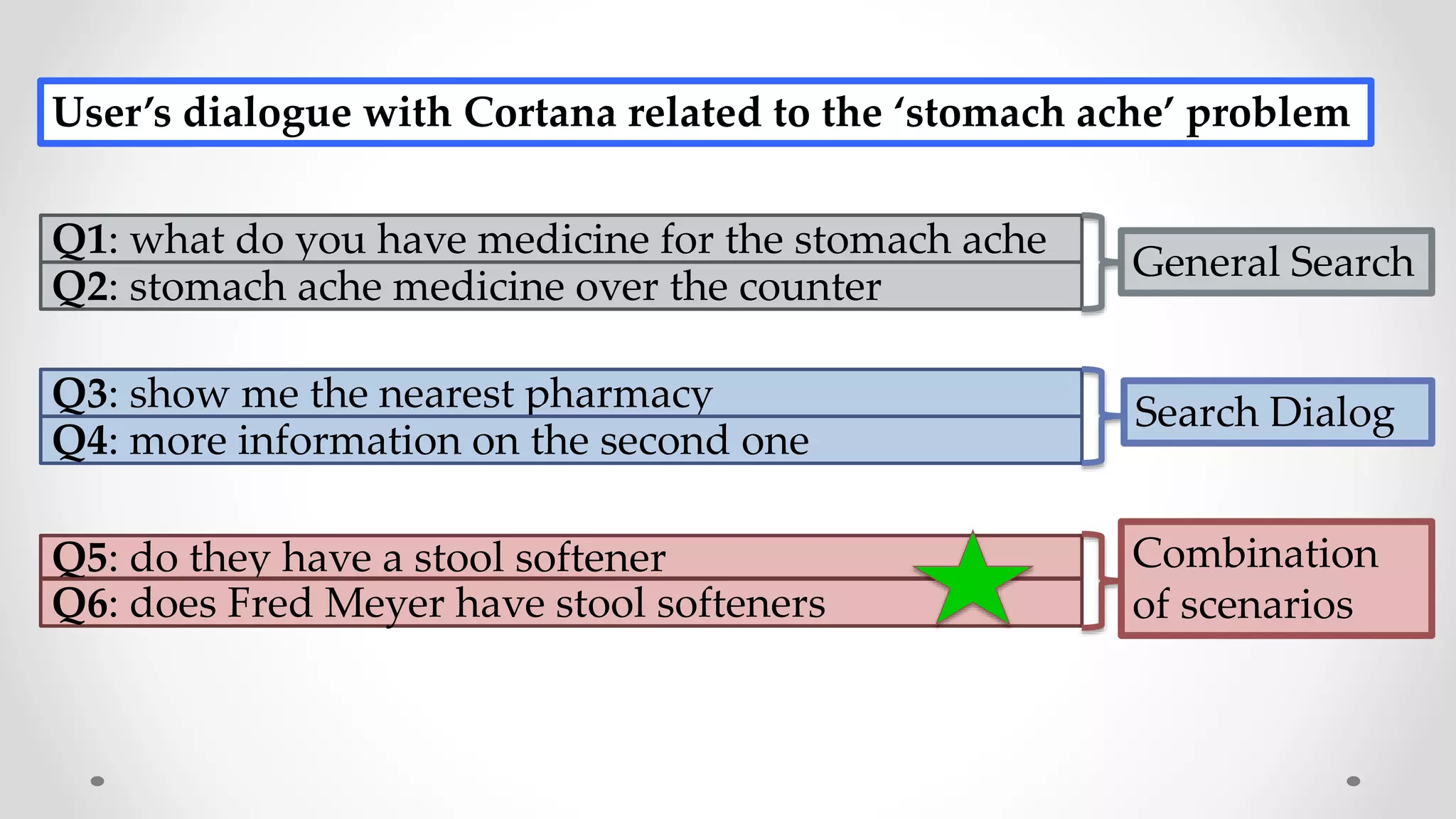
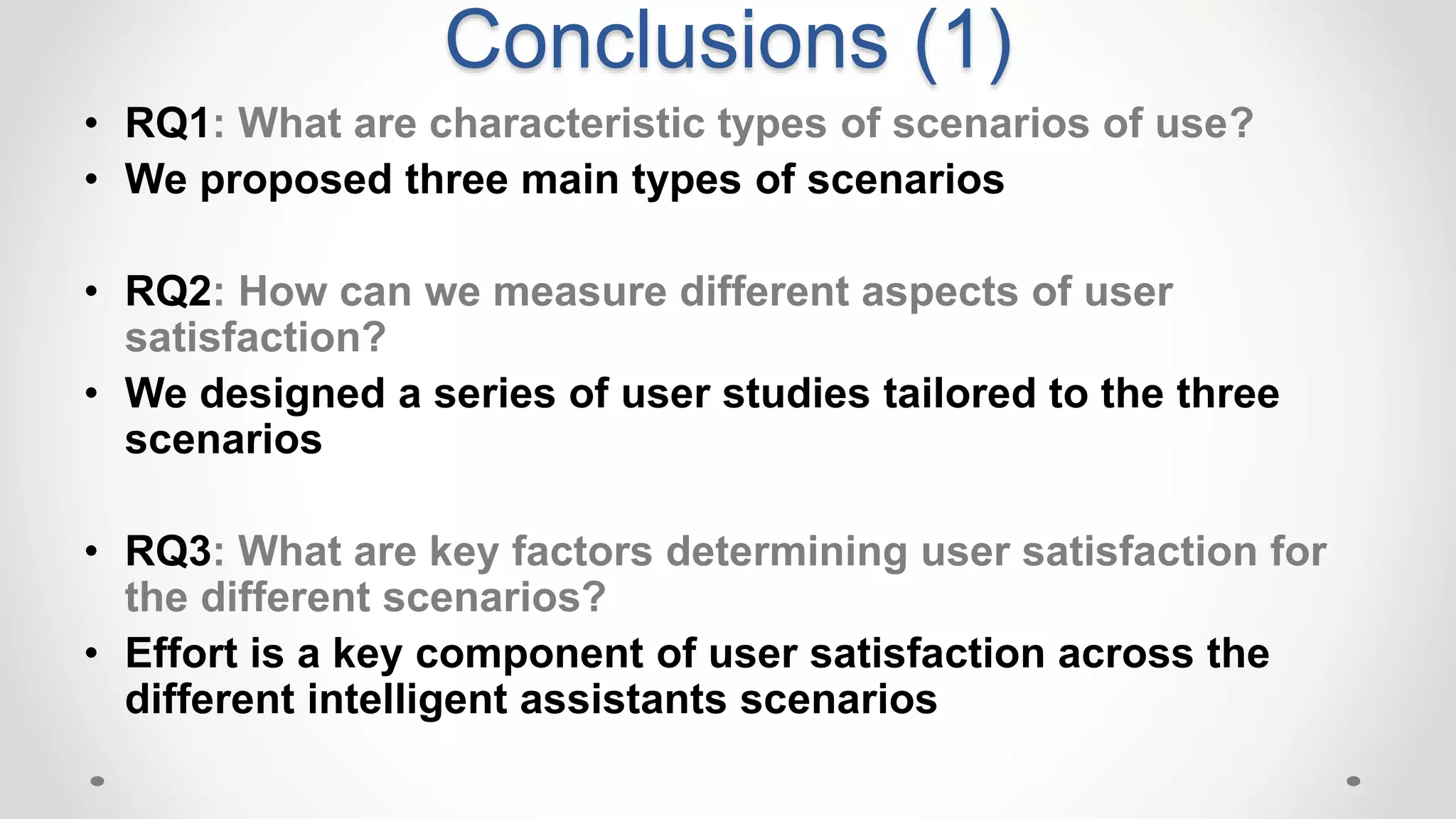
The document discusses predicting user satisfaction with intelligent assistants through a user study. It aims to (1) identify characteristic usage scenarios, (2) measure user satisfaction aspects, and (3) determine key satisfaction factors. The study involved 60 participants performing tasks from usage logs. Results showed effort is a key satisfaction factor across scenarios and query-level satisfaction relates to overall dialogue satisfaction.
































![Evaluating User Satisfaction
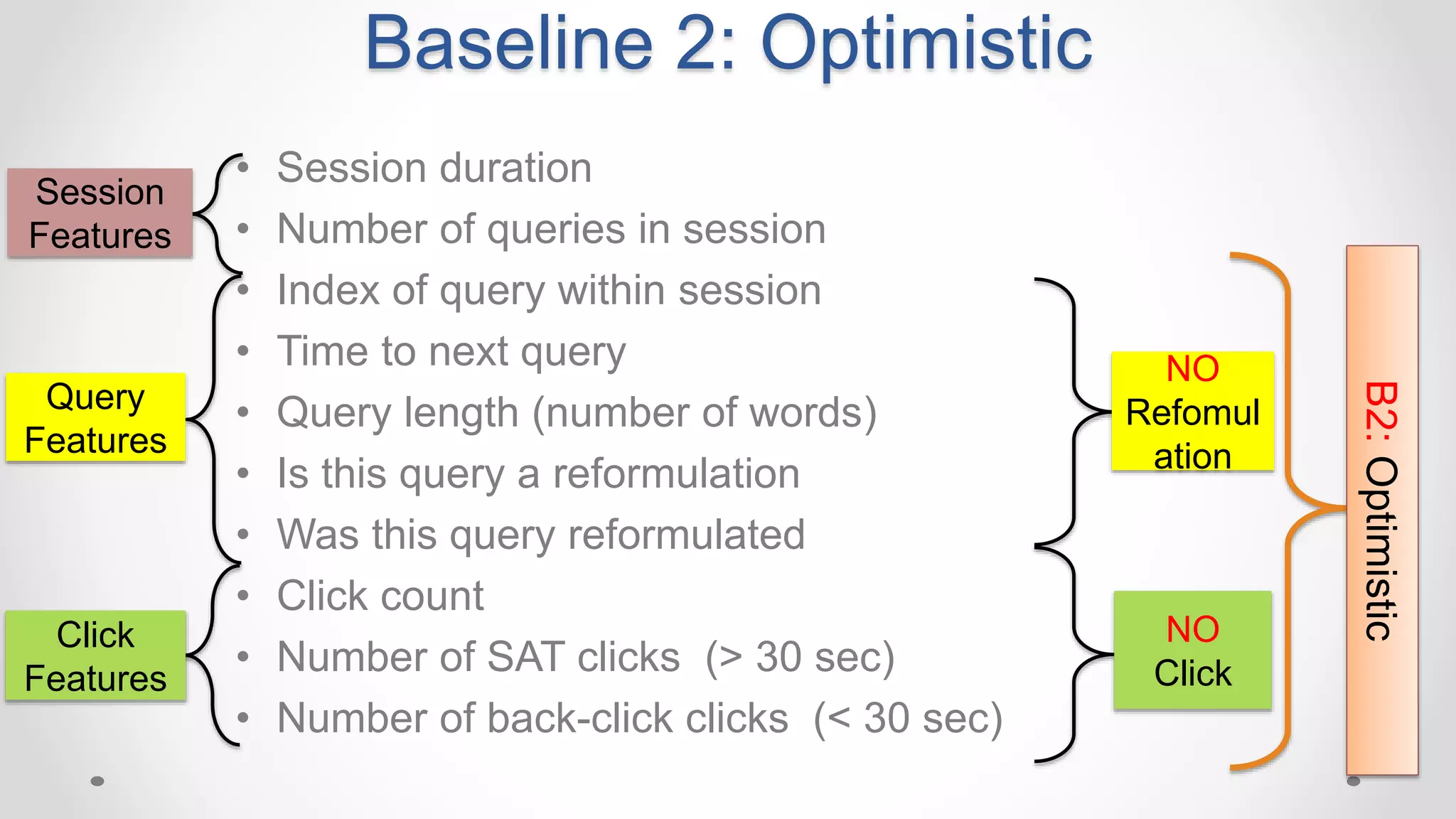
• We need metrics to evaluate user satisfaction
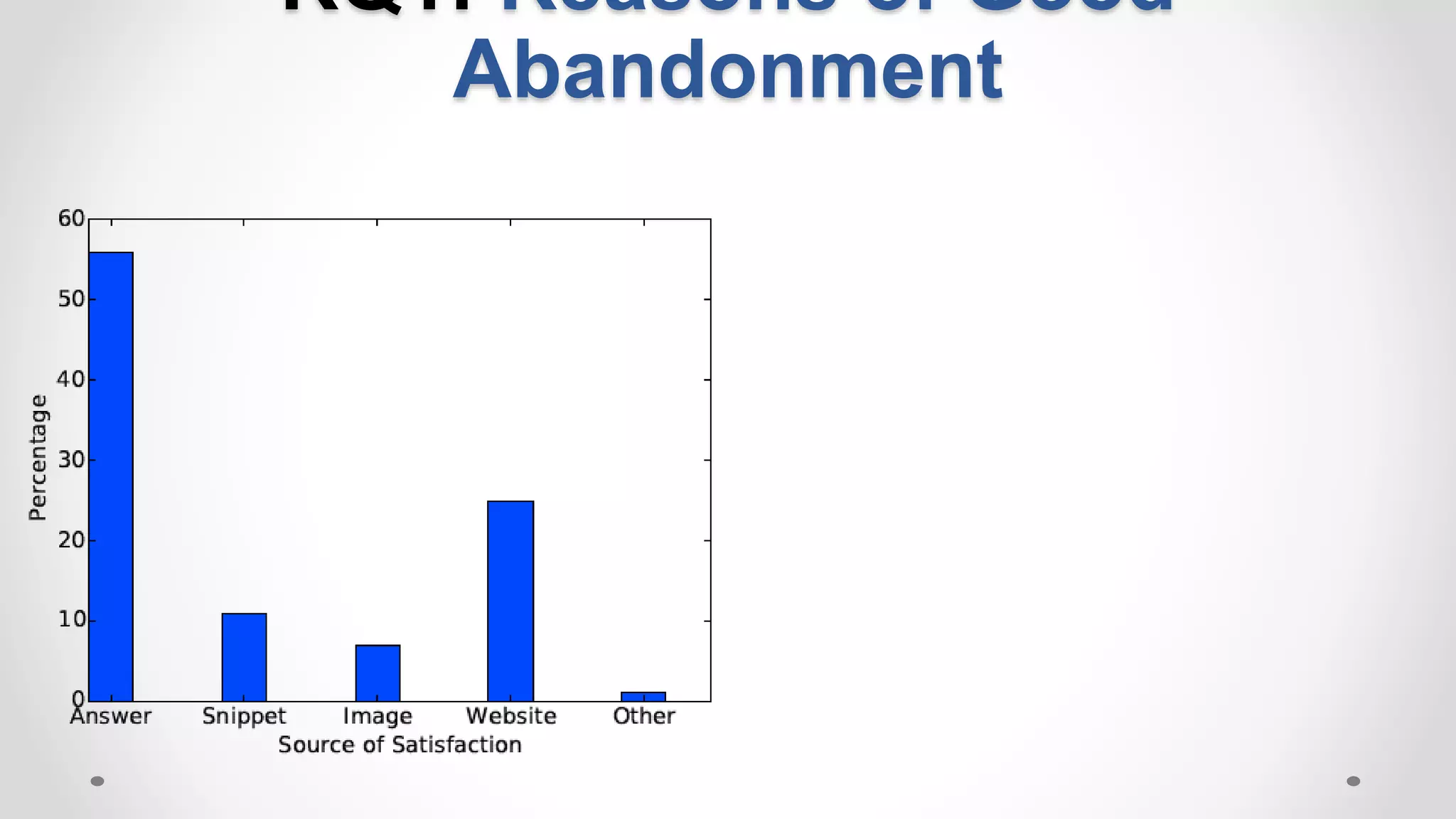
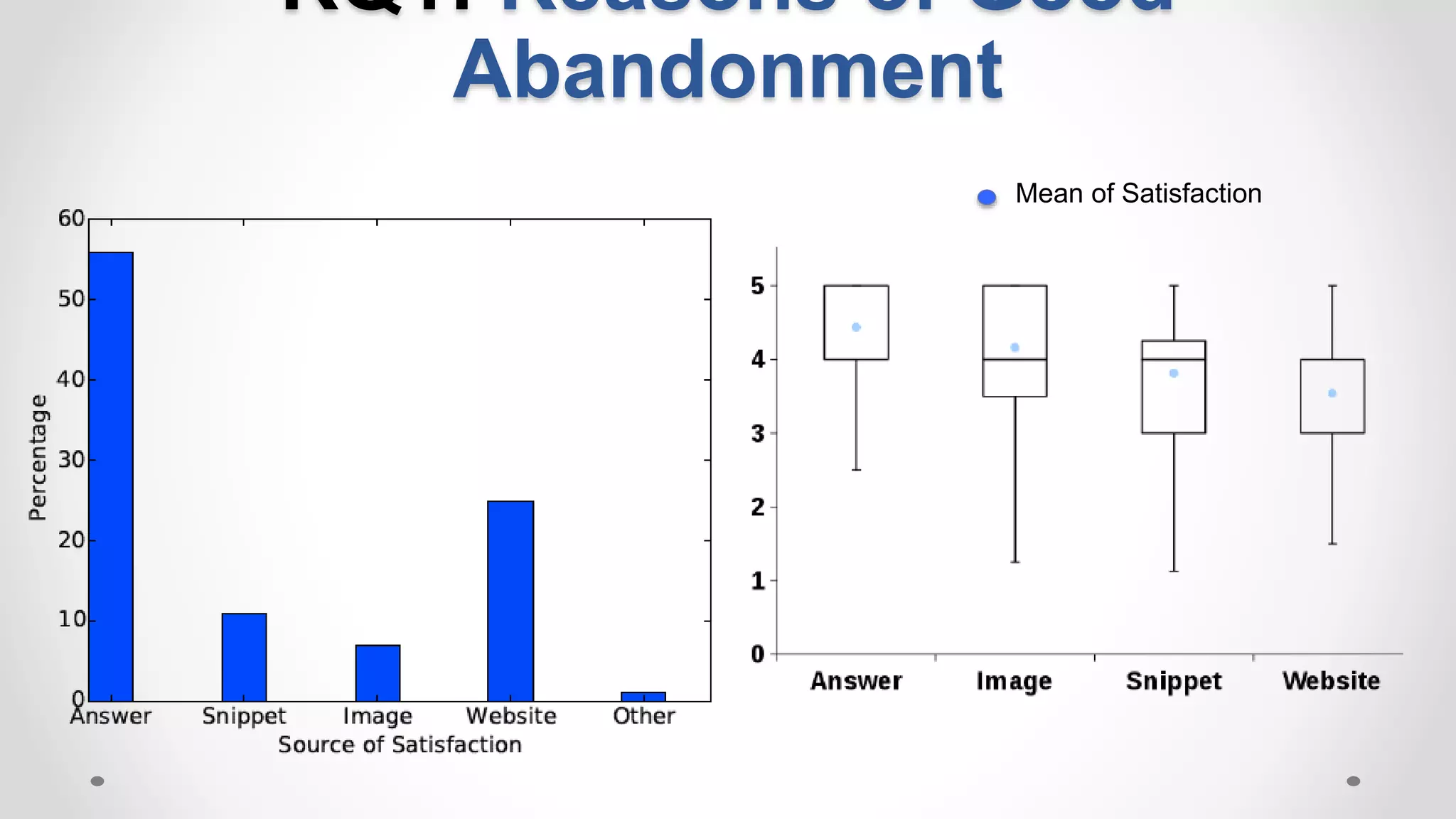
• Good abandonment [Human et. al, 2009]:
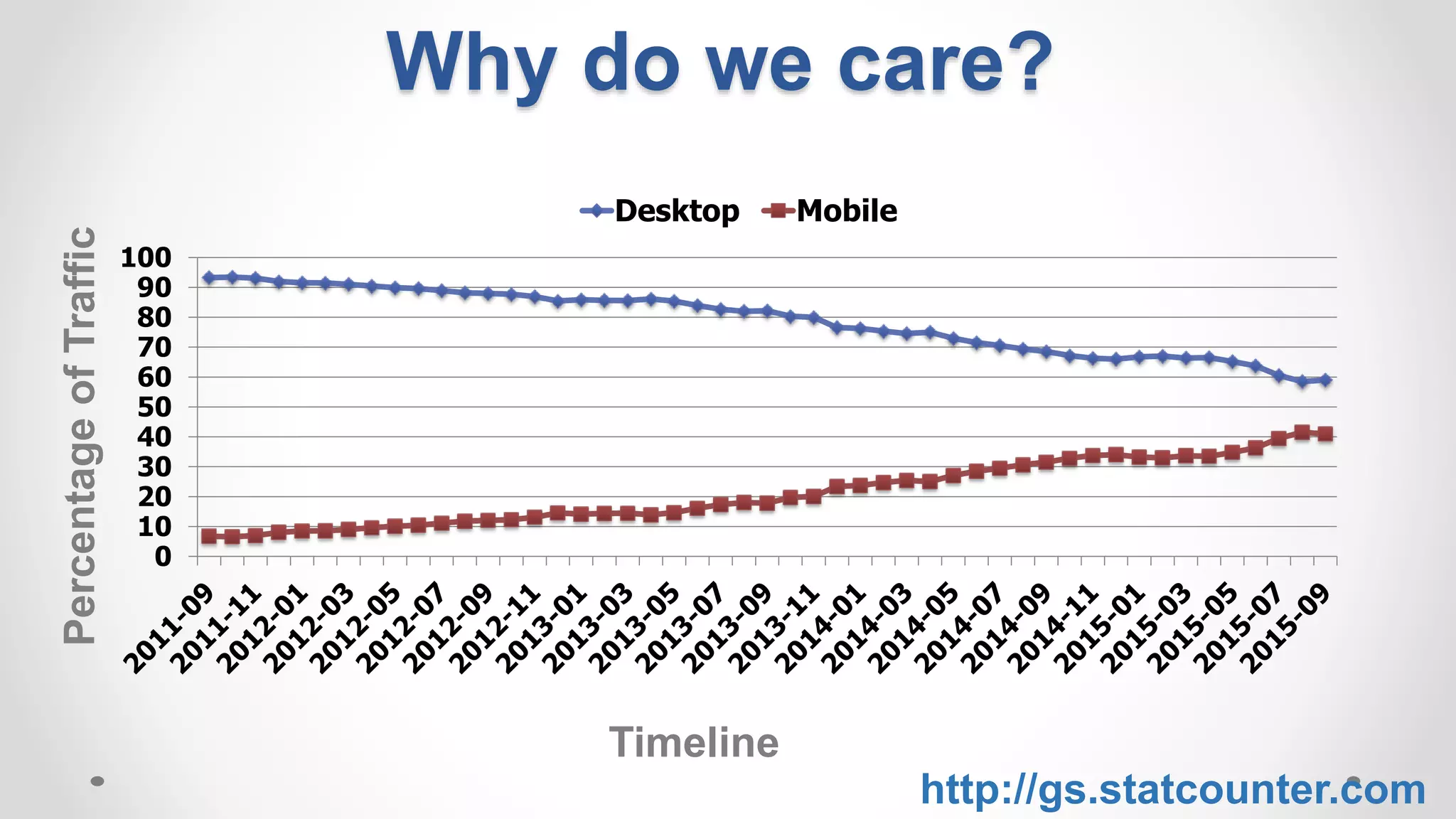
Mobile: 36% of abandoned queries in were likely good
Desktop: 14.3%
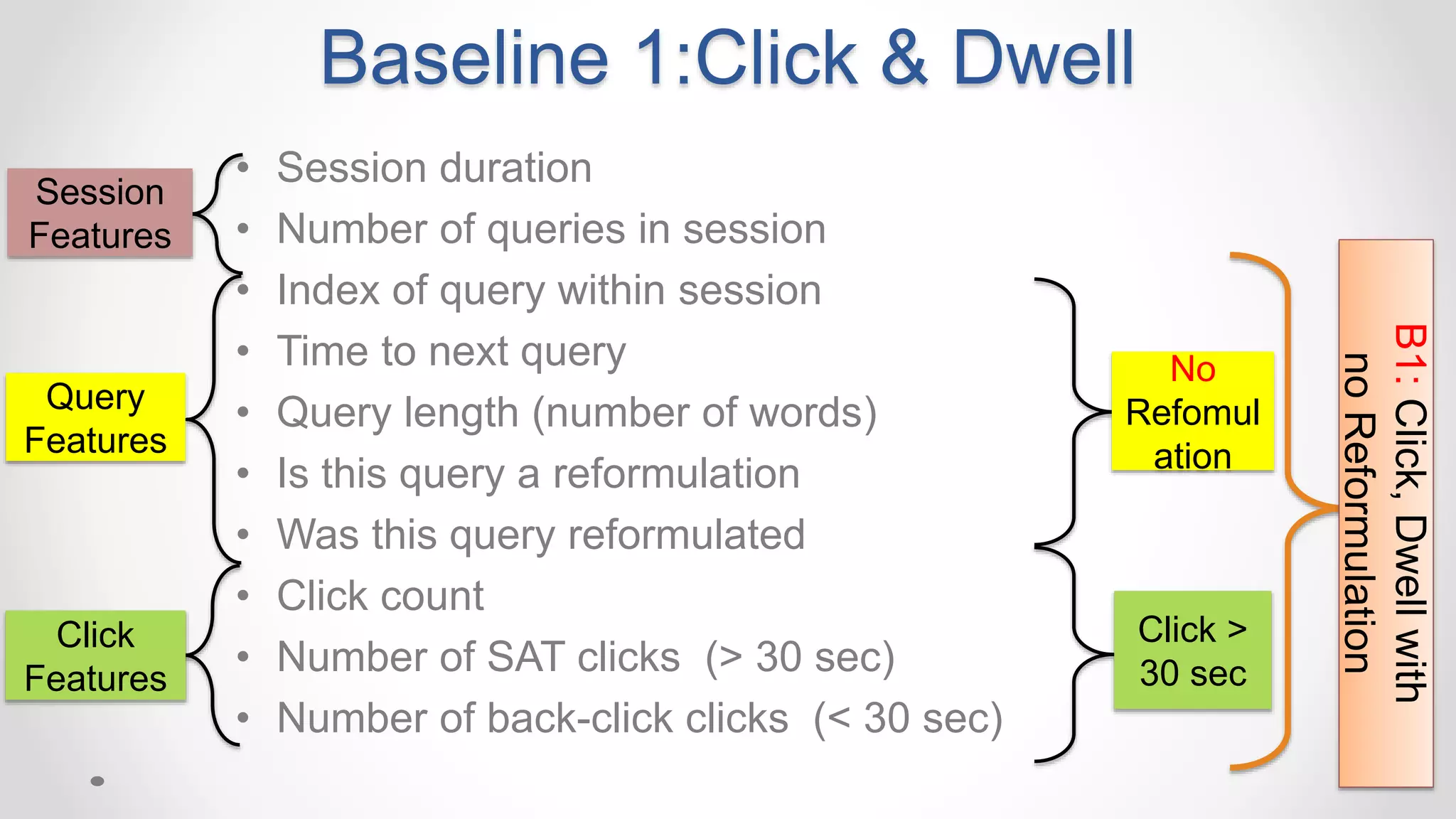
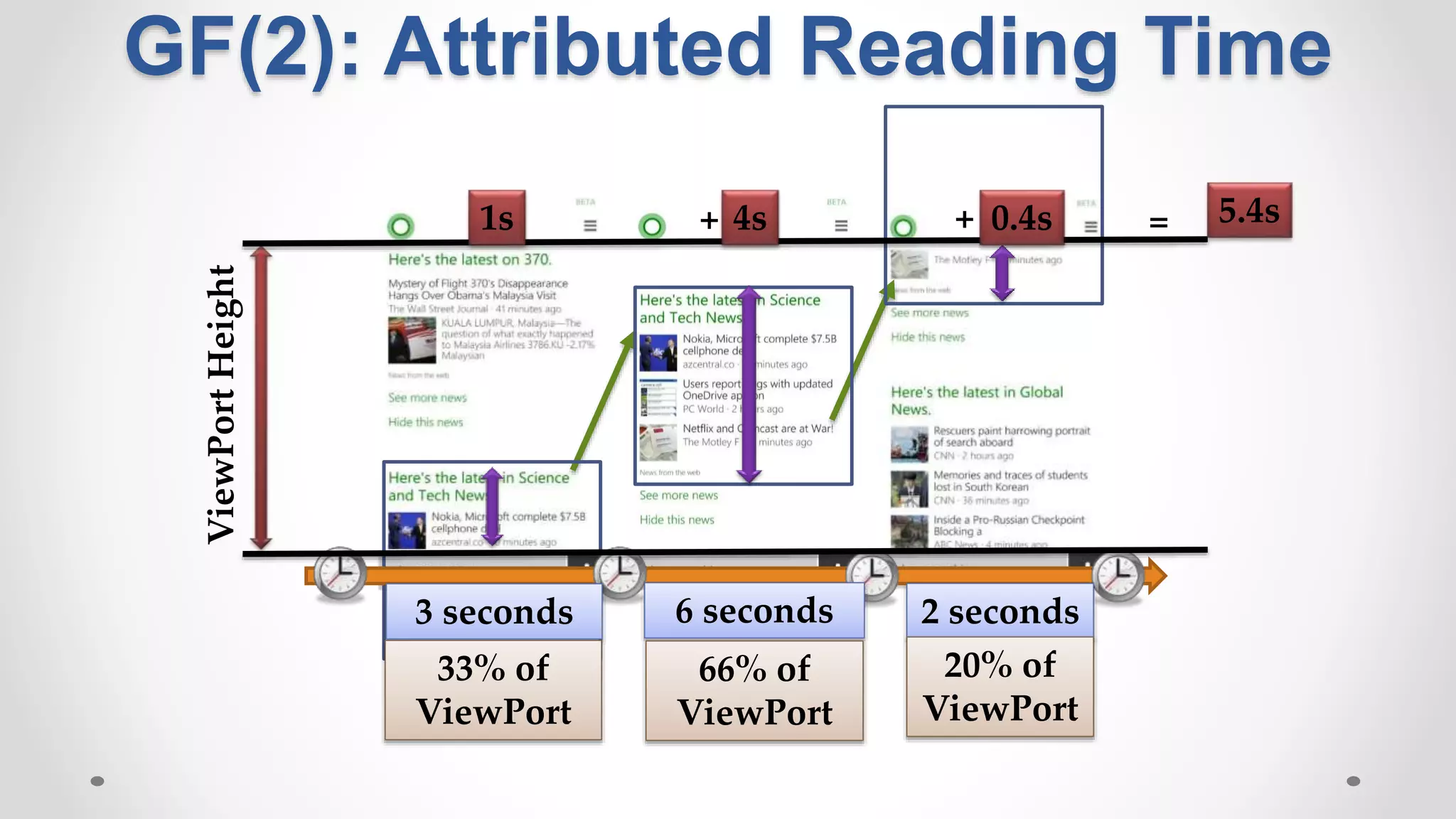
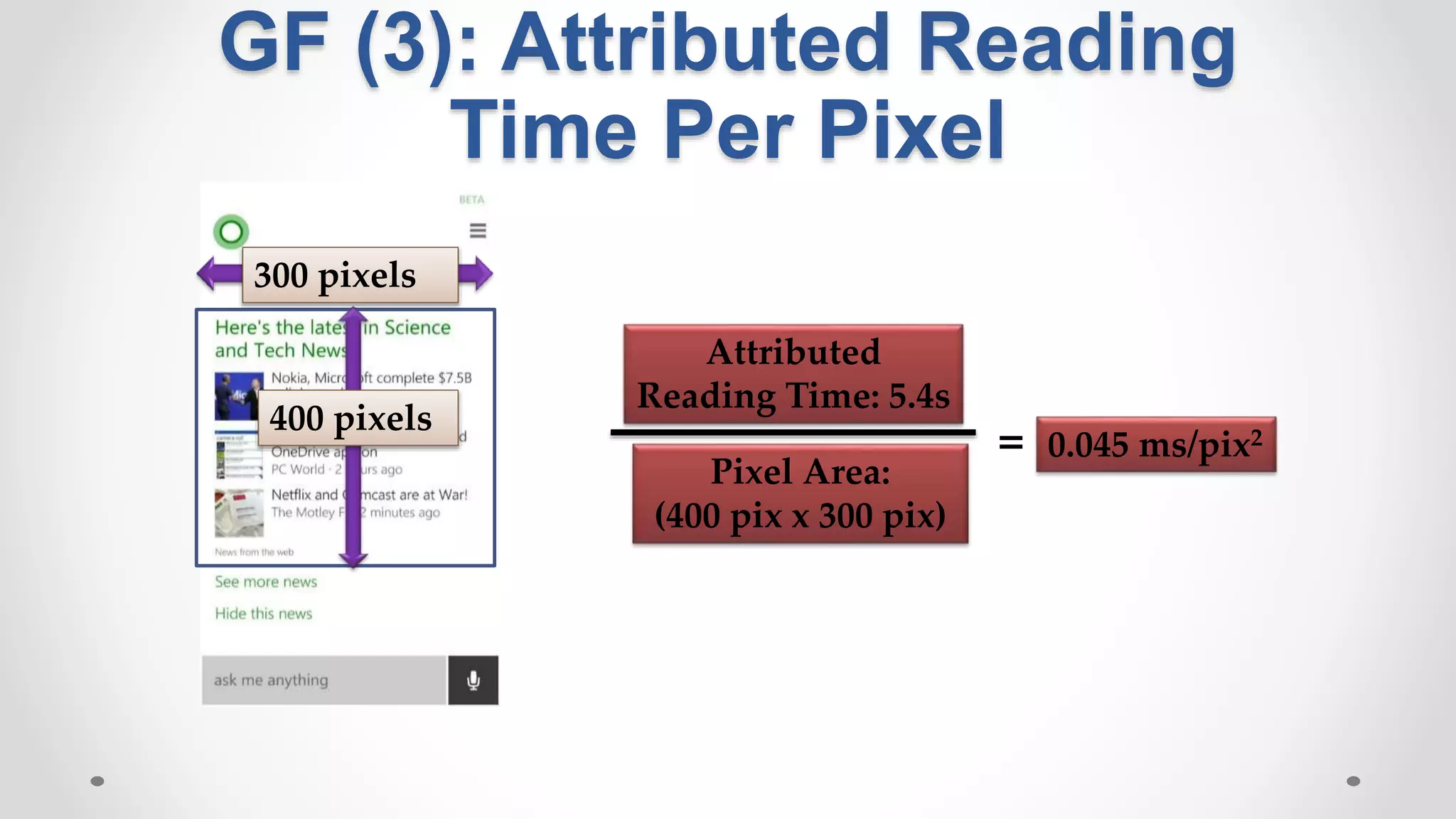
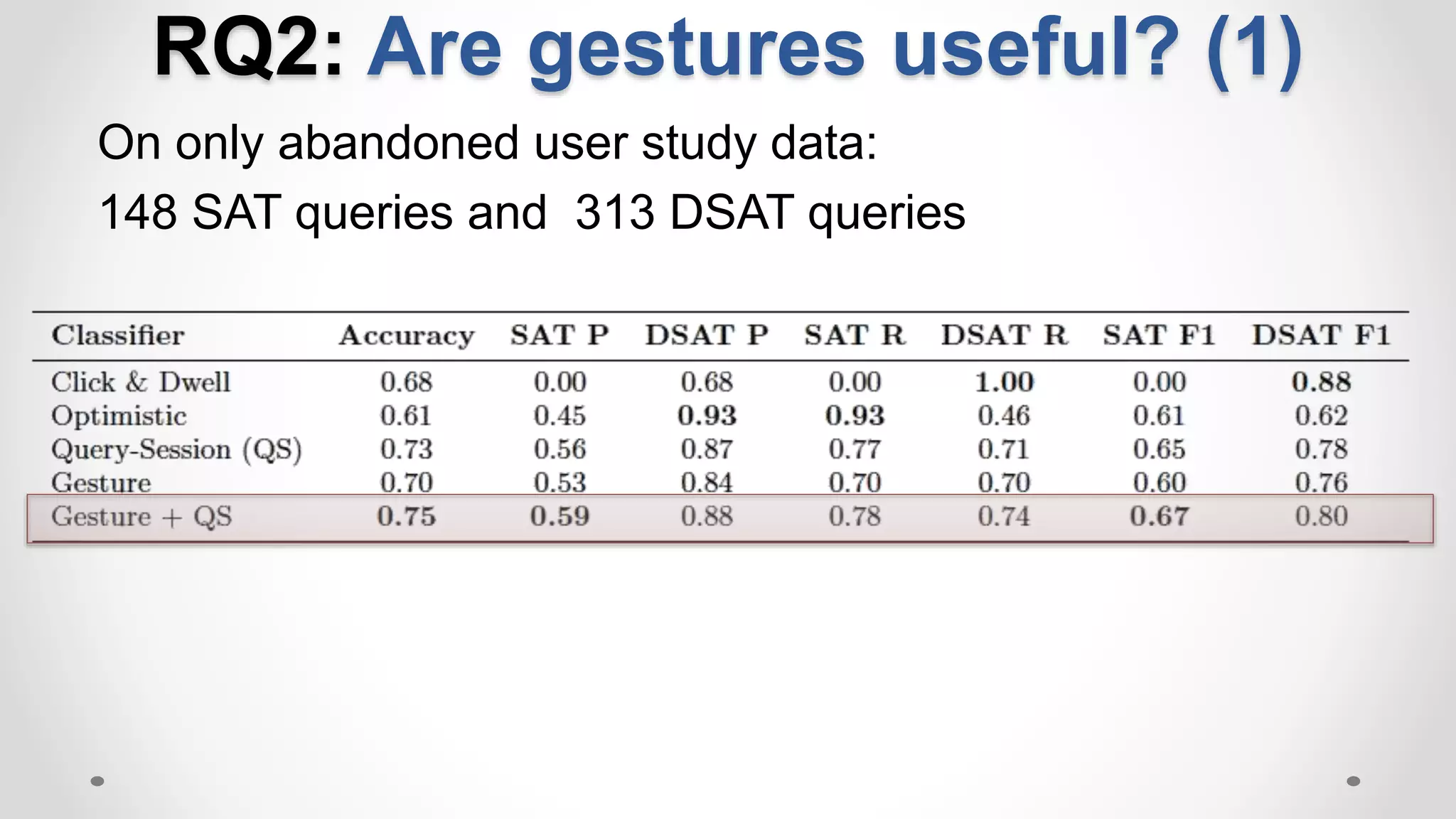
• Traditional methods use implicit signals: clicks and dwell time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siks2016-160610092114/75/Understanding-and-Predicting-User-Satisfaction-with-Intelligent-Assistants-49-2048.jpg)
![Evaluating User Satisfaction
• We need metrics to evaluate user satisfaction
• Good abandonment [Human et. al, 2009]:
Mobile: 36% of abandoned queries in were likely good
Desktop: 14.3%
• Traditional methods use implicit signals: clicks and dwell time
Don’t work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/siks2016-160610092114/75/Understanding-and-Predicting-User-Satisfaction-with-Intelligent-Assistants-50-2048.jpg)