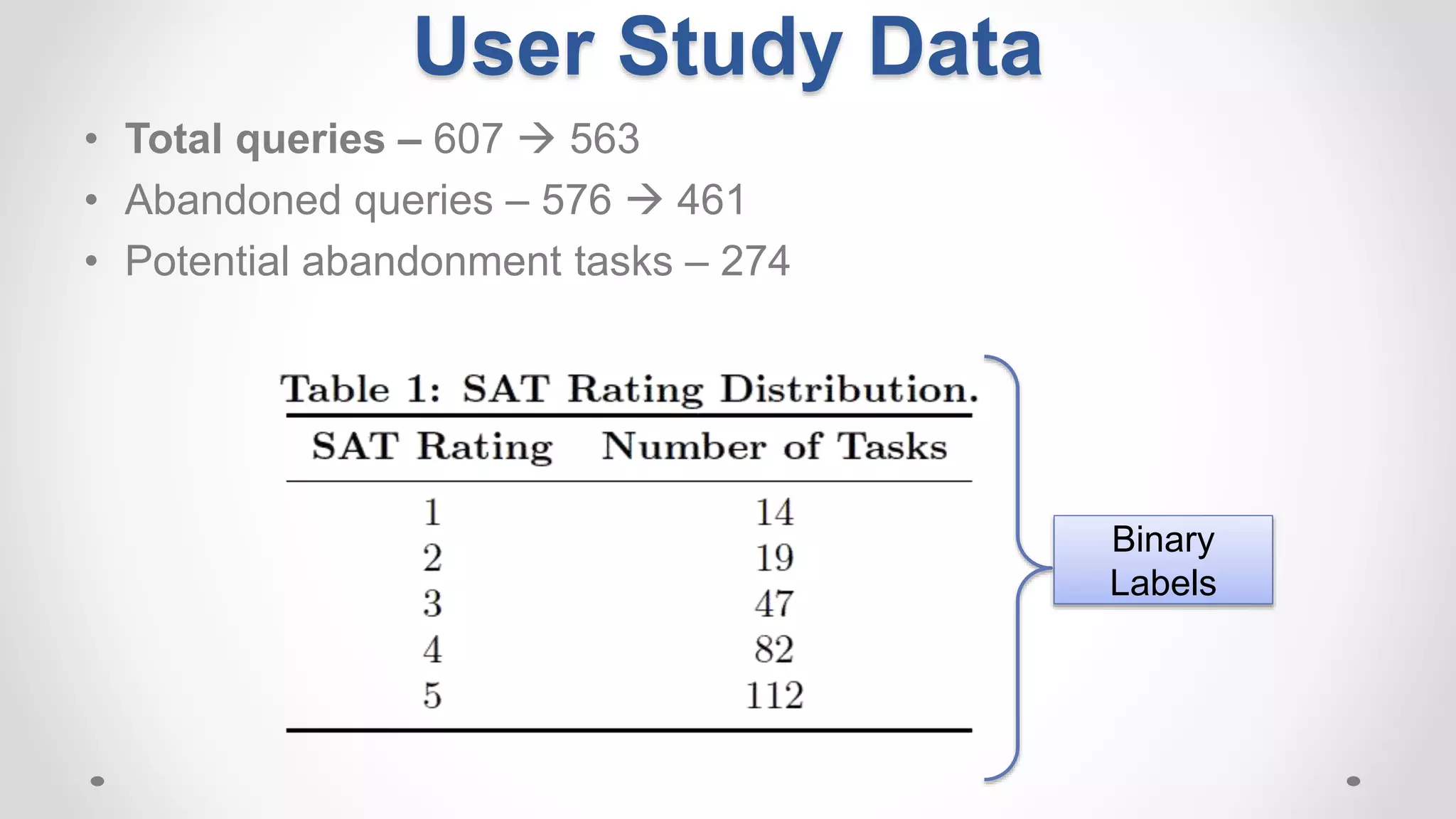
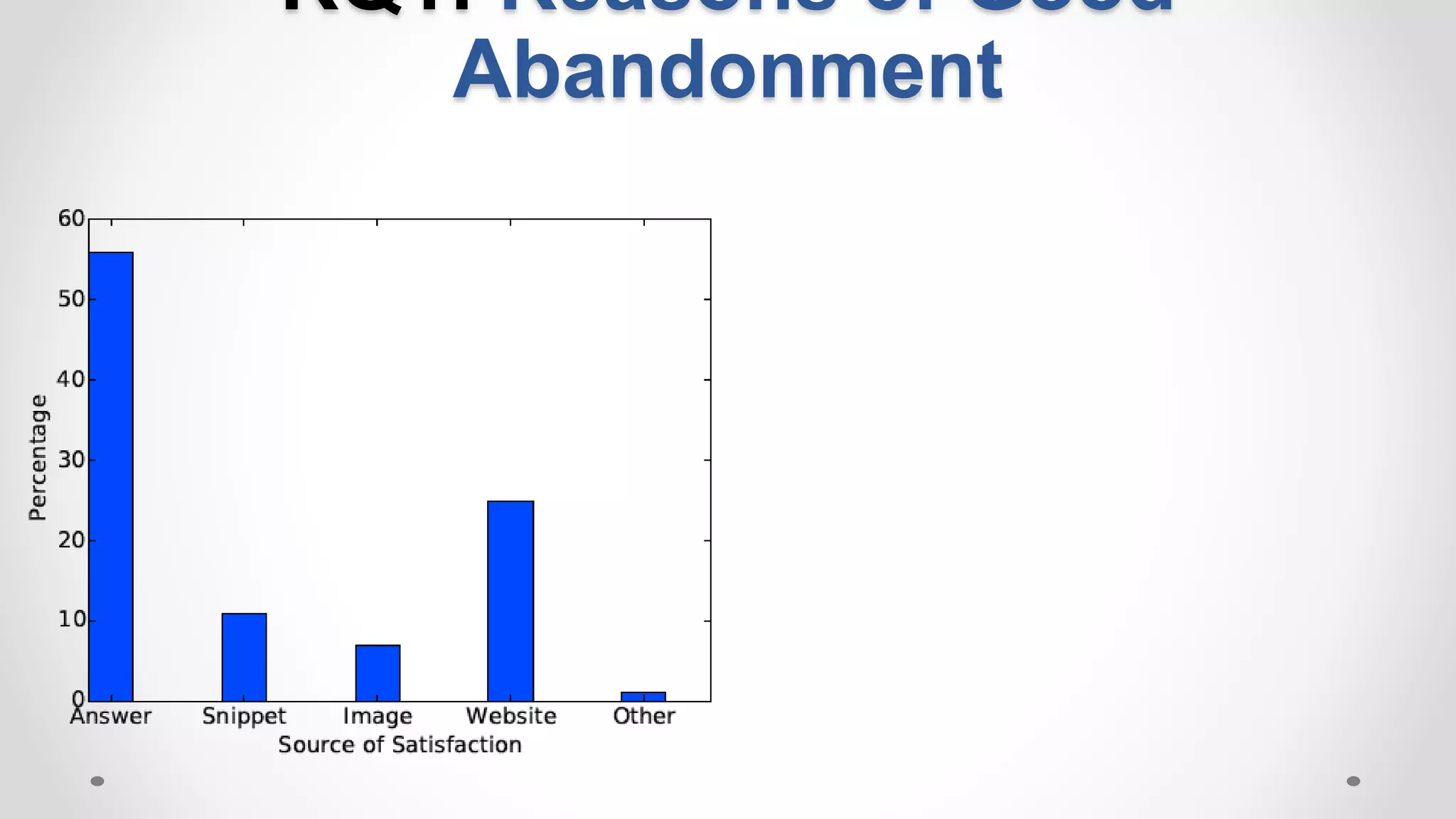
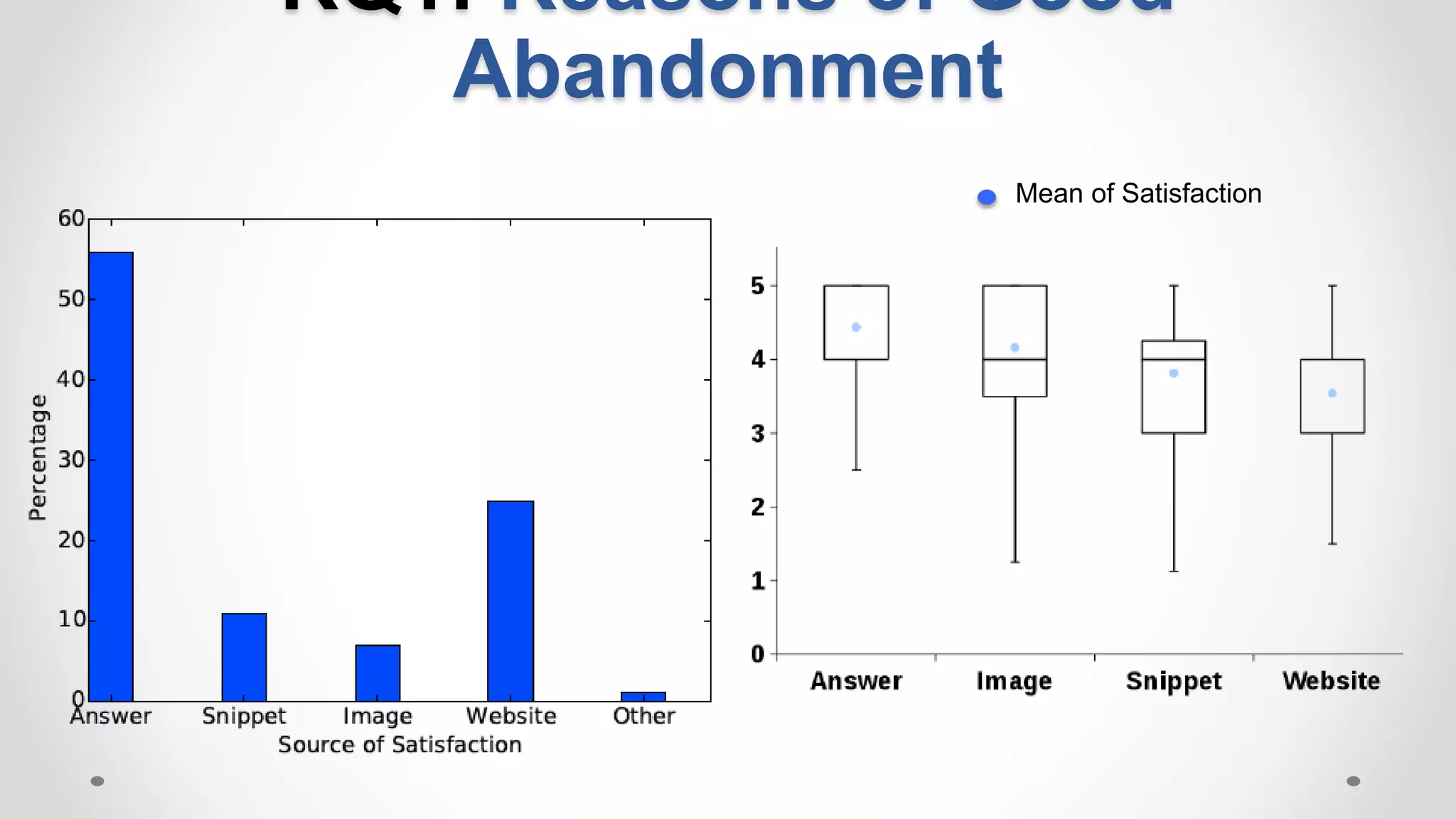
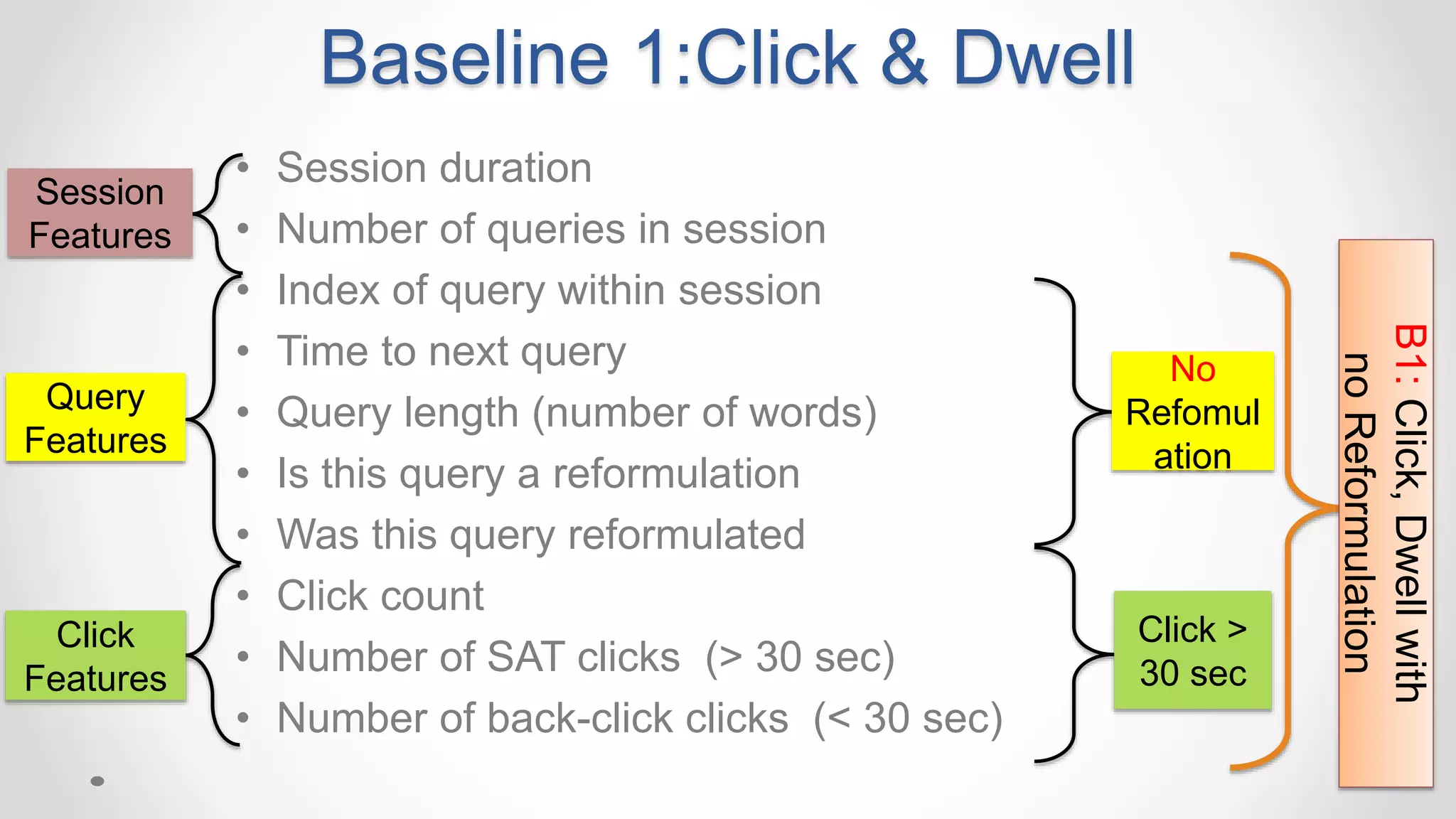
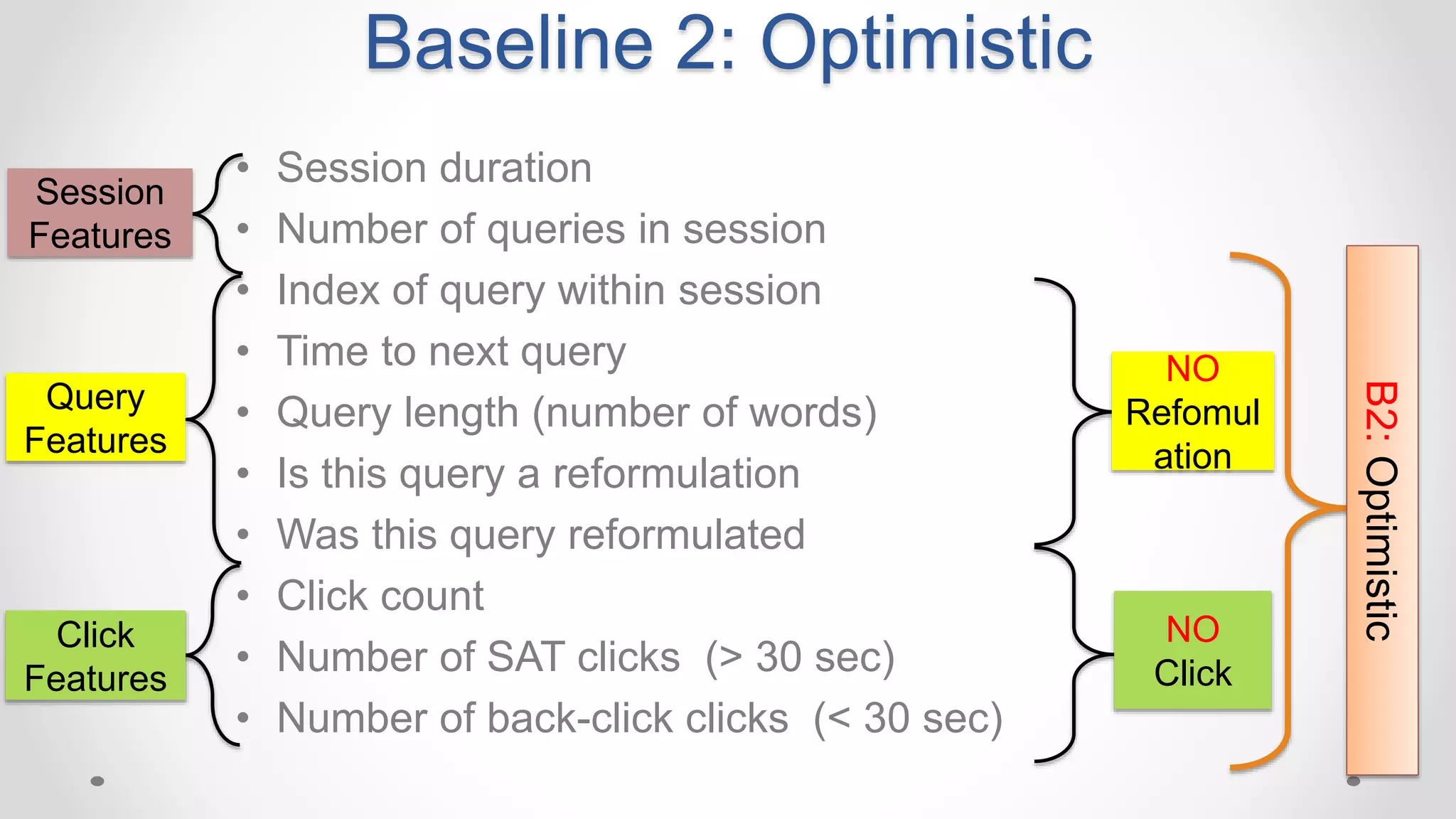
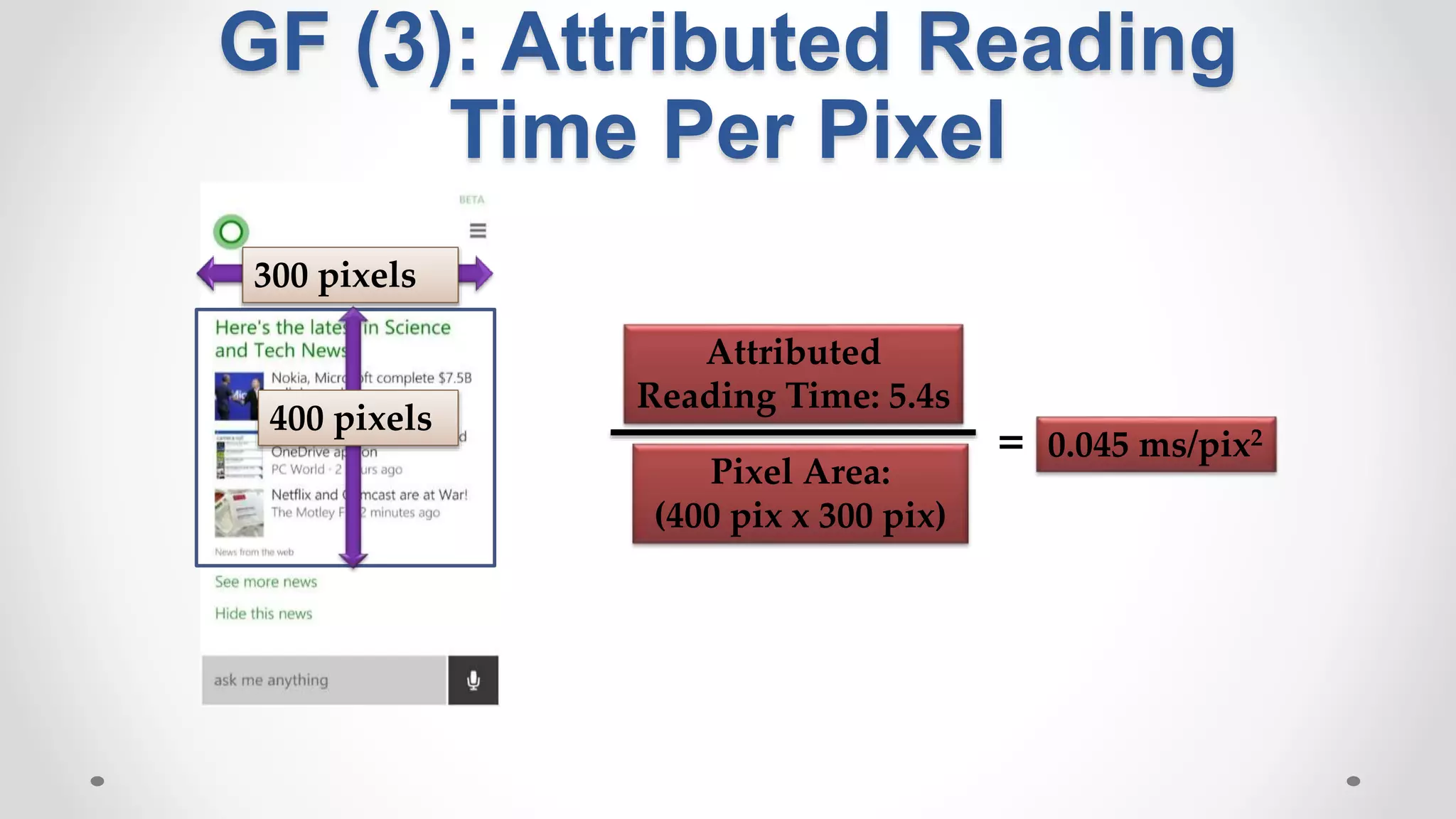
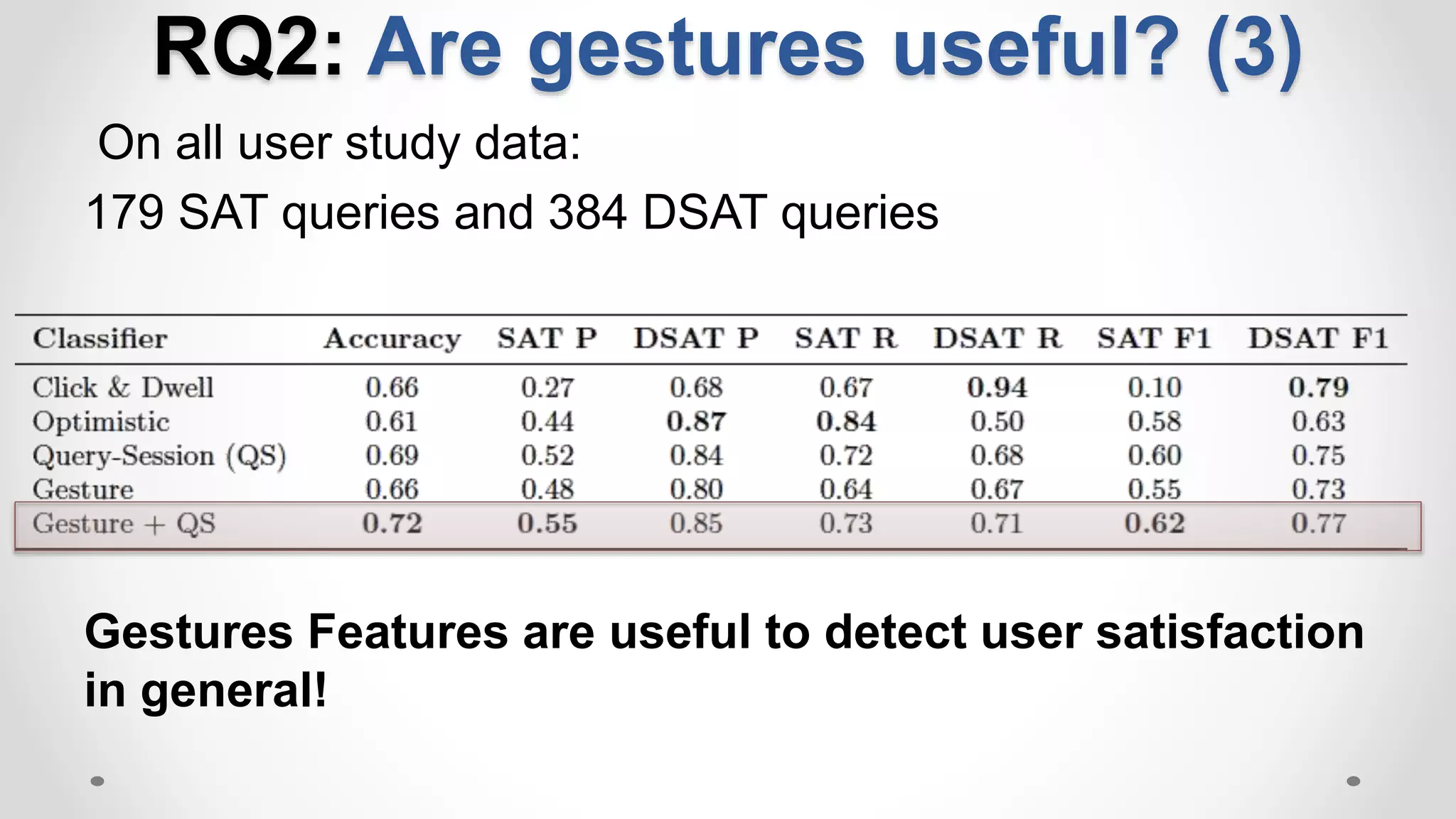
This document discusses the increasing popularity of mobile search and the concept of 'good abandonment', where users abandon queries that may still provide satisfactory results. It presents research questions to explore which elements of search engine results pages contribute to good abandonment, and whether user gestures can signal satisfaction. The findings indicate that certain SERP elements, like answers and images, are sources of good abandonment, and user gestures can indeed provide useful signals for detecting satisfaction.

![Mobile Search
• More and more popular: 2008 31% 2013 63%
• Mobile Search differs from traditional search [Human et. al, 2009]
• On Mobiles users are satisfied by the SERP [Li et. al, 2009]
• Mobiles screen is much smaller
• Mobiles are used on the way](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/goodabandomentfinal14april-160414182715/75/Detecting-Good-Abandonment-in-Mobile-Search-3-2048.jpg)
![Mobile Search
• More and more popular: 2008 31% 2013 63%
• Mobile Search differs from traditional search [Human et. al, 2009]
• On Mobiles users are satisfied by the SERP [Li et. al, 2009]
• Mobiles screen is much smaller
• Mobiles are used on the way
Search Engines need to adapt
And to Evaluate!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/goodabandomentfinal14april-160414182715/75/Detecting-Good-Abandonment-in-Mobile-Search-4-2048.jpg)

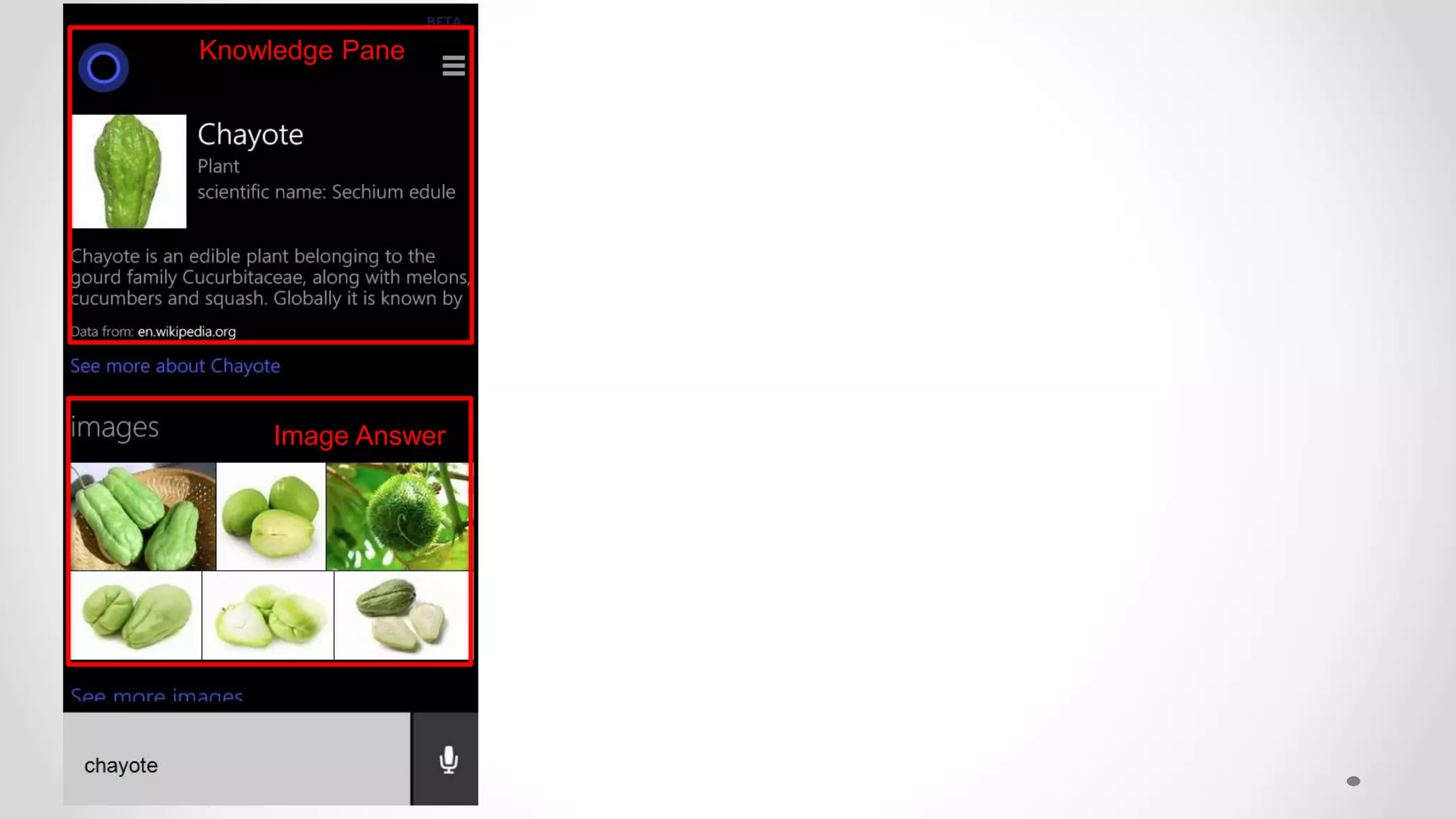
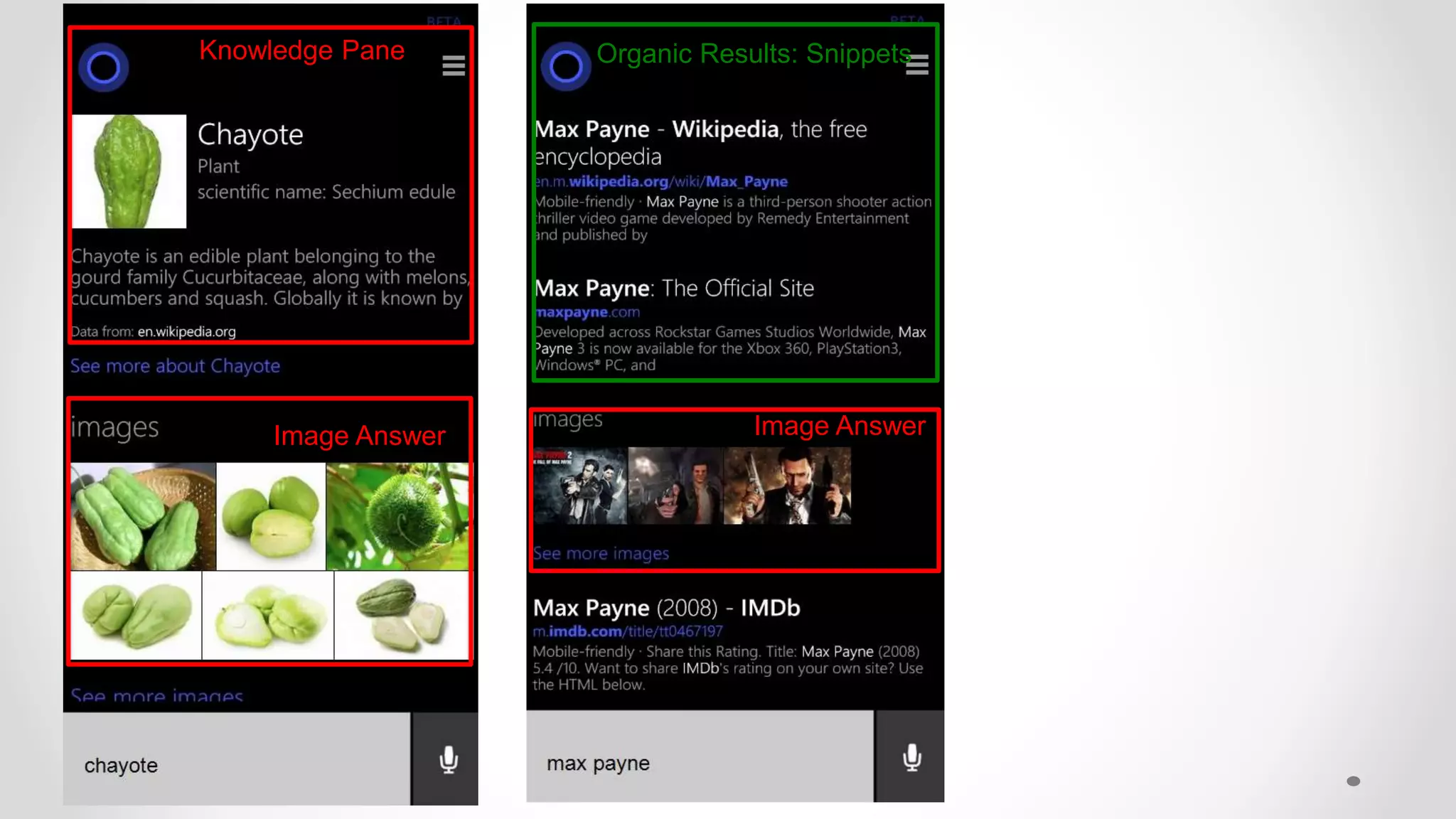
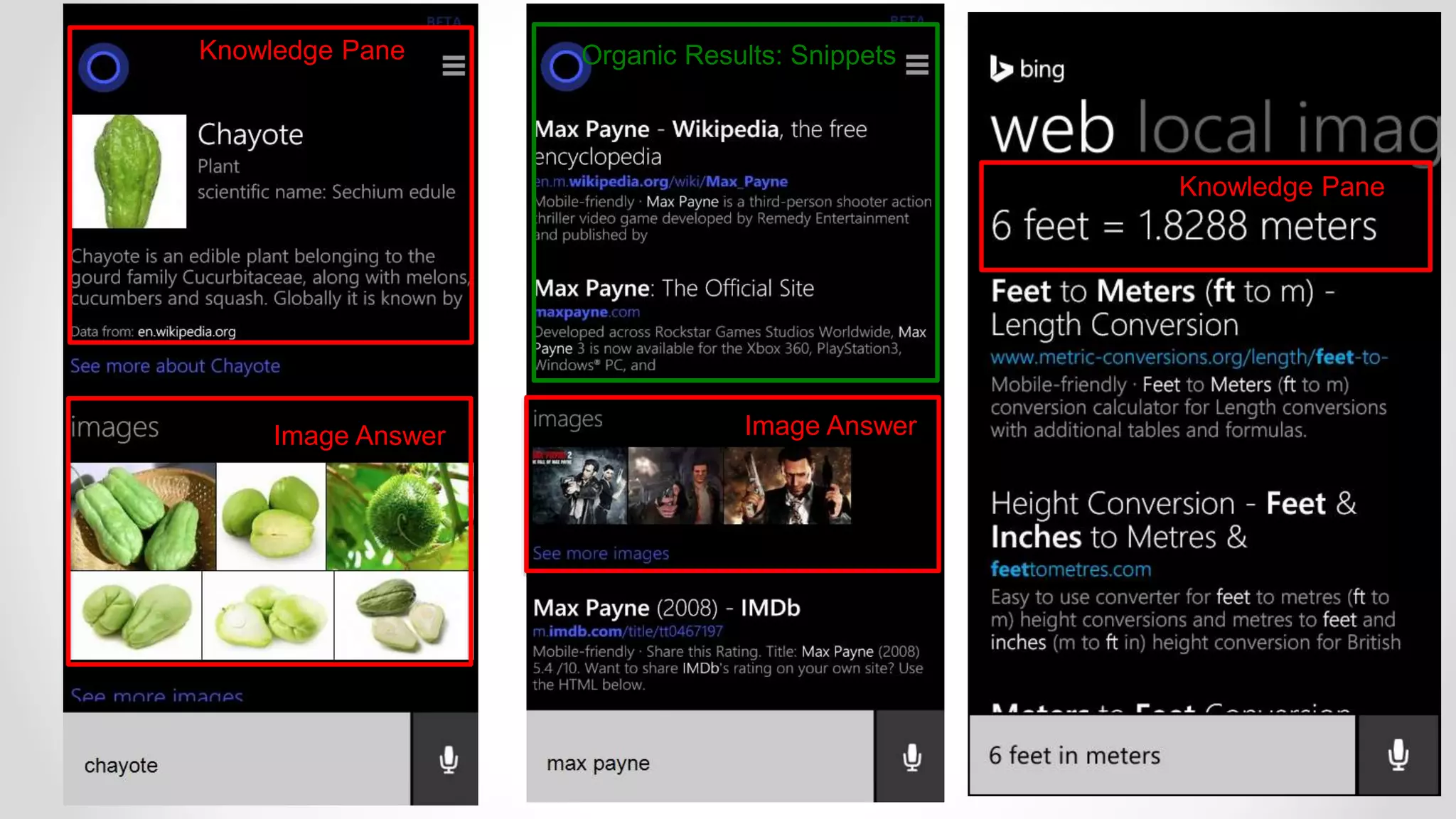
![Evaluating User Satisfaction
• We need metrics to evaluate user satisfaction
• Good abandonment [Human et. al, 2009]:
Mobile: 36% of abandoned queries in were likely good
Desktop: 14.3%
• Traditional methods use implicit signals: clicks and dwell time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/goodabandomentfinal14april-160414182715/75/Detecting-Good-Abandonment-in-Mobile-Search-9-2048.jpg)
![Evaluating User Satisfaction
• We need metrics to evaluate user satisfaction
• Good abandonment [Human et. al, 2009]:
Mobile: 36% of abandoned queries in were likely good
Desktop: 14.3%
• Traditional methods use implicit signals: clicks and dwell time
Don’t work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/goodabandomentfinal14april-160414182715/75/Detecting-Good-Abandonment-in-Mobile-Search-10-2048.jpg)