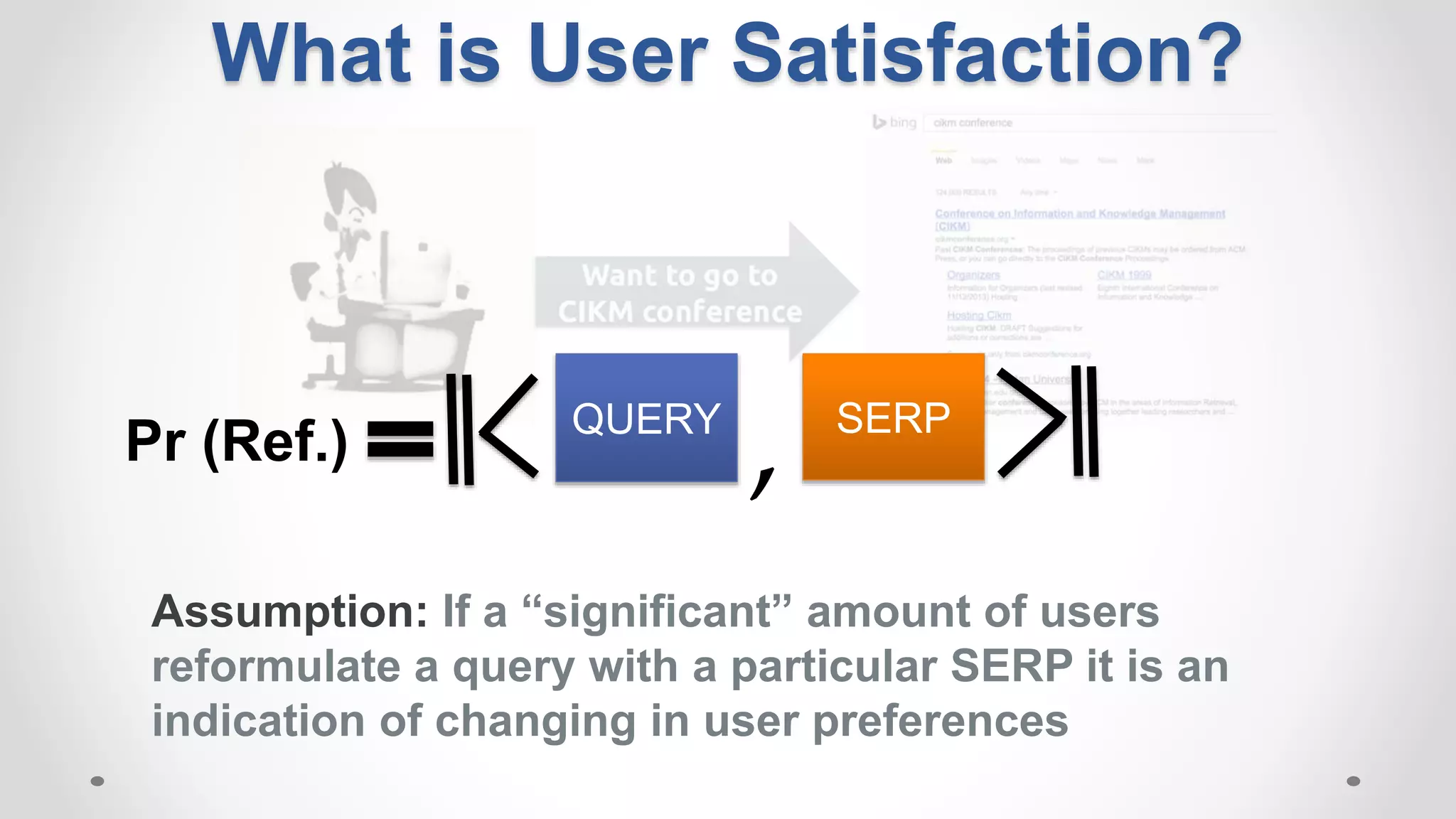
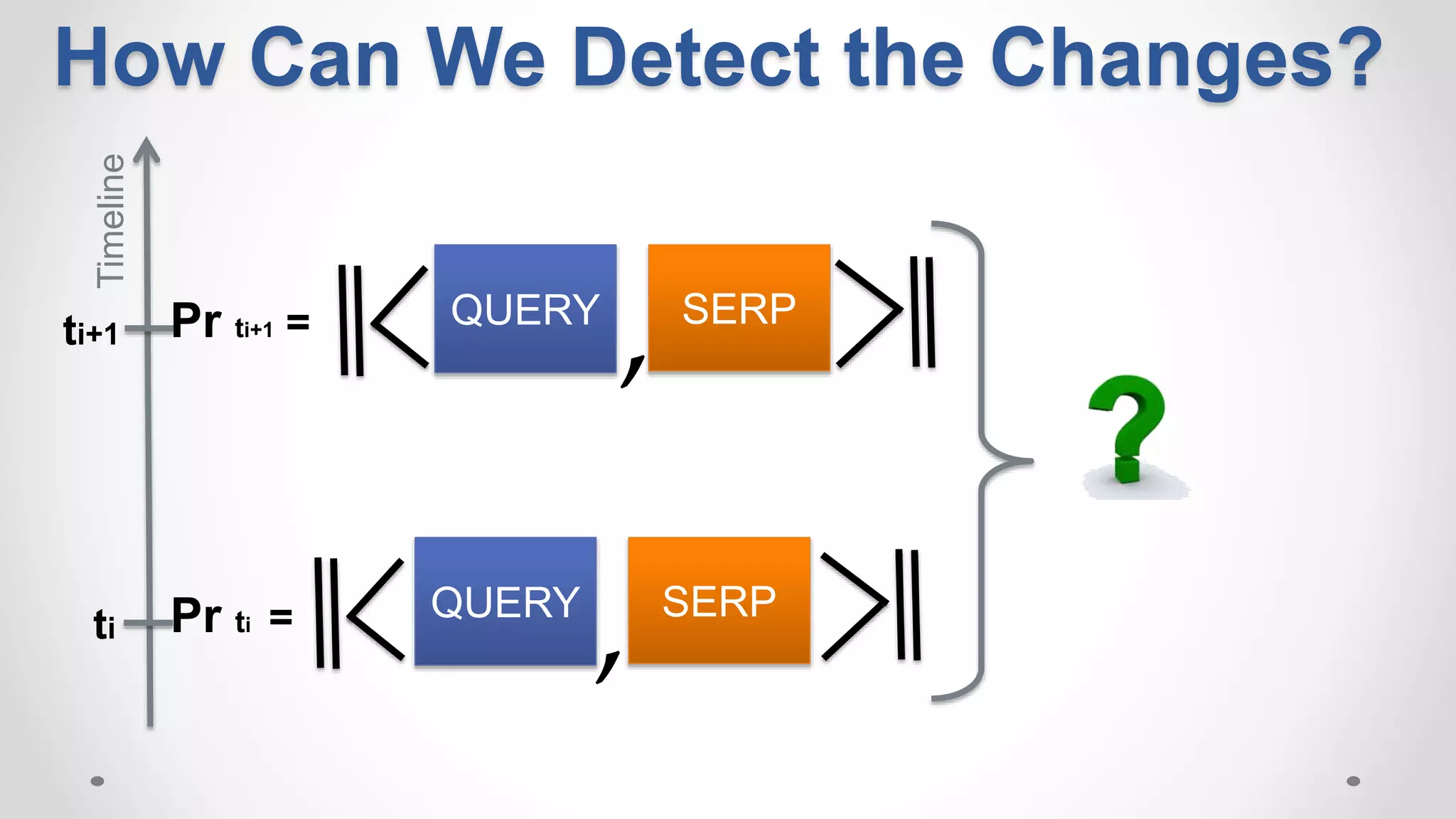
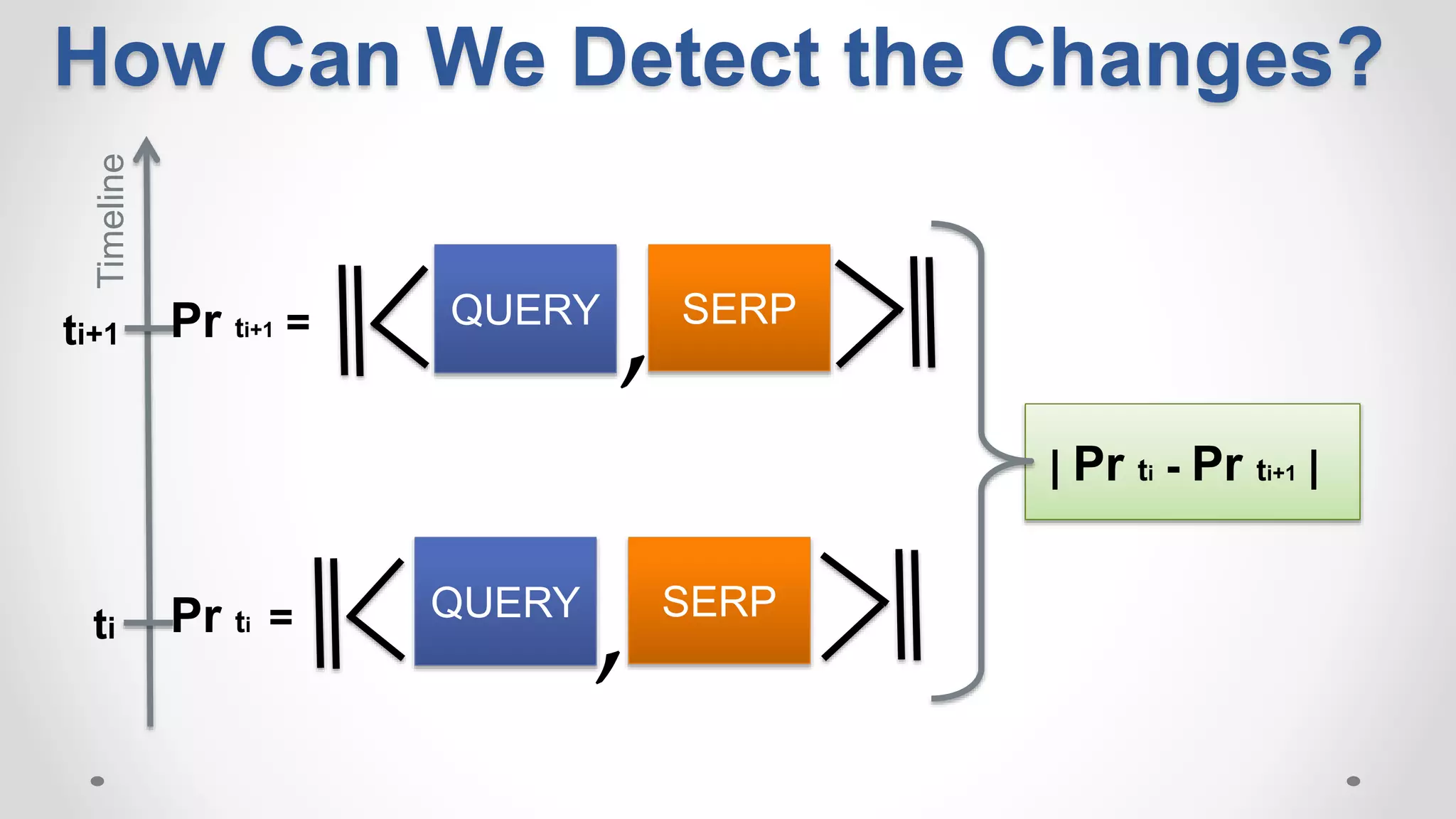
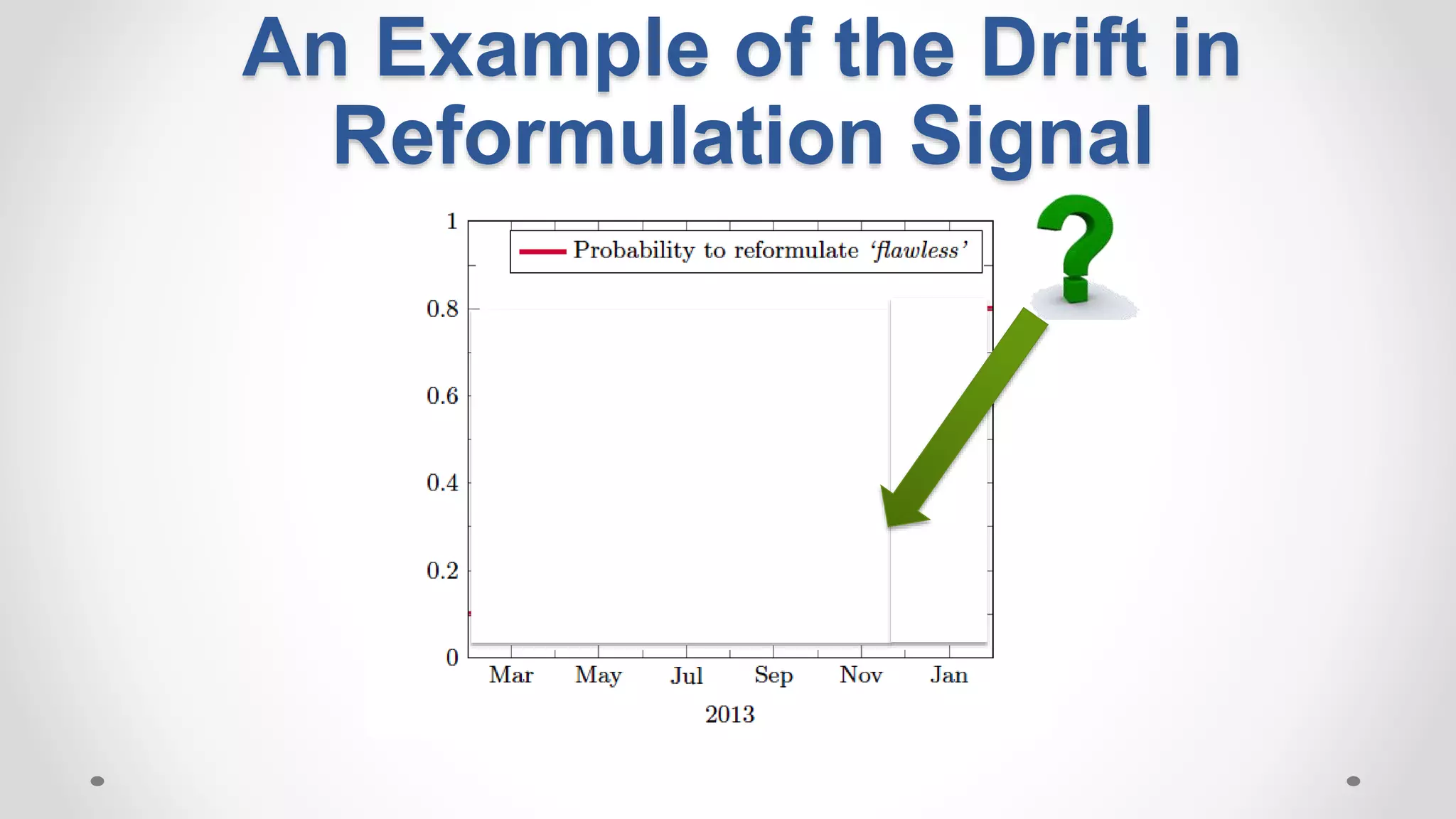
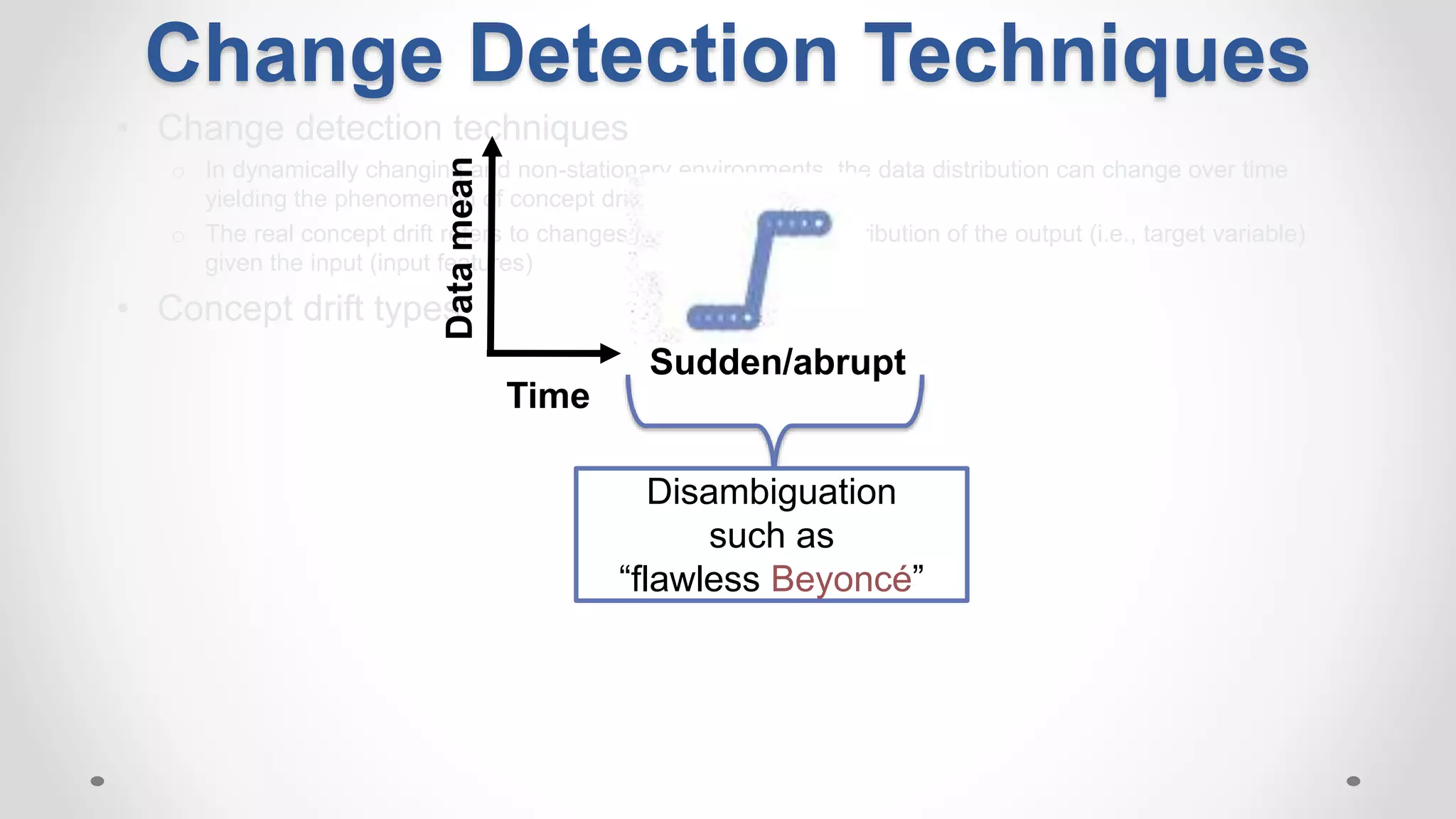
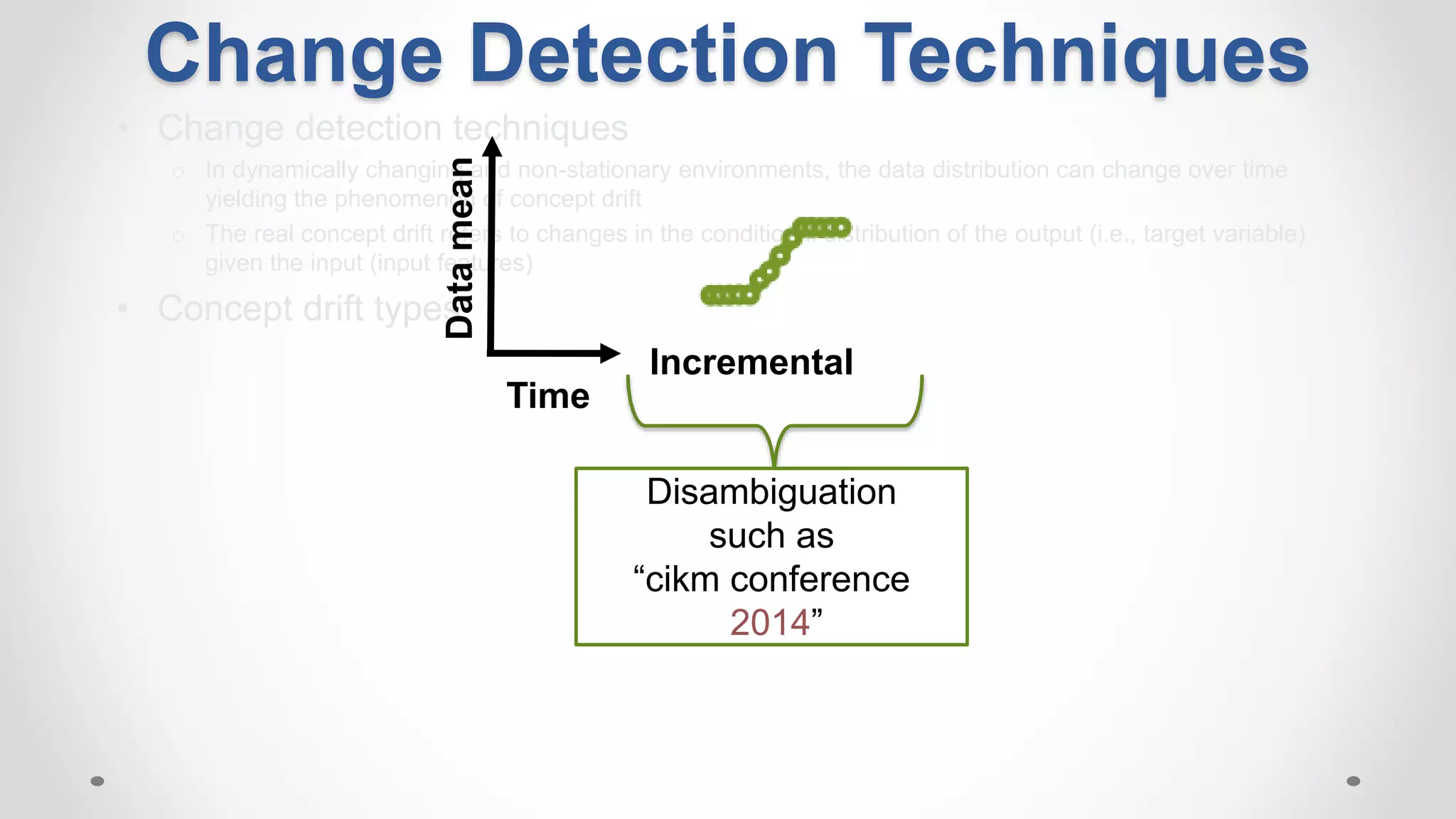
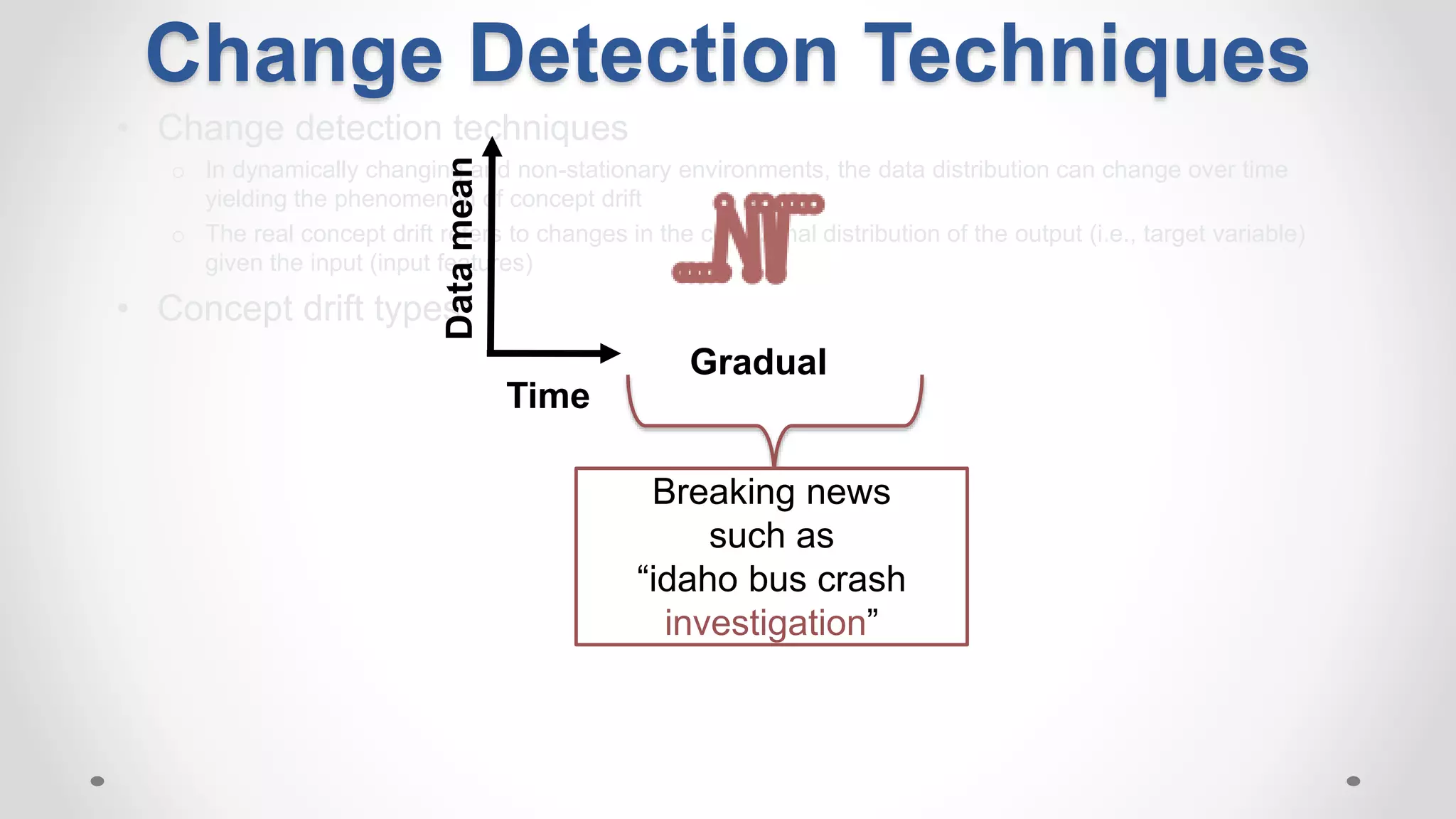
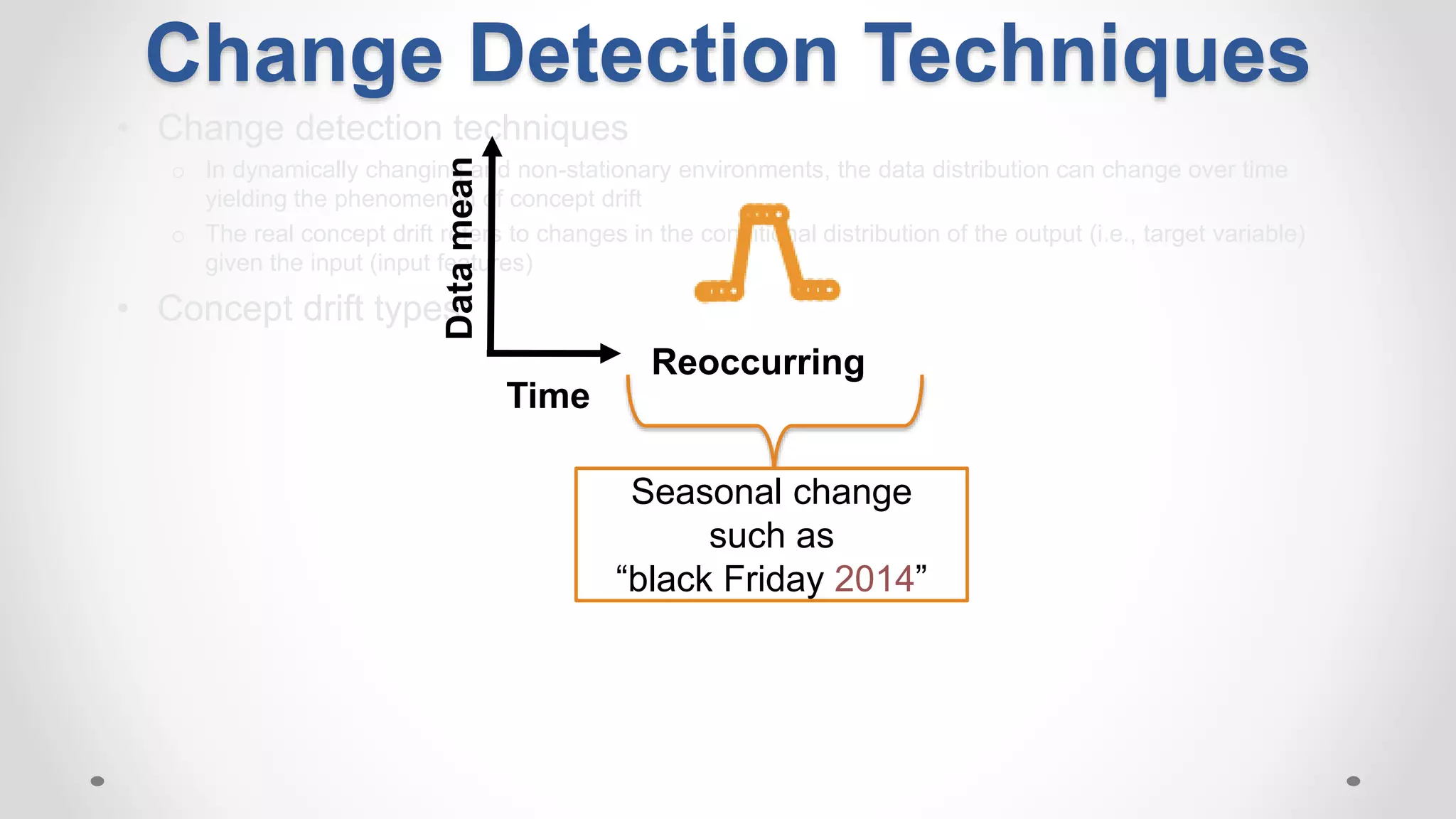
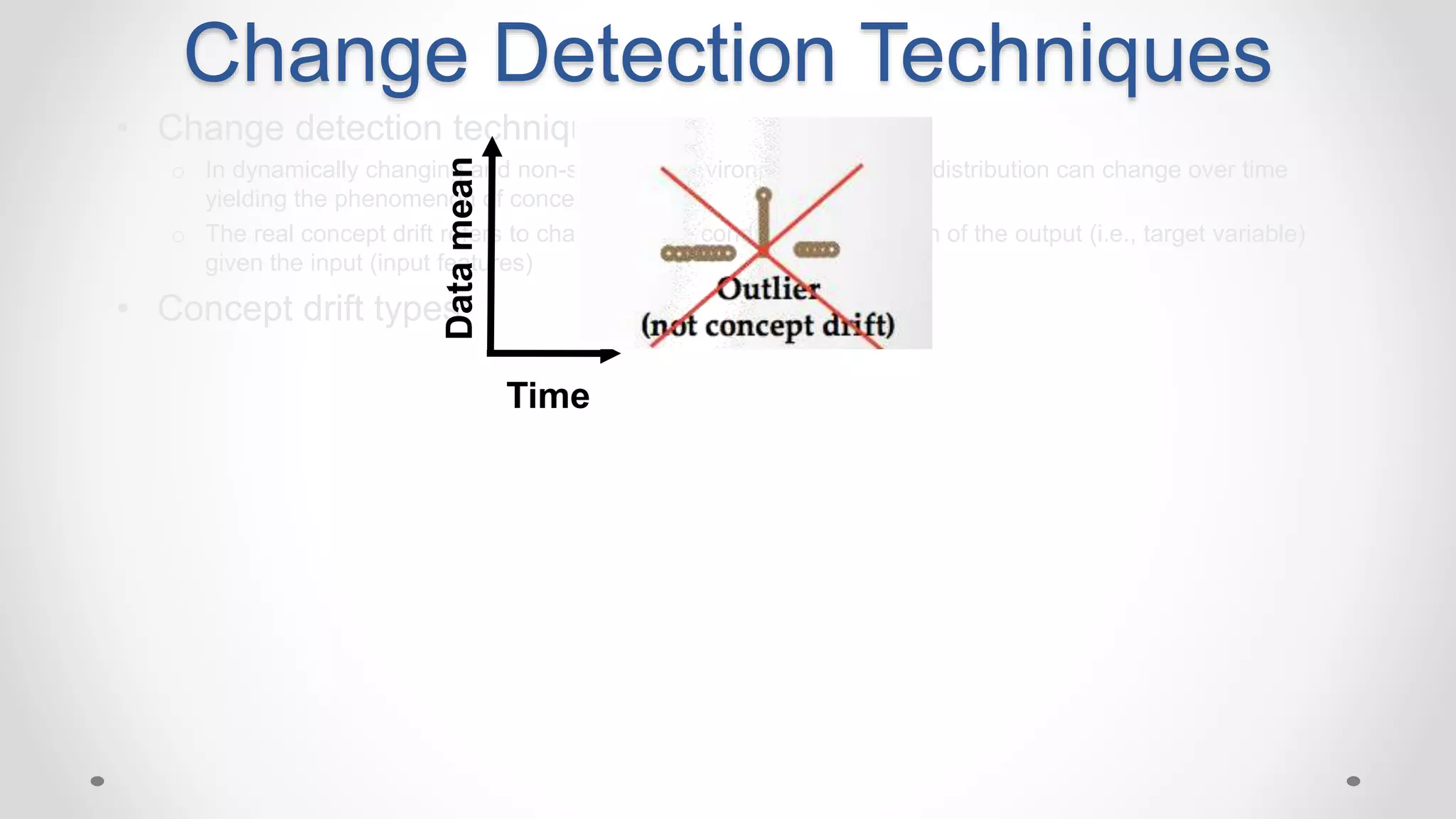
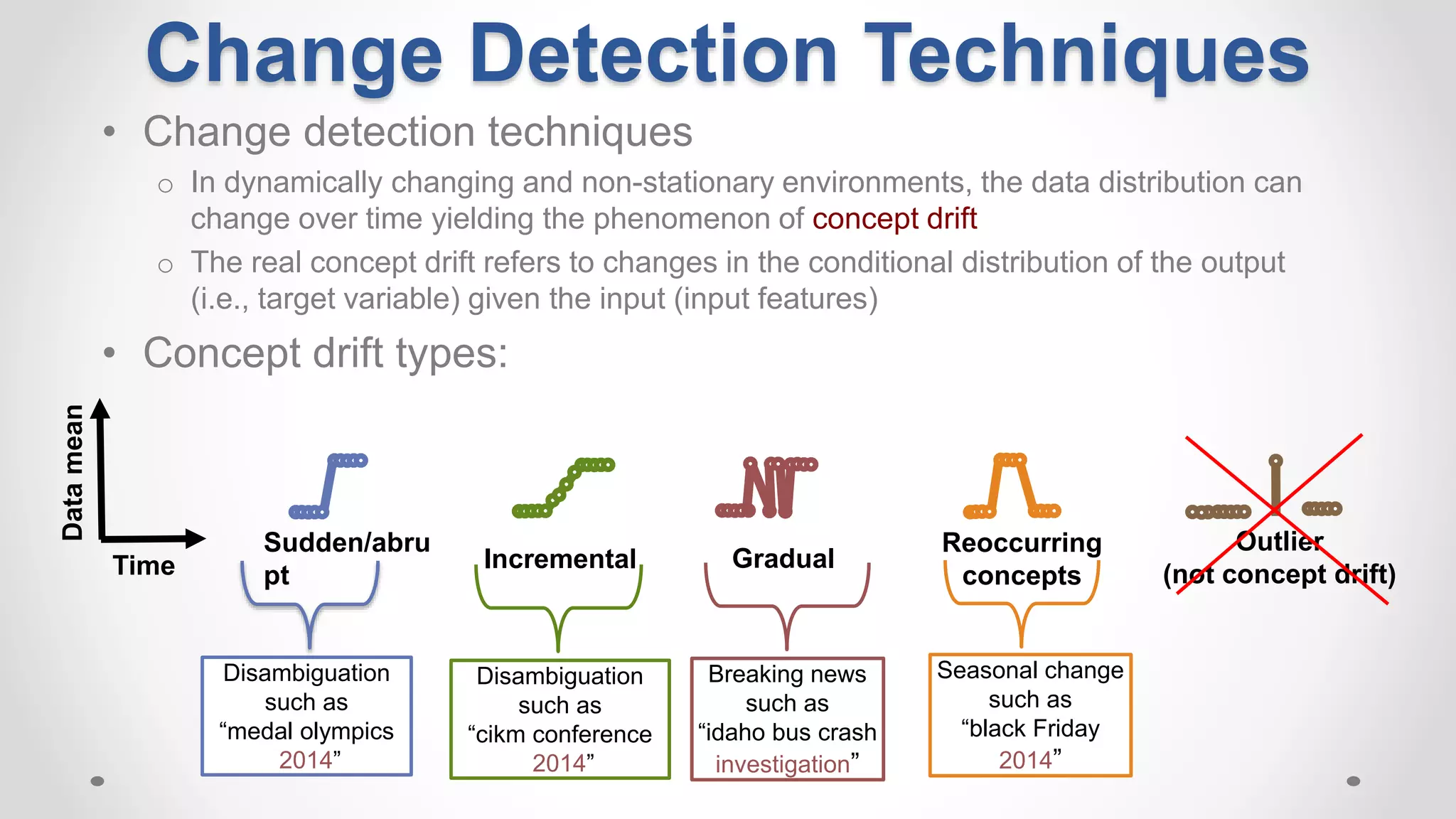
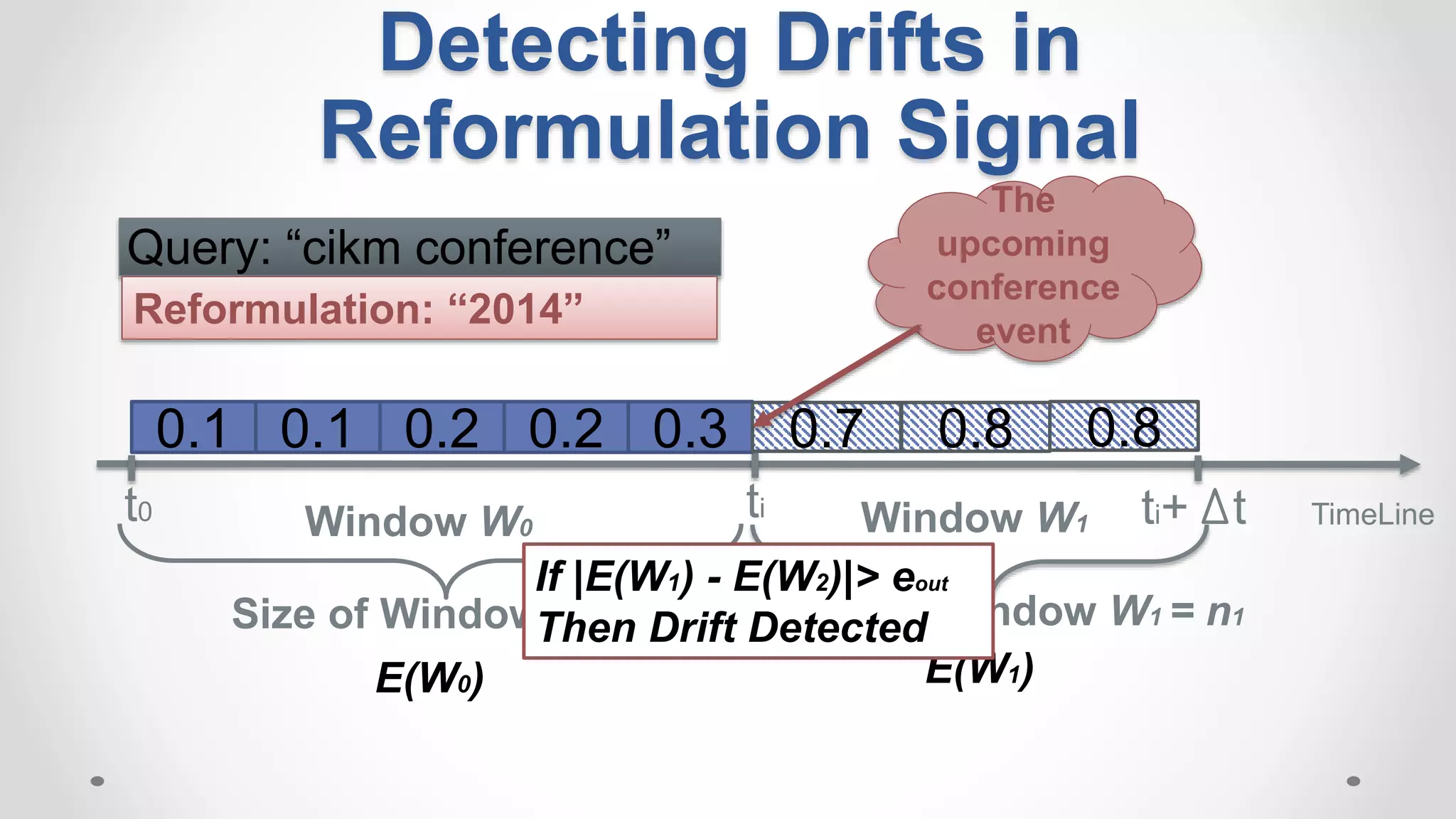
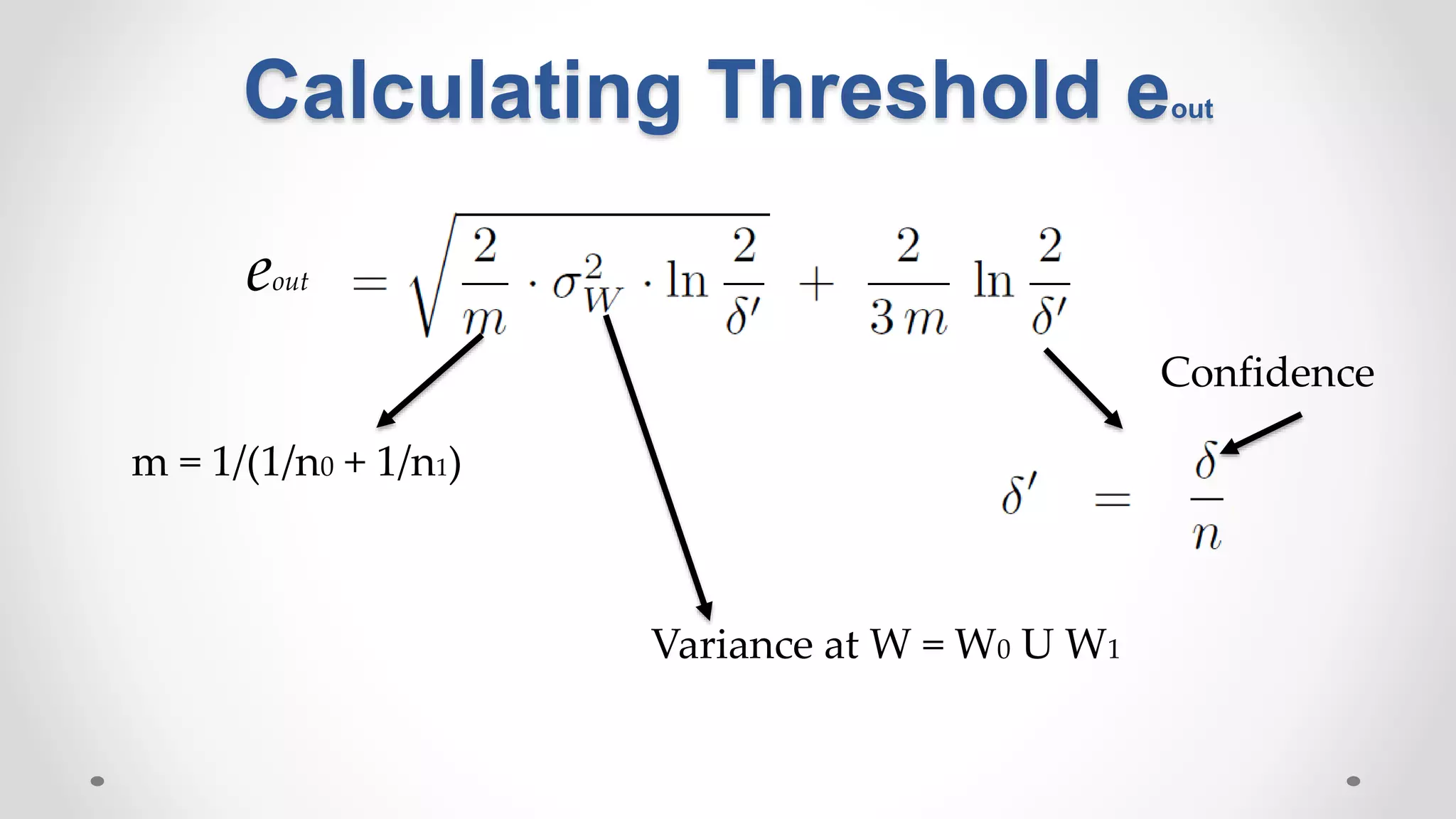
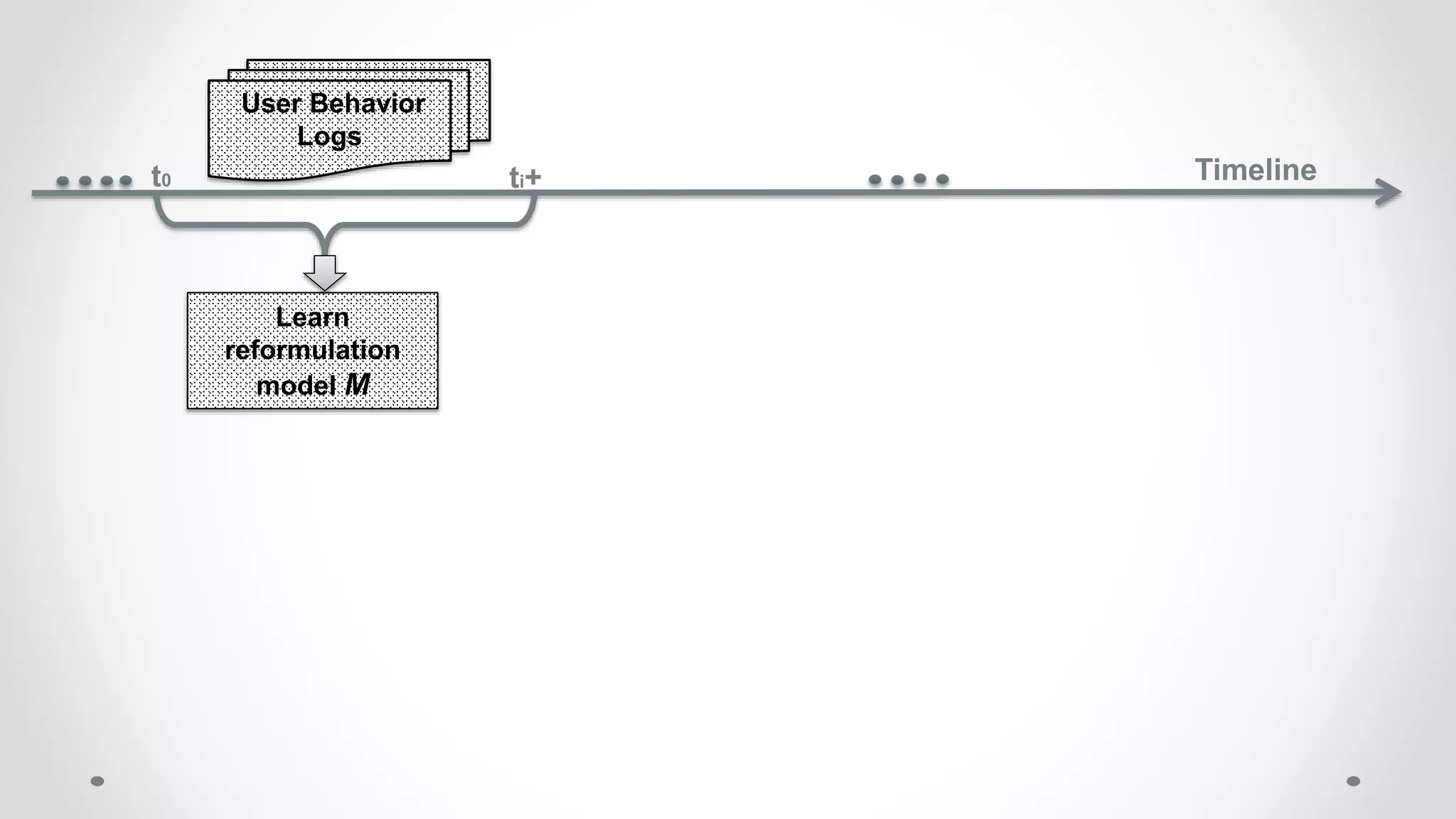
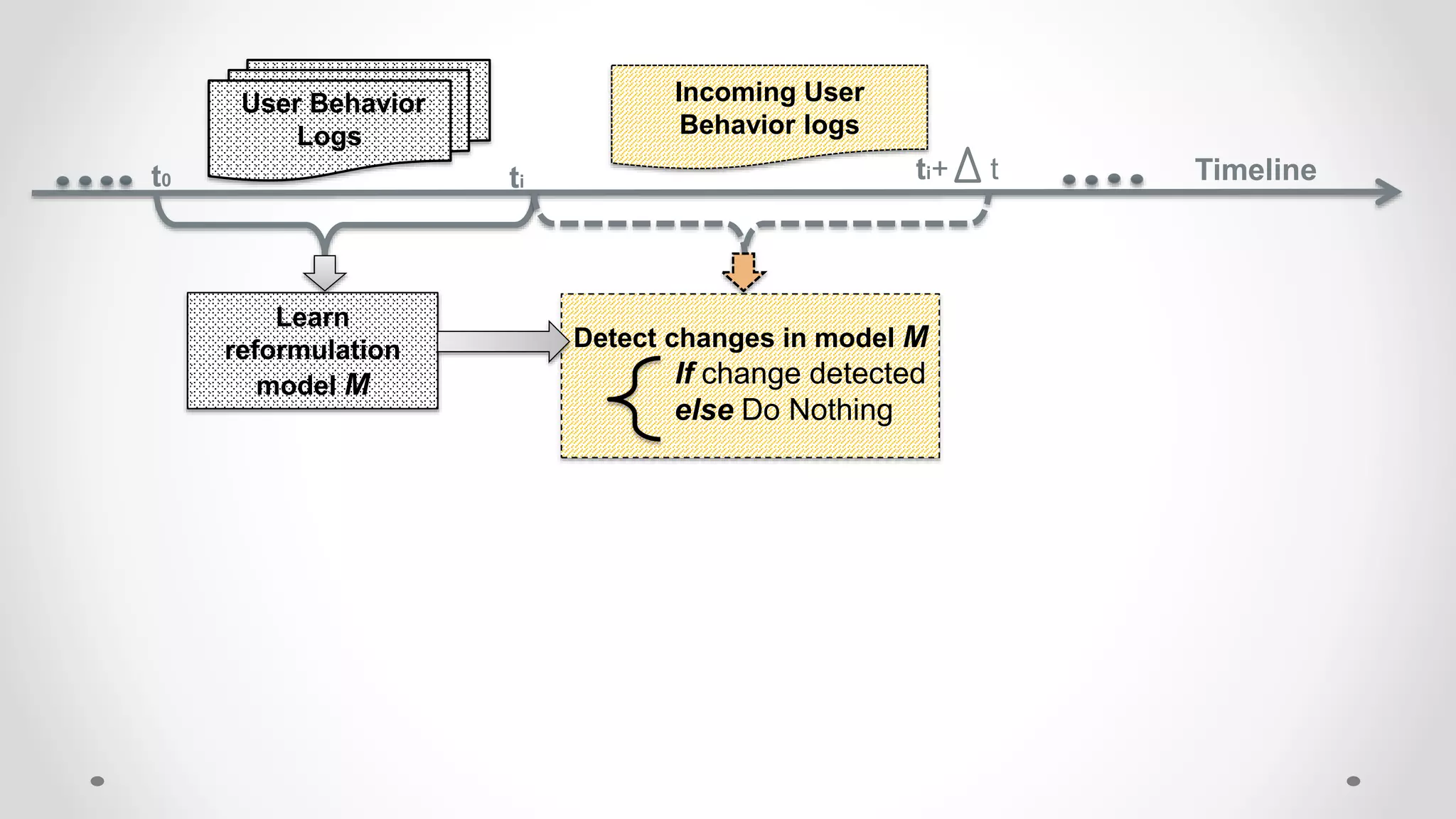
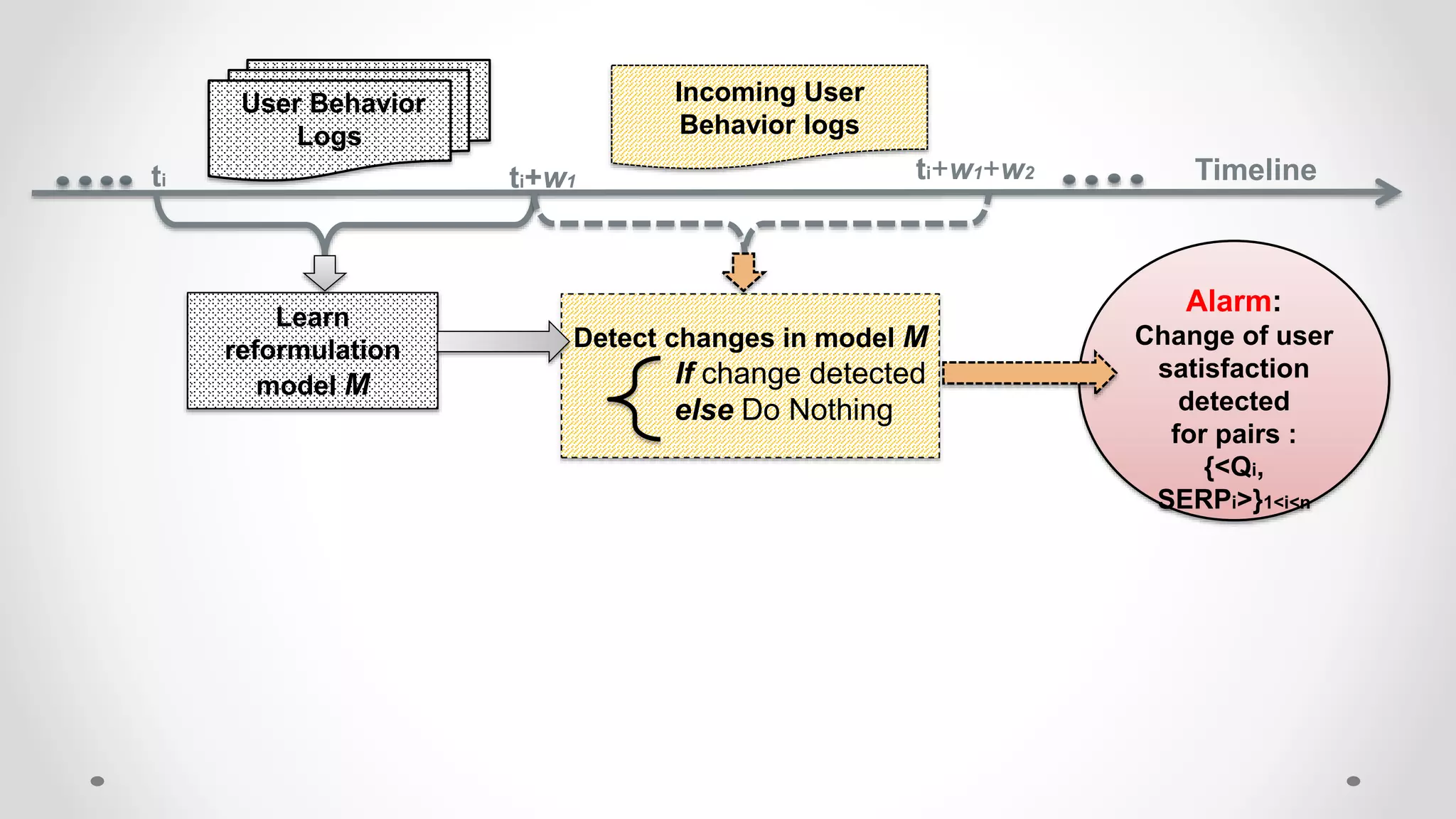
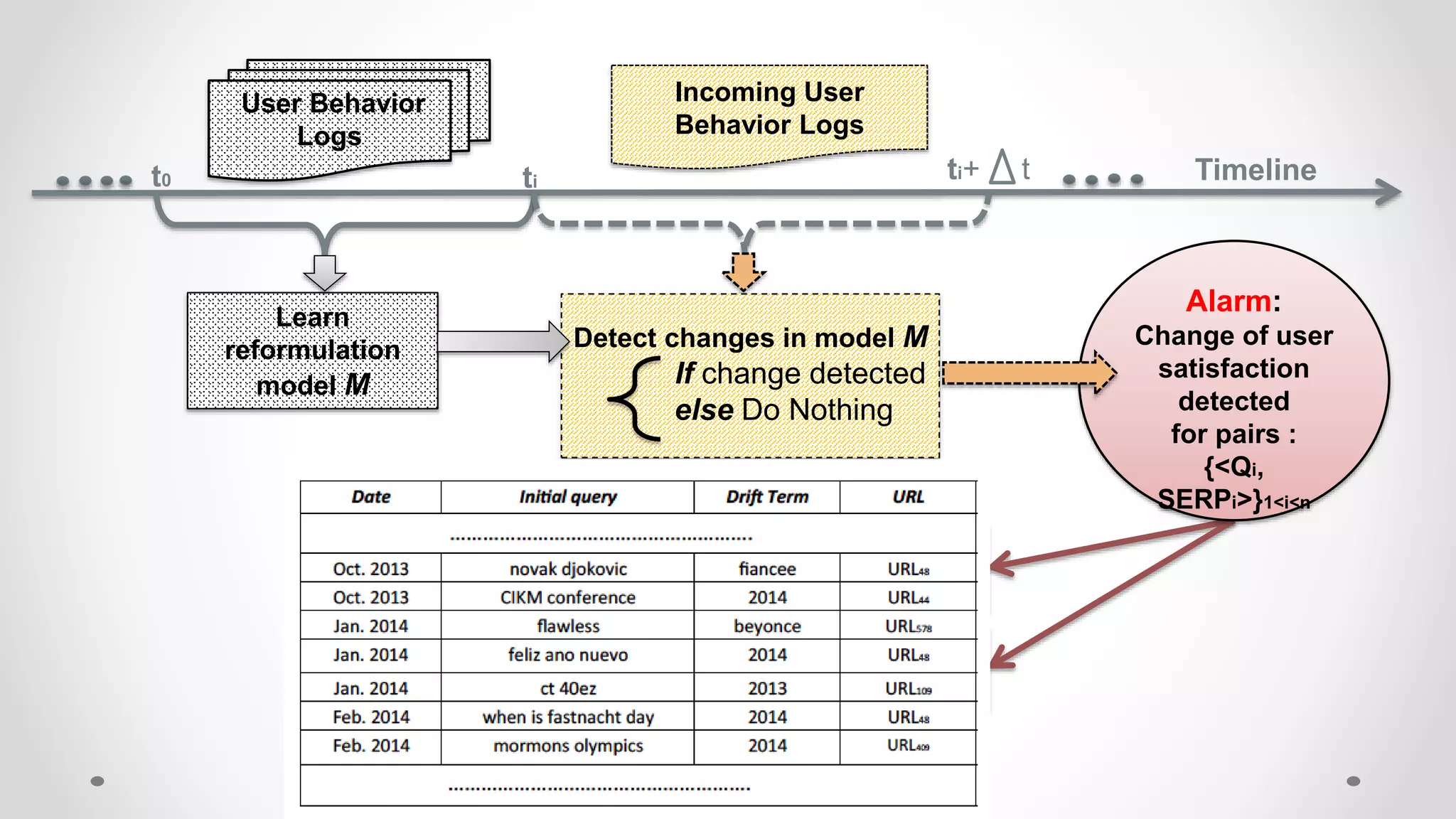
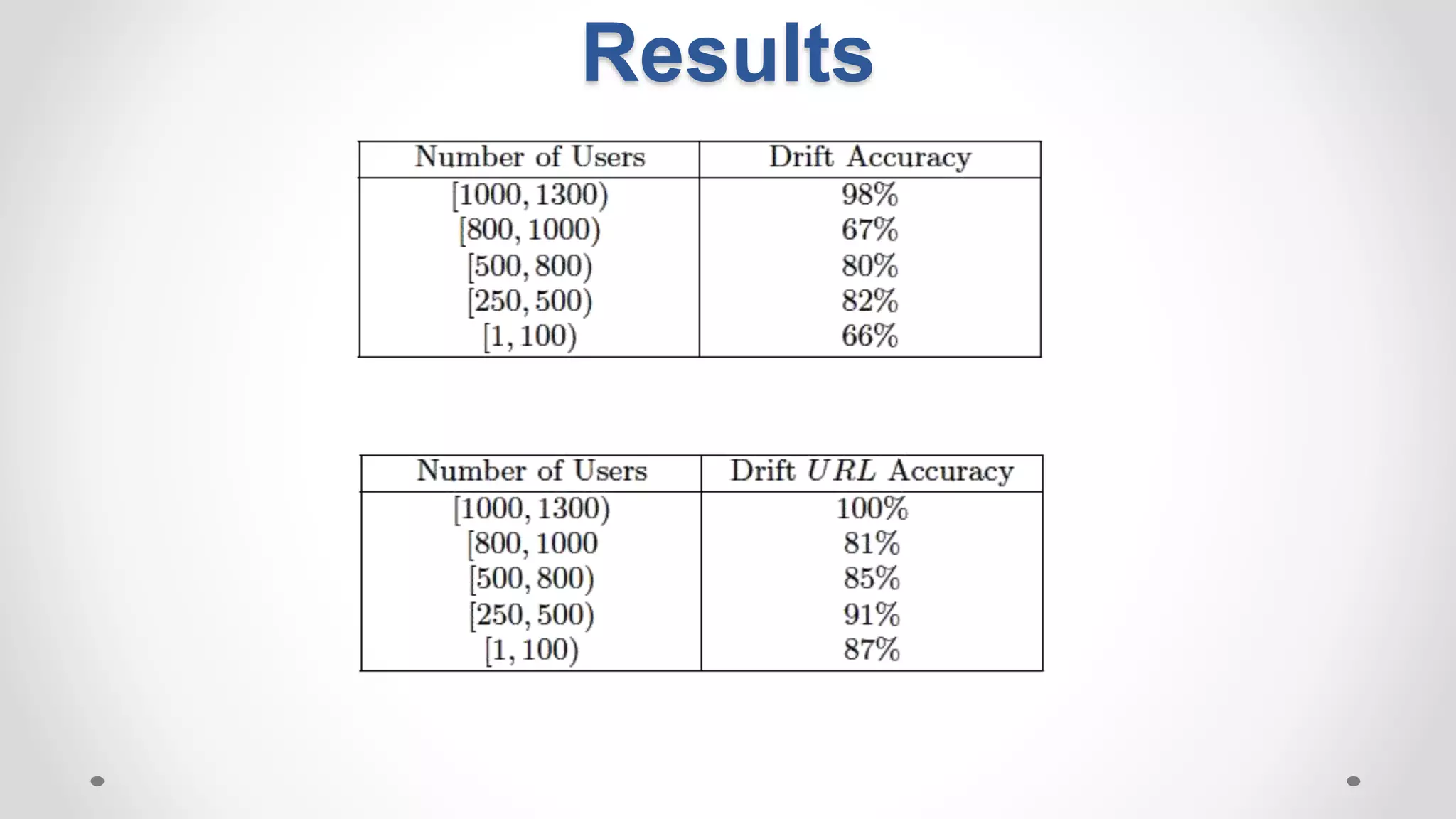
This document discusses modeling and detecting changes in user satisfaction based on query reformulation data from search logs. It proposes using concept drift detection techniques to identify changes in a reformulation model over time, which could indicate changes in user preferences. The techniques include learning an initial reformulation model, monitoring for changes by comparing windows of new log data, and alerting if differences exceed a threshold. An experiment on 6 months of search log data evaluated the approach. The results demonstrated the viability of using concept drift detection for this task, though future work could classify drift types and predict durations.