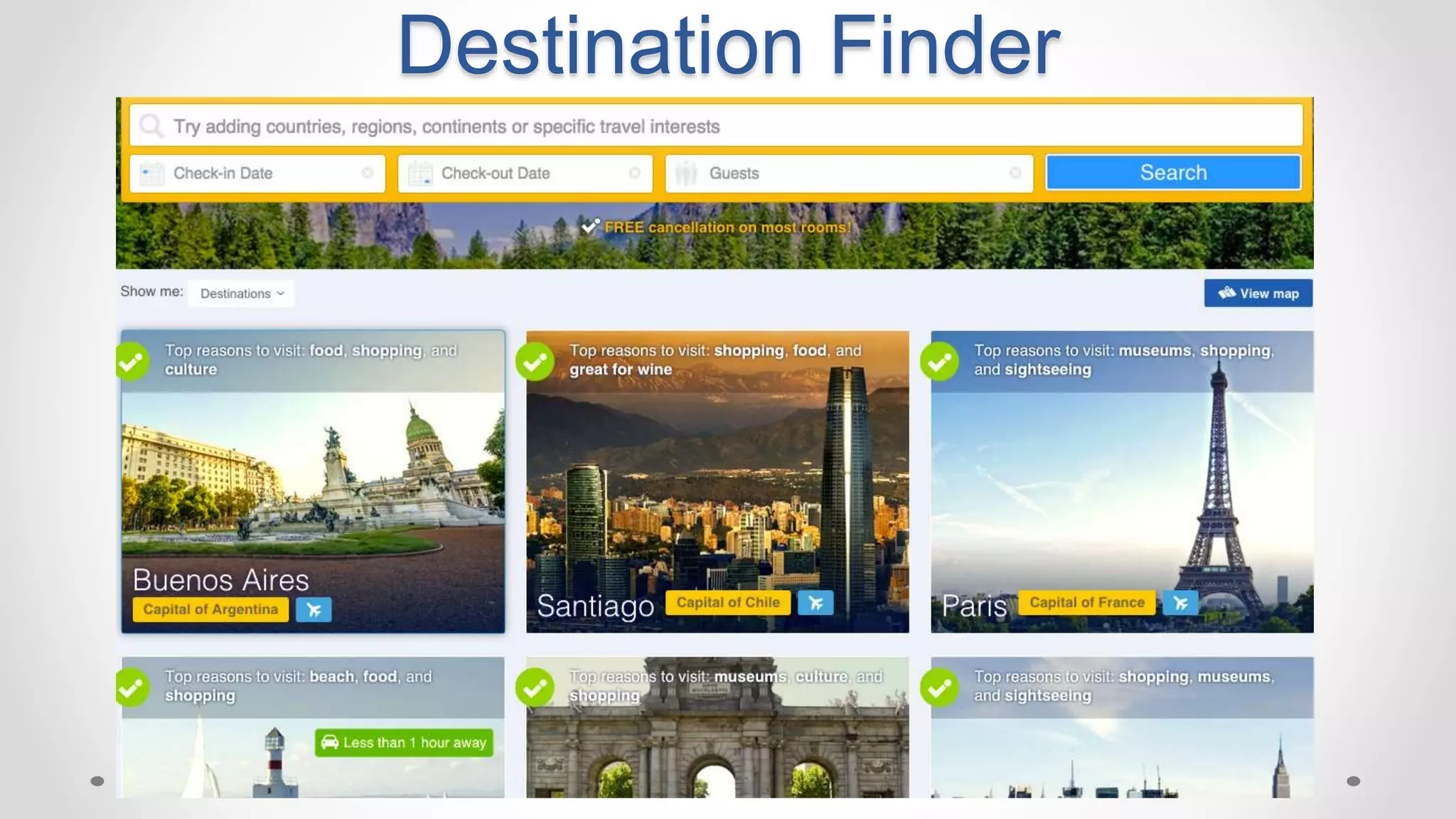
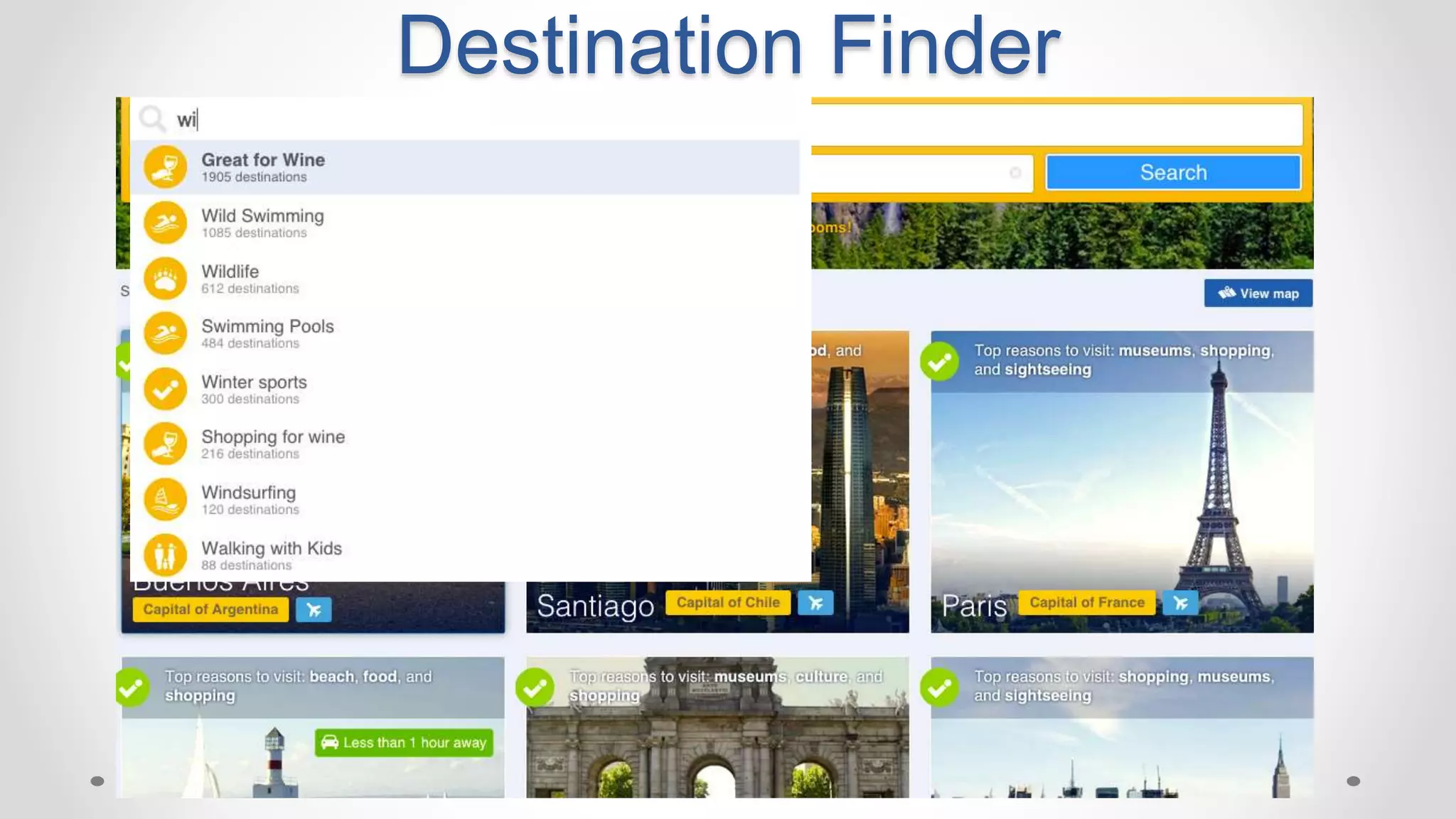
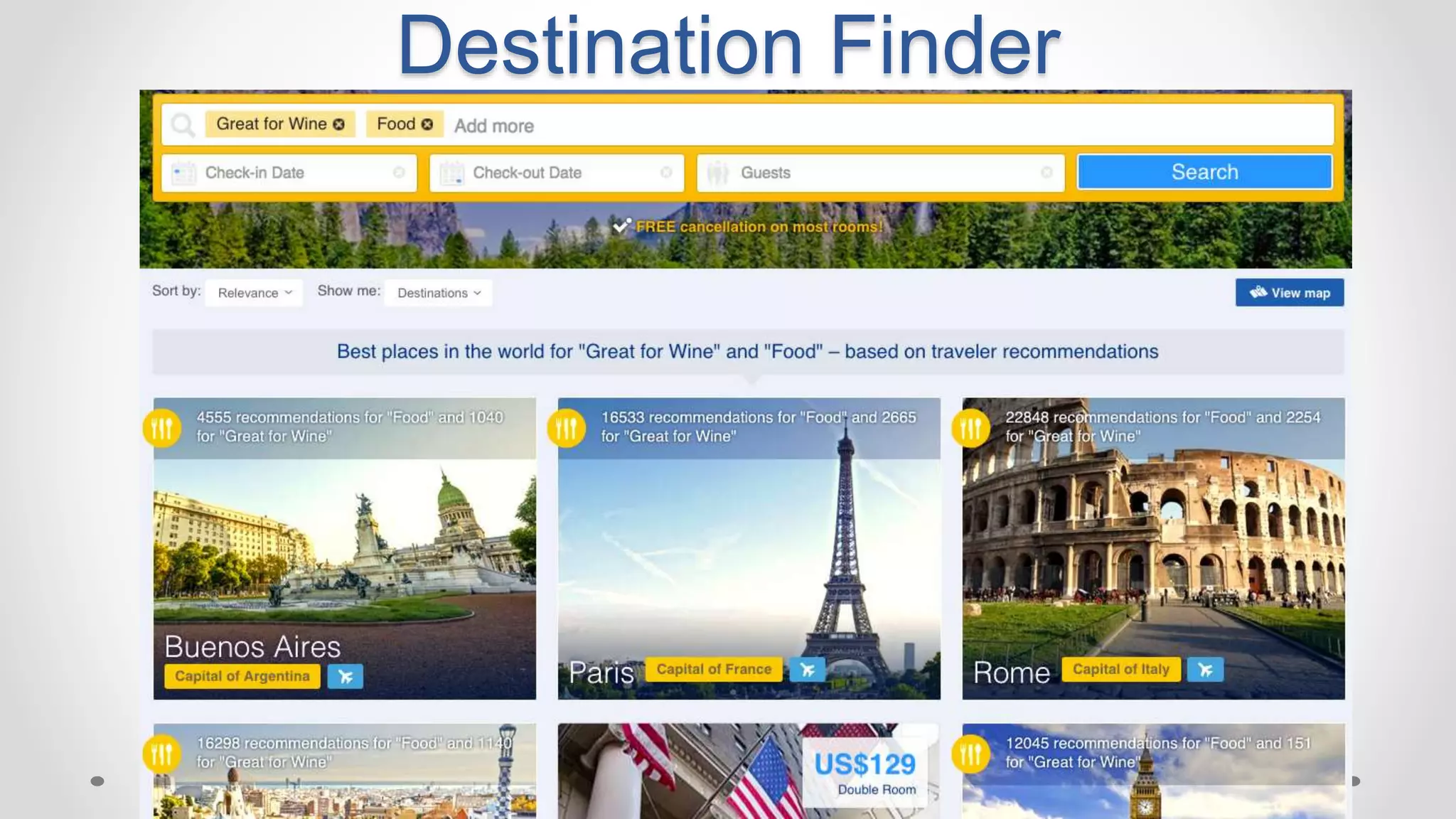
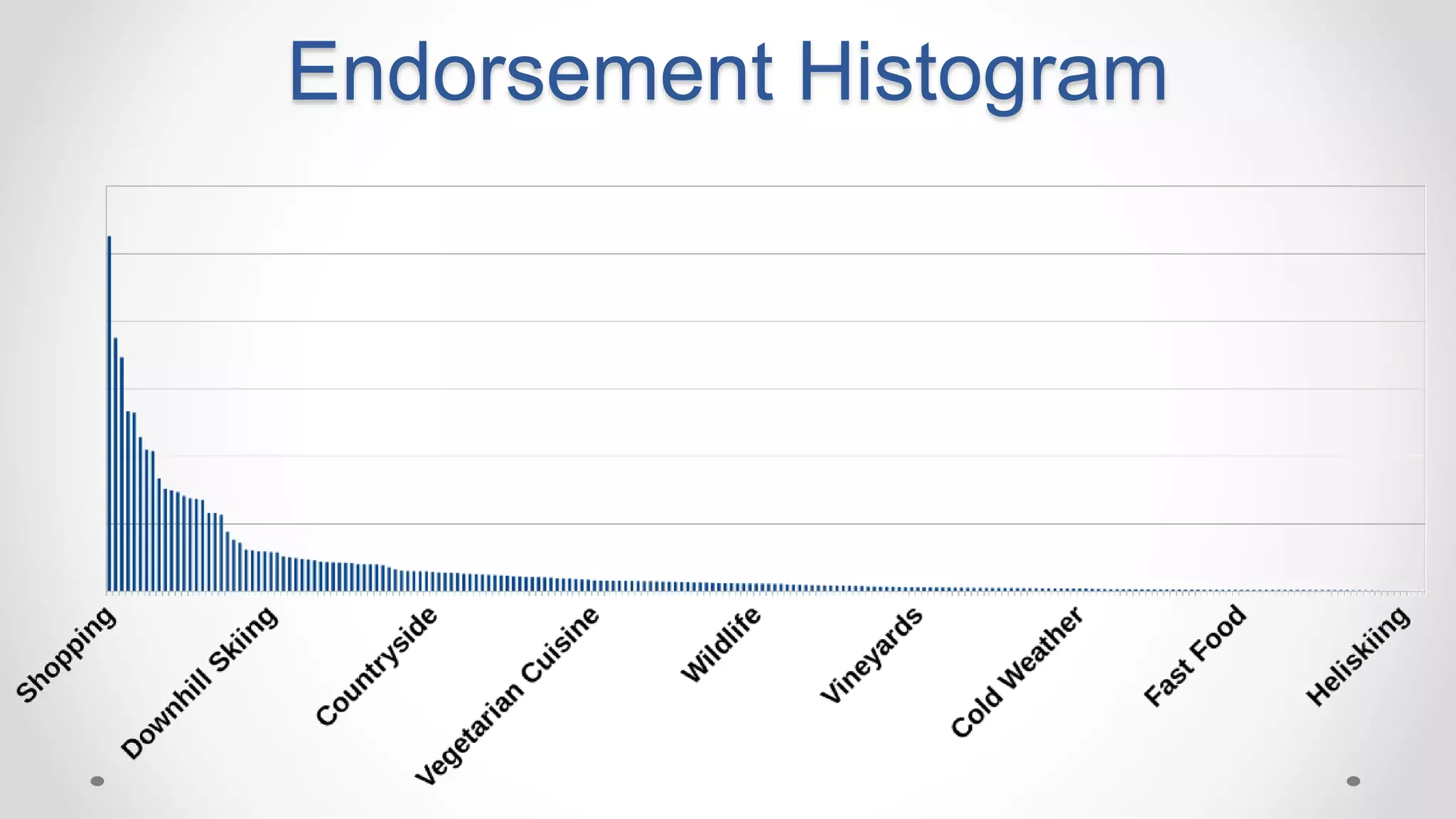
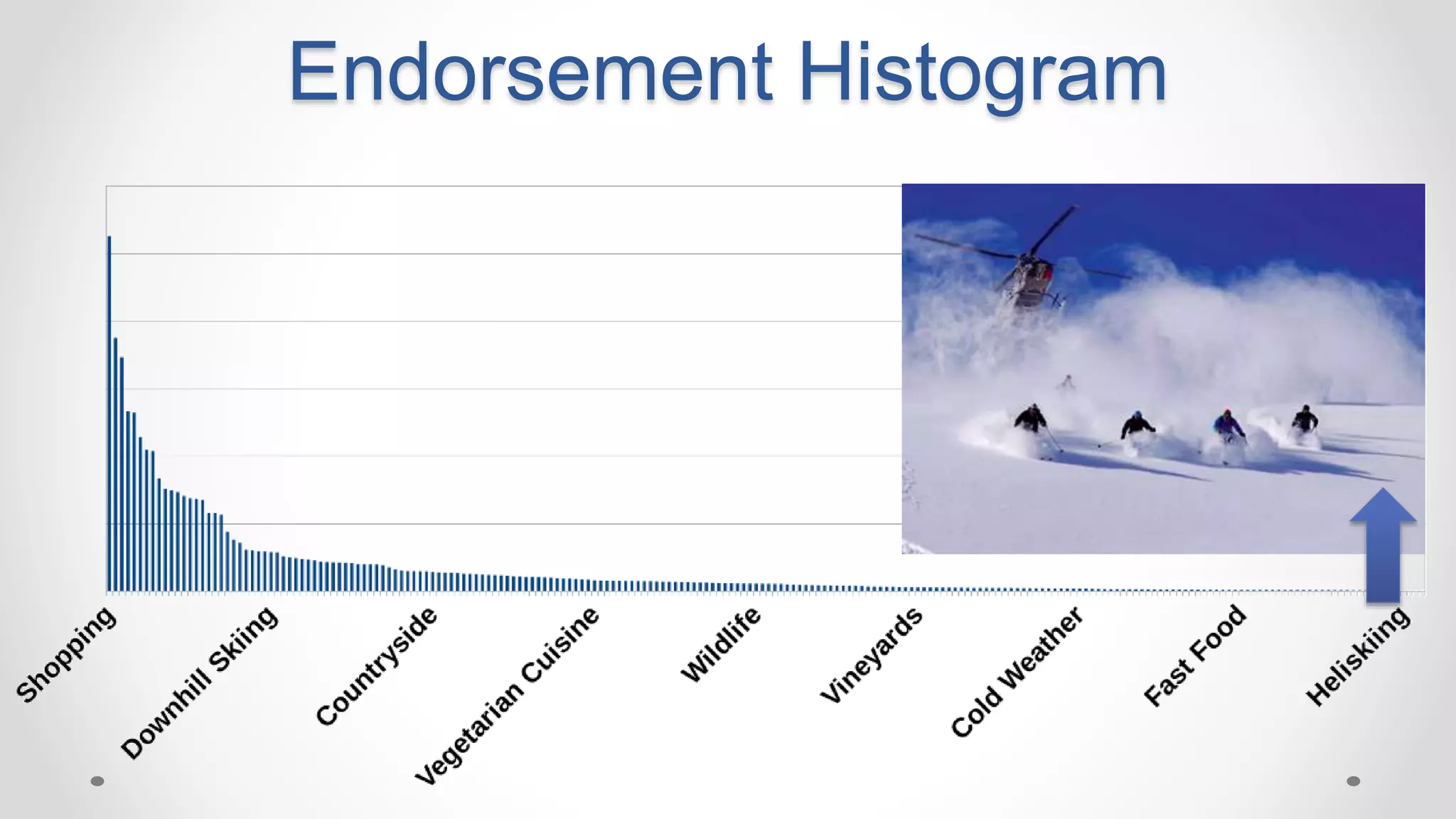
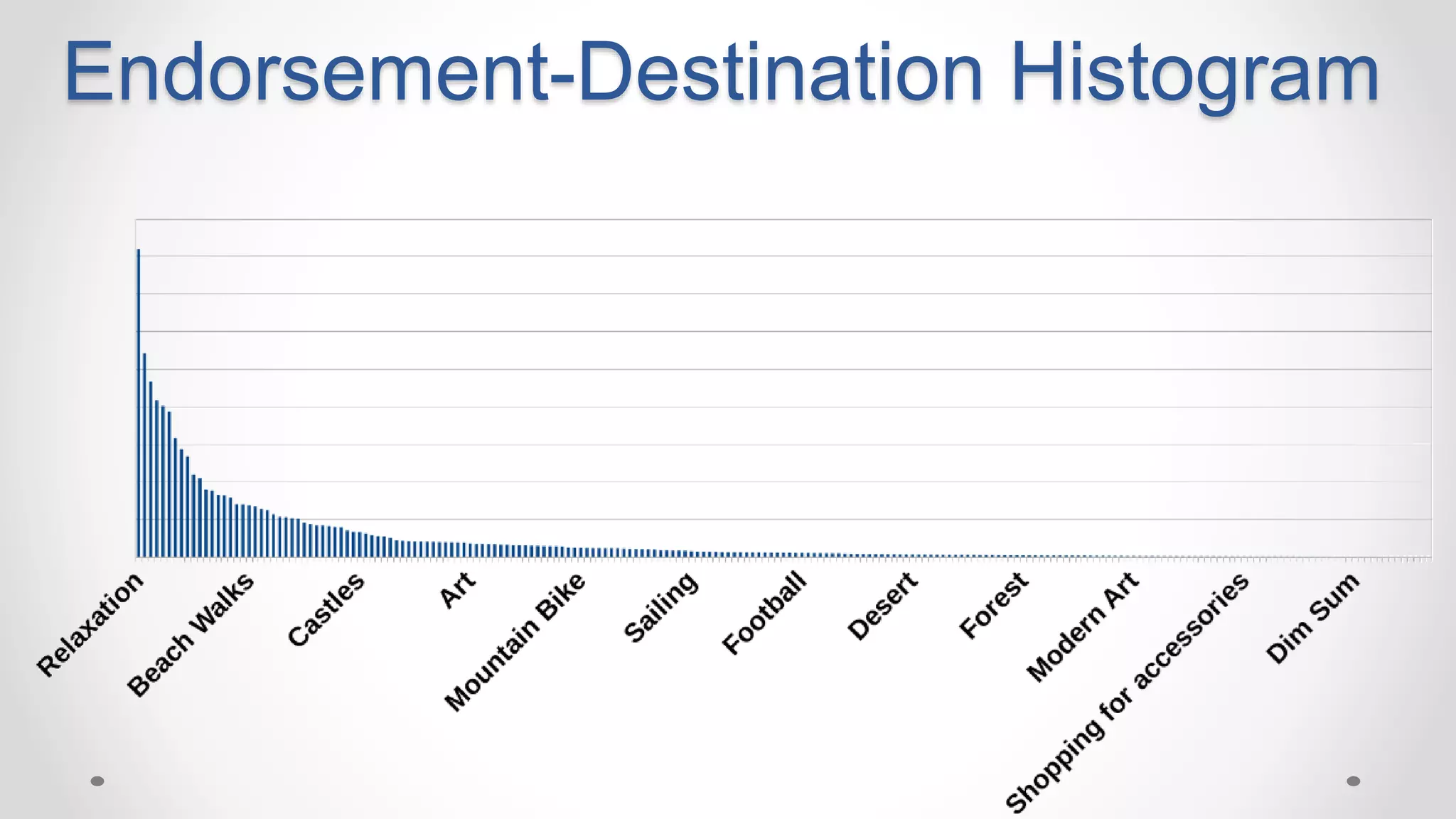
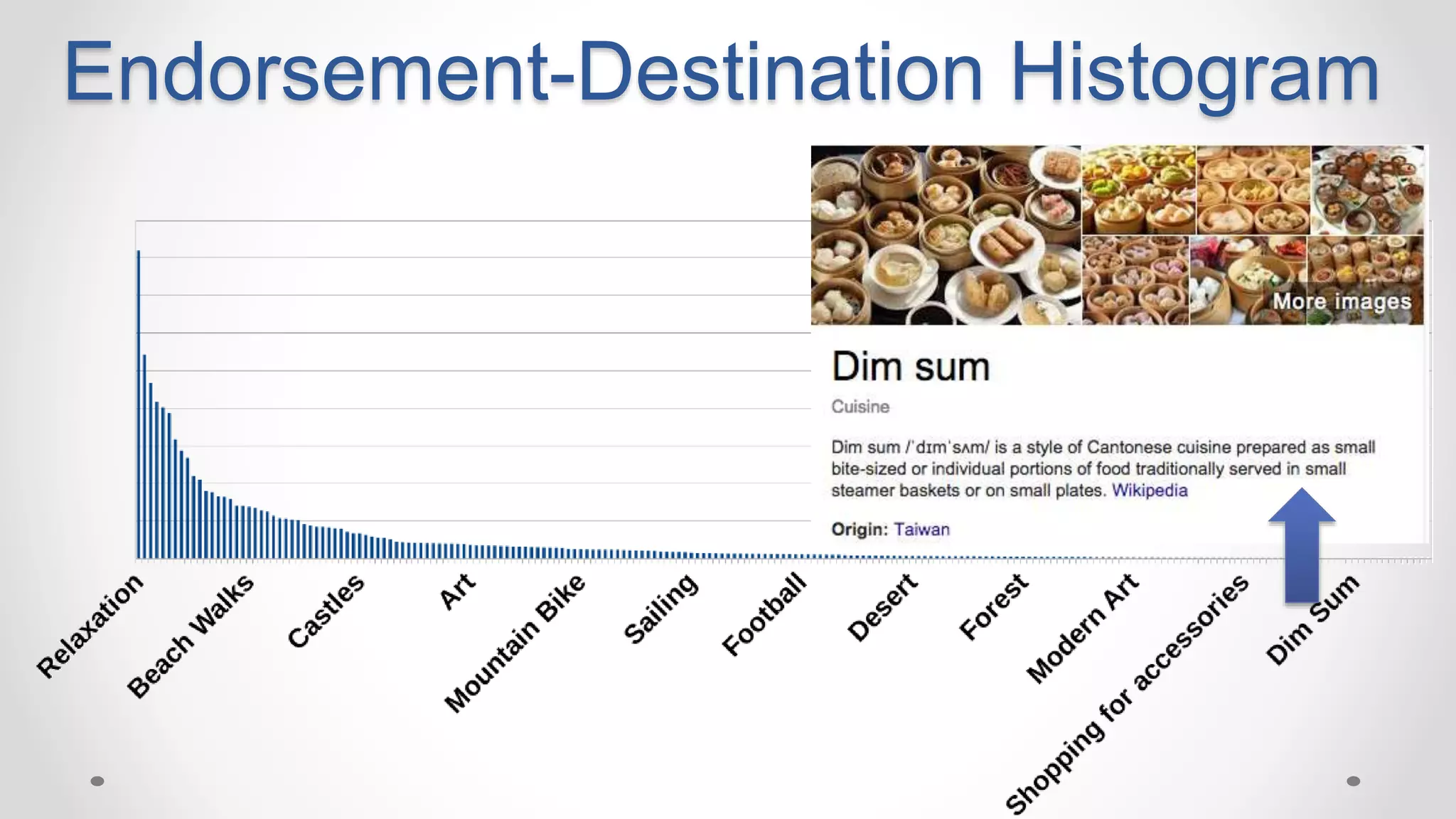
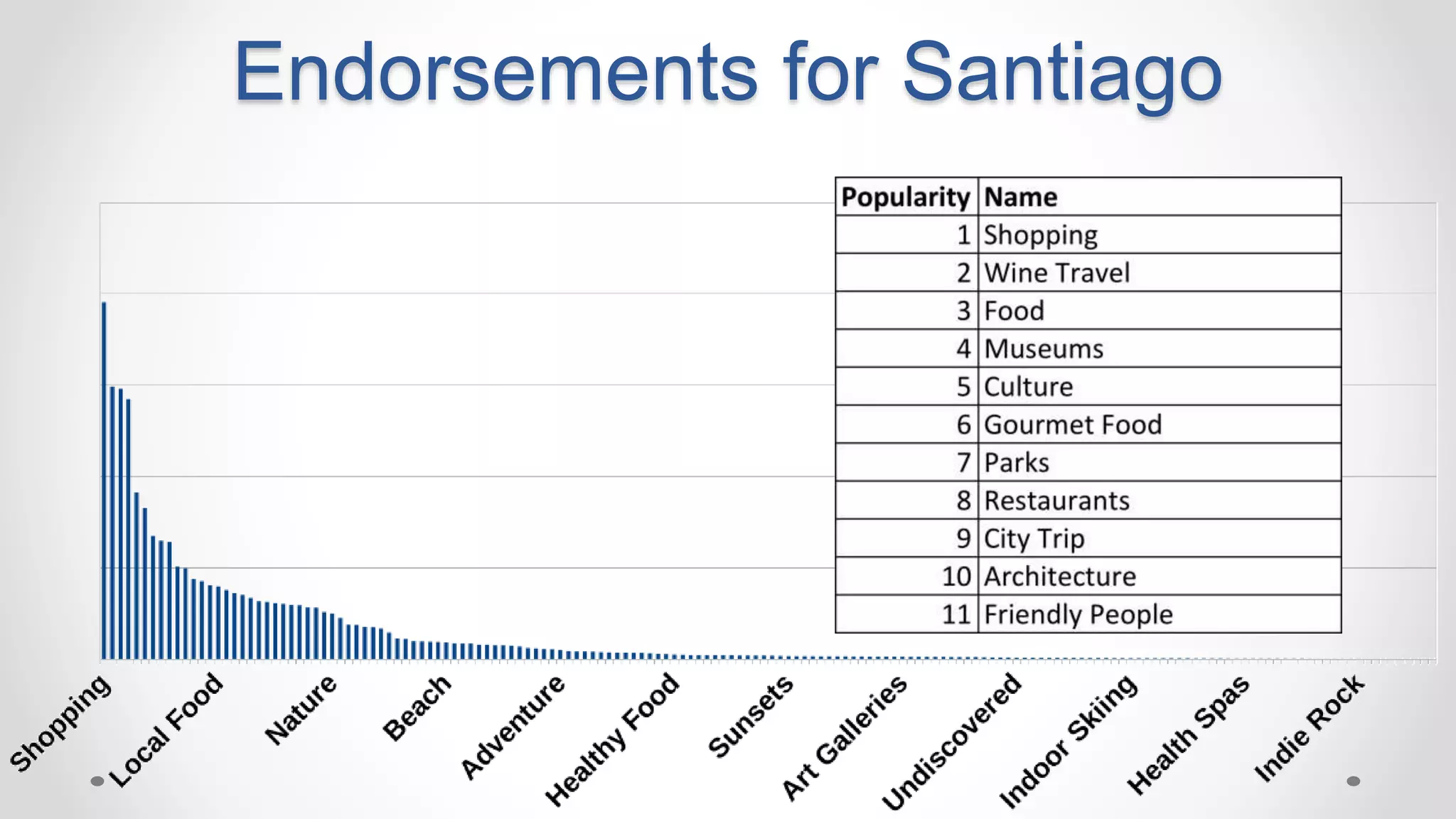
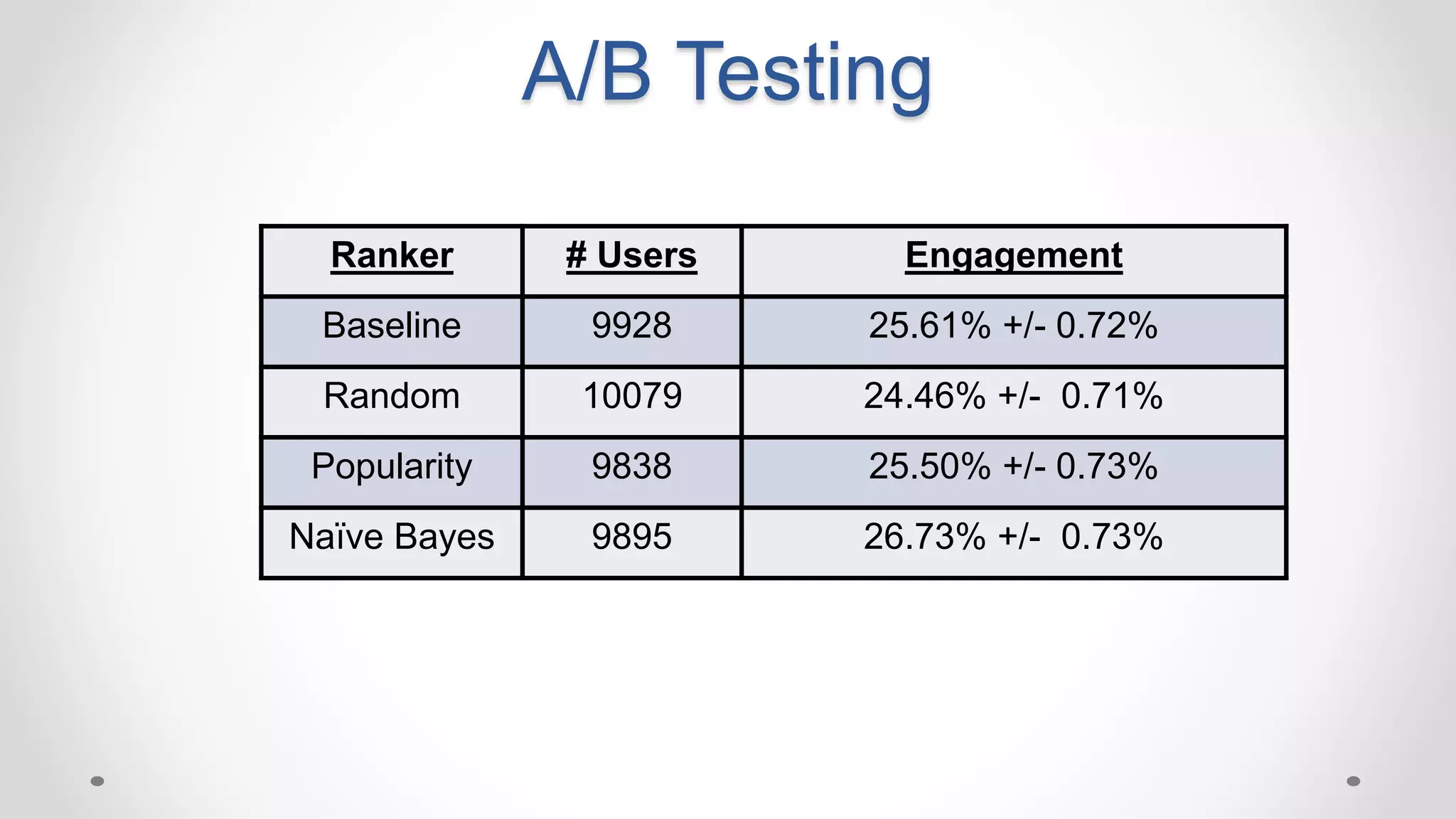
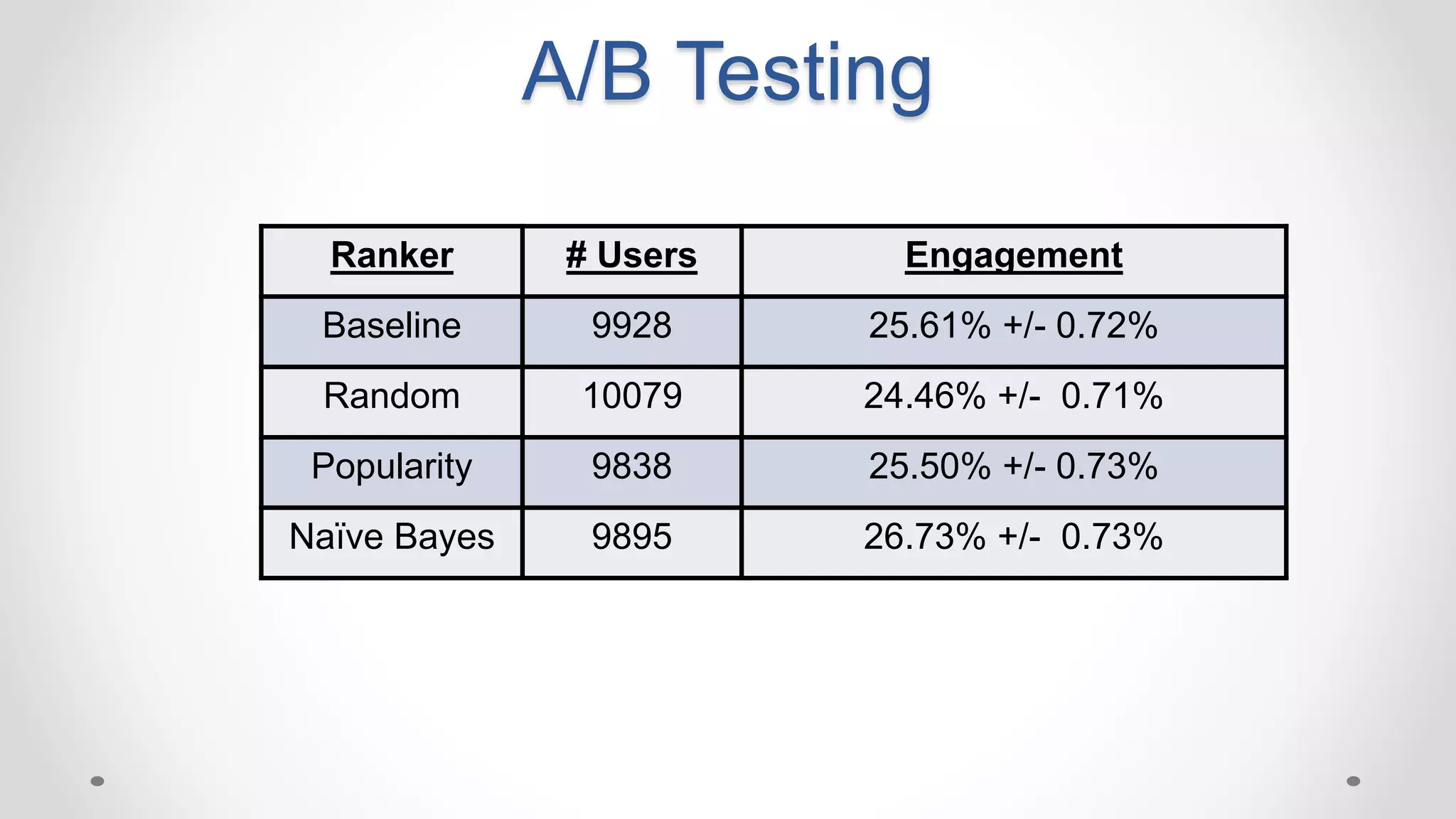
This document discusses optimizing travel destination recommendations based on user preferences using data from Booking.com. It describes Booking.com's data on destinations, endorsements from past users, and challenges in ranking destinations for new users due to sparsity, volatility and cold start problems. An A/B test is run comparing different ranking methods (baseline, random, popularity, naive Bayes) to maximize user engagement, finding that a simple naive Bayes approach outperforms others. Future work to improve rankings by considering user context is discussed.