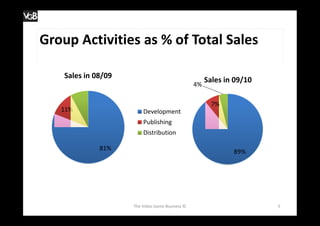
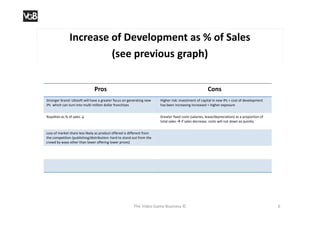
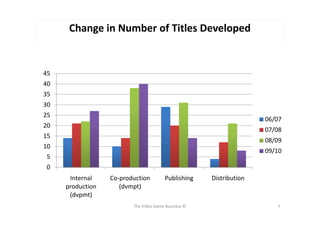
The document outlines Ubisoft's business activities, including development, publishing, and distribution of video games, along with their historical expansion and acquisition strategies from 1986 to 2009. It provides insights on sales performance and the increasing focus on development titles, highlighting the pros and cons of this approach. Additional references to sources such as annual reports and relevant articles are also included.