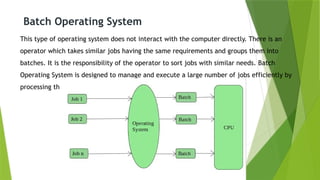
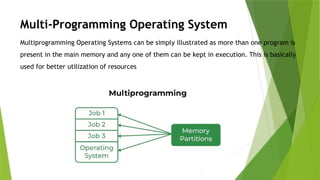
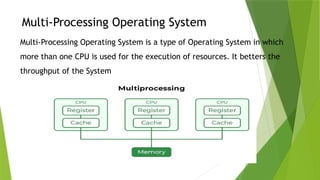
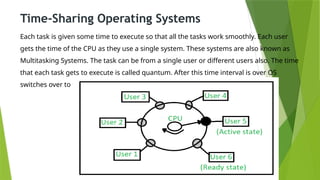
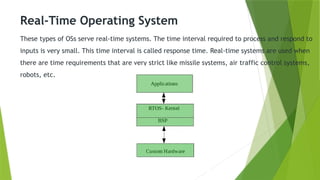
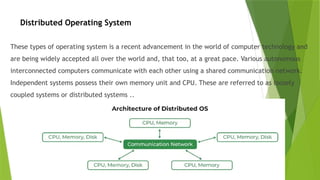
An operating system (OS) interfaces between system programs and hardware, with types including batch, multi-programming, multi-processing, time-sharing, real-time, and distributed systems. Each type has unique advantages and disadvantages regarding efficiency, user interaction, and complexity. Real-time and distributed operating systems are notable advancements, offering strict response times and communication between interconnected systems.