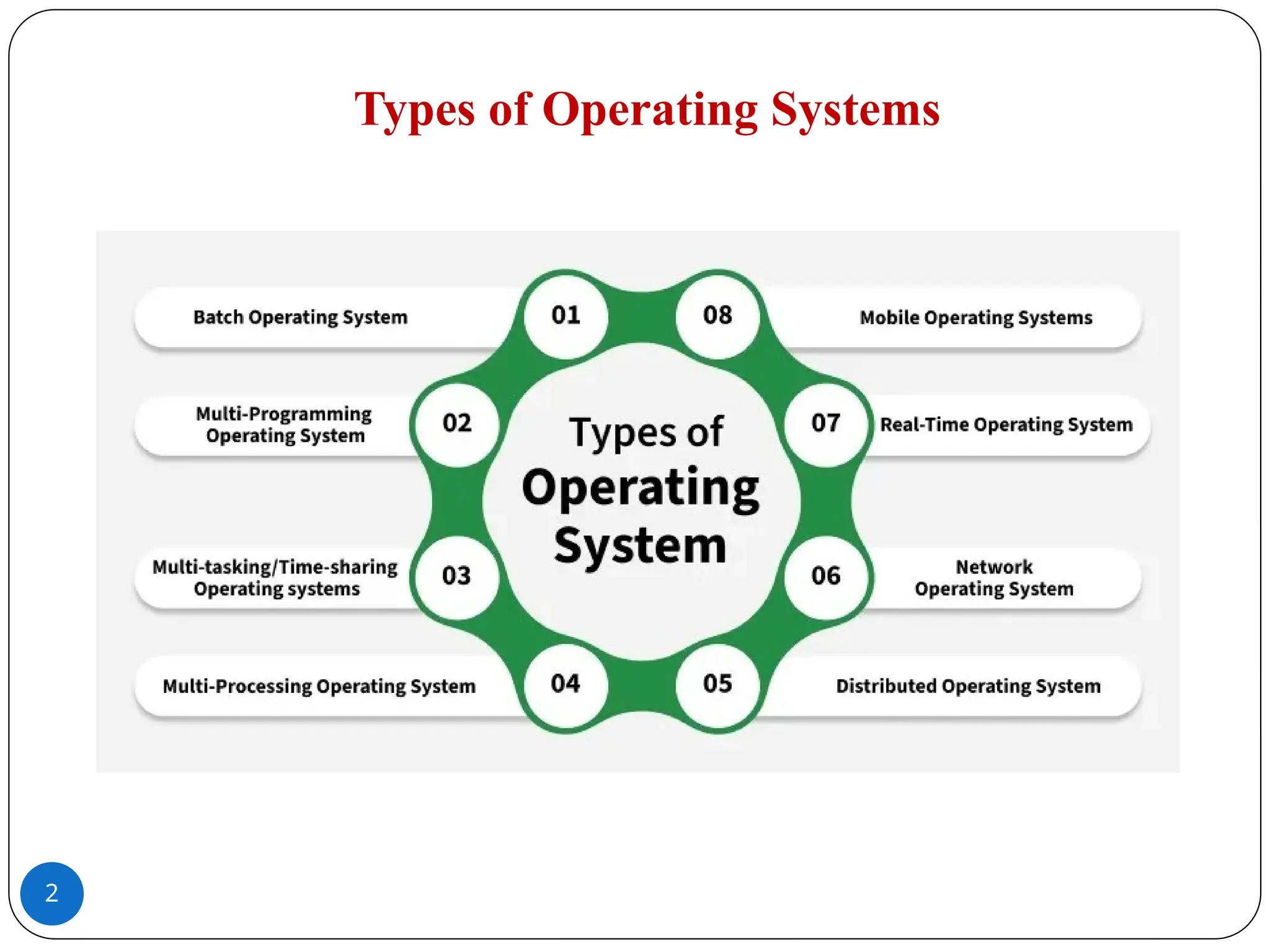
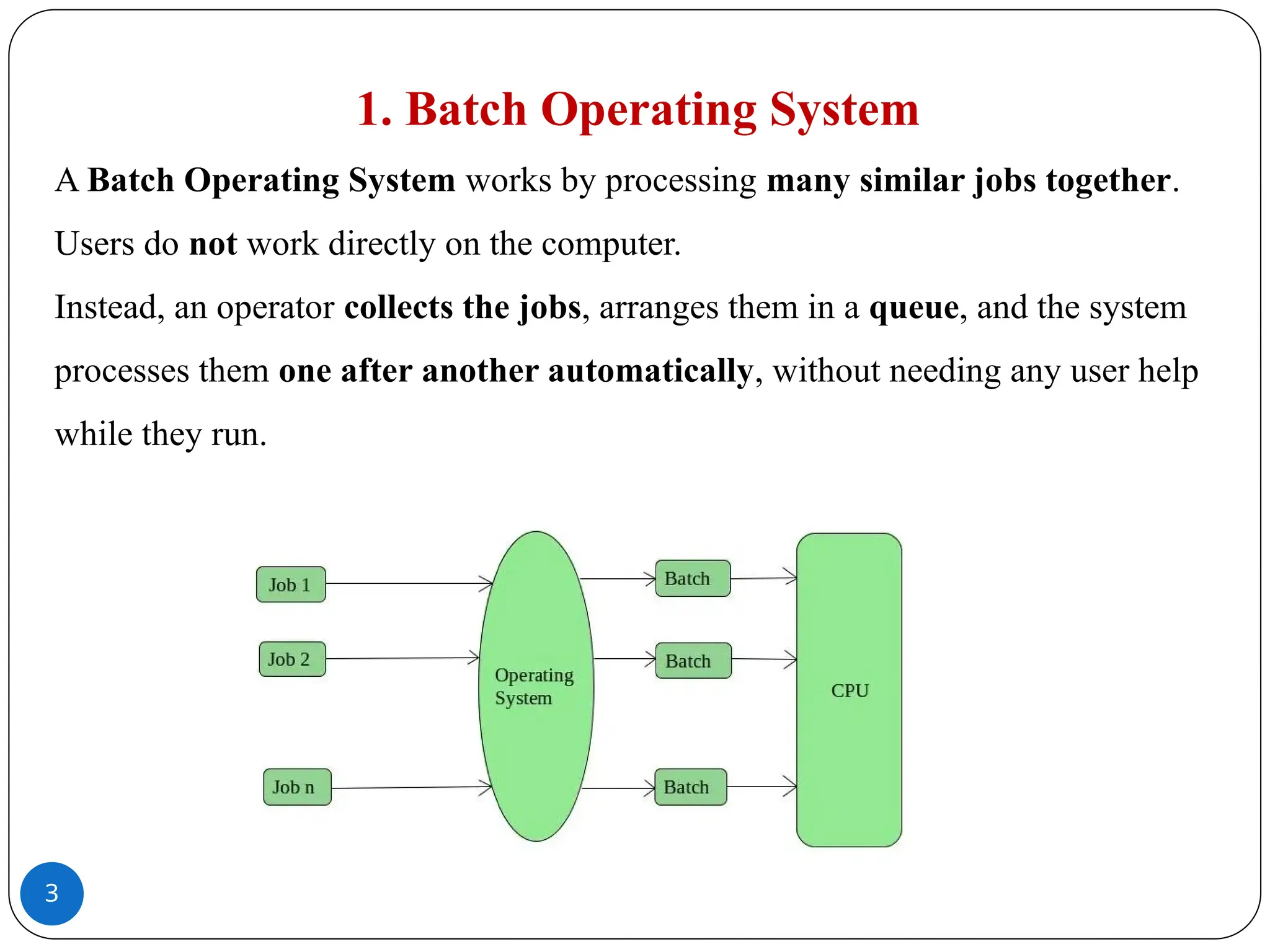
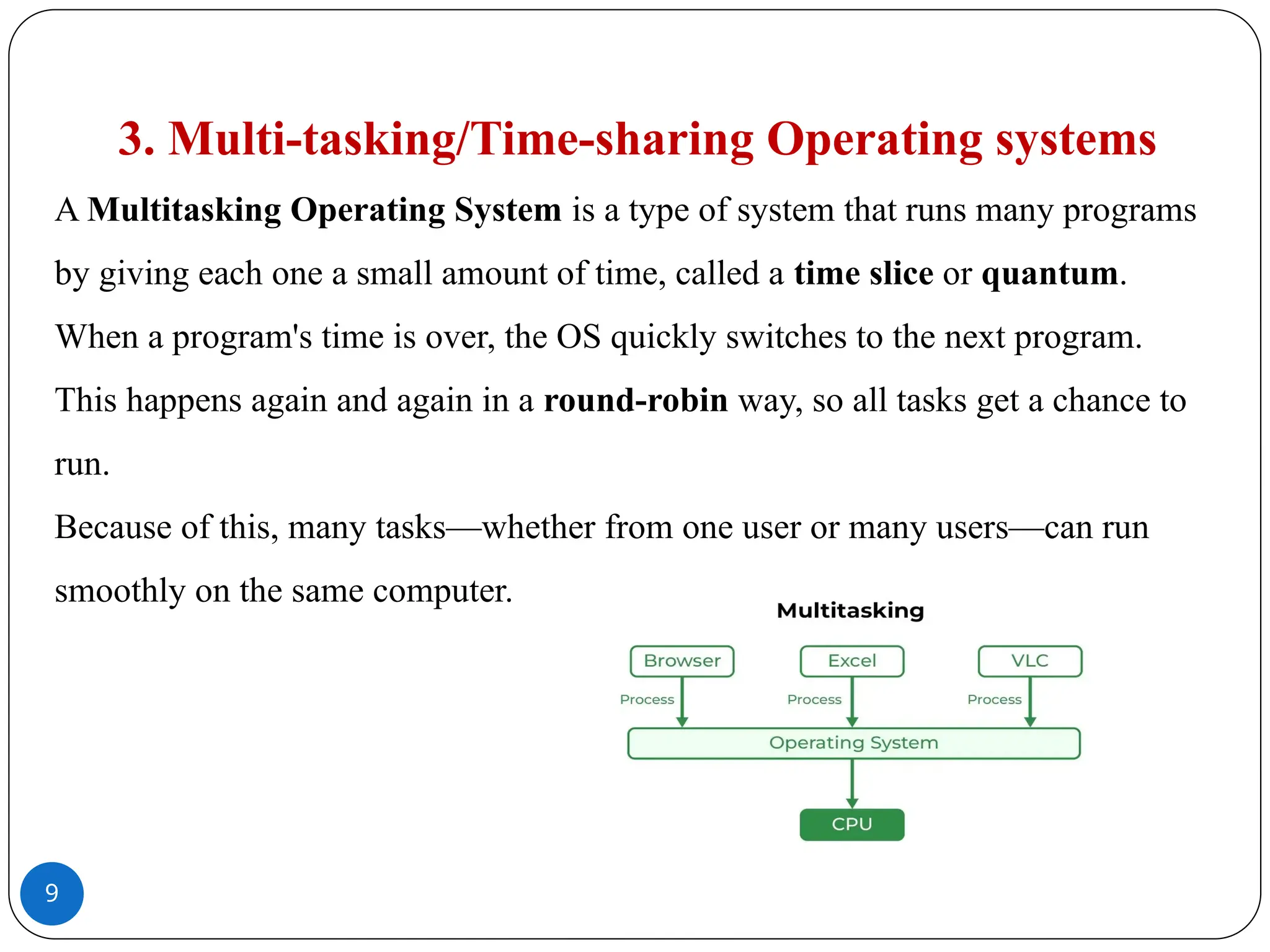
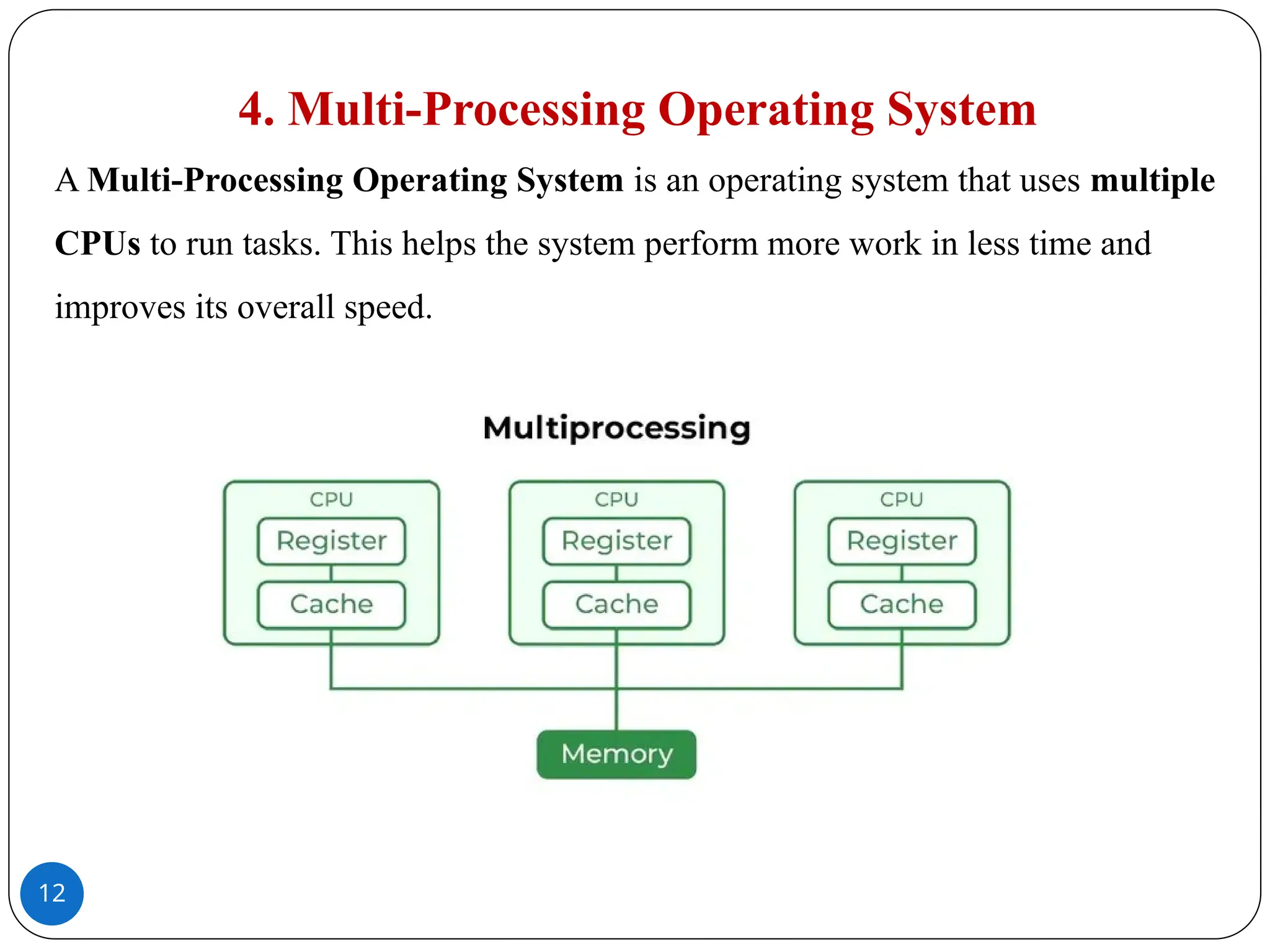
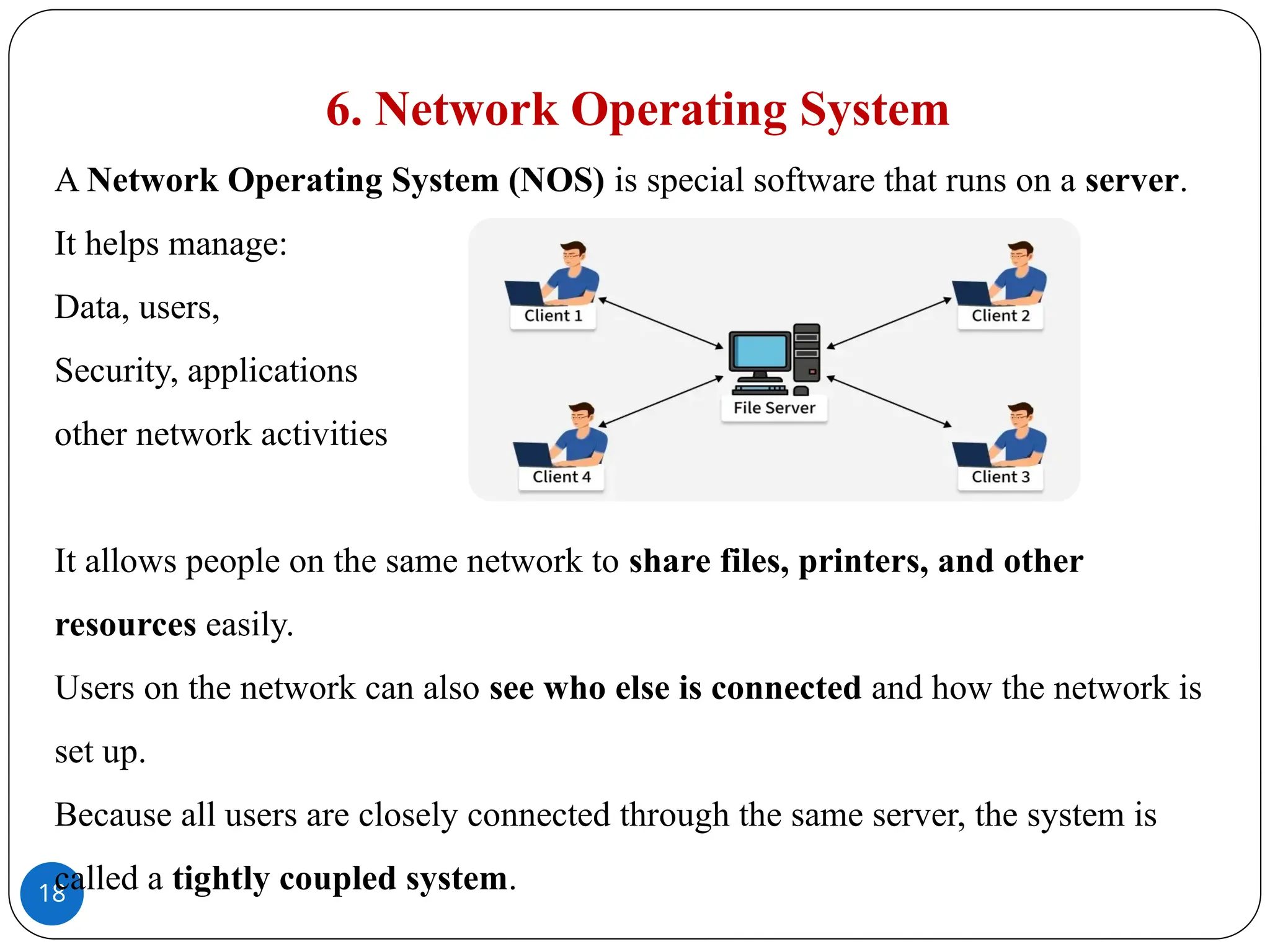
A Batch Operating System works by processing many similar jobs together.�Users do not work directly on the computer.�Instead, an operator collects the jobs, arranges them in a queue, and the system processes them one after another automatically, without needing any user help while they run.