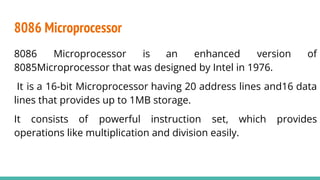
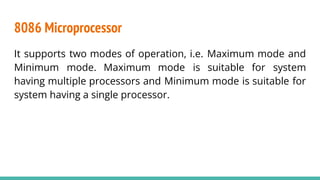
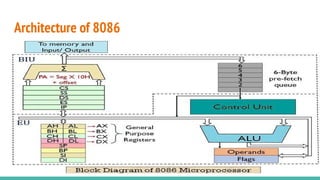
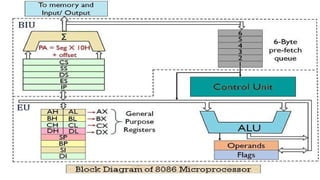
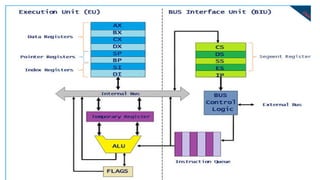
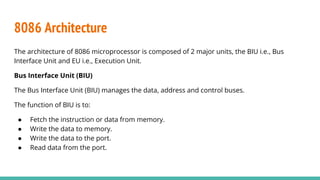
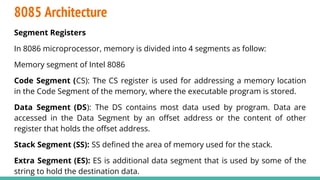
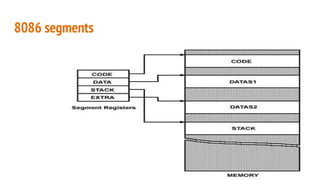
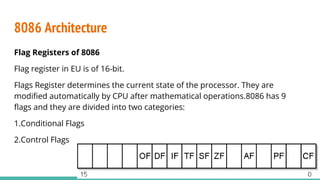
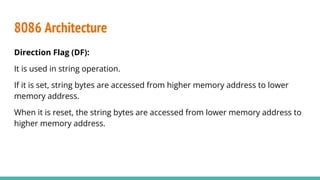
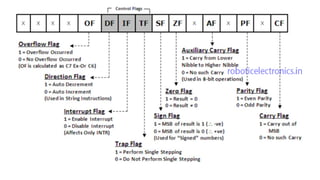
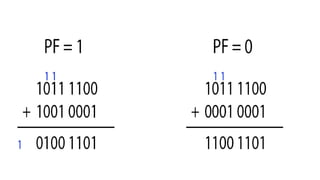
The 8086 microprocessor, introduced by Intel in 1976, is a 16-bit processor with a powerful instruction set and supports two modes of operation - maximum and minimum mode. Its architecture consists of a Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and an Execution Unit (EU), and it utilizes an instruction queue to enhance execution speed. Memory is organized into segments, and it features a 16-bit flag register with various conditional and control flags to manage processor state and execution flow.










![1. Immediate Addressing Mode
In this type of Addressing Mode immediate data is the part of the
instruction itself.
Example: MOV Ax, 0020H 16- bit data transfer
2. Absolute/ Direct Addressing Mode
In Absolute/ Direct Addressing Mode the effective address of memory
location where operand is present is written directly in the instruction.
Example: Mov Ax, [5000H]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microprocessormodule4-250211173556-7c256350/85/Microprocessor-module-4-pdfbabssbabanjxnsb-26-320.jpg)

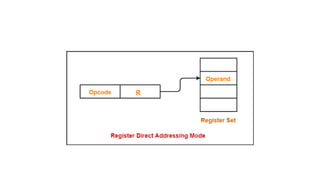
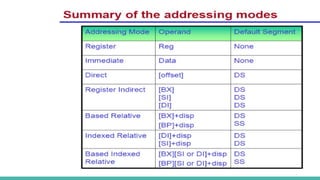
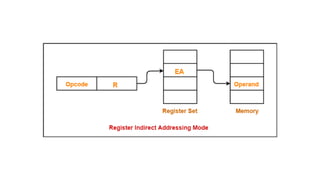
![4. Register Indirect Addressing
In this addressing mode effective address of memory is
calculated from baseregister (BX) or index register (SI, DI),
specified in the instruction. Then it is added to the segment
register to generate physical address.
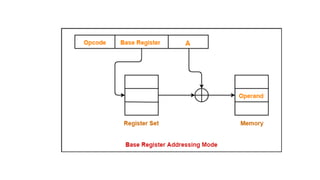
5.Based mode – In this the effective address is the sum of base
register and displacement.
Example:
MOV AL, [BP+ 0100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microprocessormodule4-250211173556-7c256350/85/Microprocessor-module-4-pdfbabssbabanjxnsb-29-320.jpg)
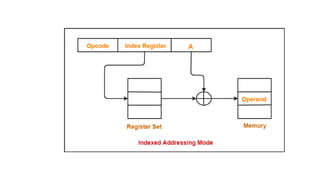
![6.Indexed mode – In this type ofaddressing mode the
effective address is sum of index register and
displacement.
Example:
MOV AX, [SI+2000]
MOV AL, [DI+3000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microprocessormodule4-250211173556-7c256350/85/Microprocessor-module-4-pdfbabssbabanjxnsb-32-320.jpg)
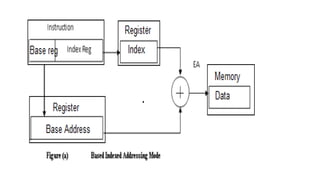
![7.Based indexed mode – In this the effective address is sum of base
register and index register.
Base register: BX, BP
Index register: SI, DI
The physical memory address is calculated according to the base
register.
Example:
MOV AL, [BP+SI]
MOV AX, [BX+DI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microprocessormodule4-250211173556-7c256350/85/Microprocessor-module-4-pdfbabssbabanjxnsb-34-320.jpg)